- Overview
- Apple Mail
- Apple Numbers
- Apple Scripting
- Excel
- Release Notes
- About the Excel activity package
- Project compatibility
- Supported character encoding
- Project settings
- Add or Update Excel Sensitivity Label
- Append Range
- Auto Fill
- Autofit Range
- Change Pivot Data Source
- Clear Sheet/Range/Table
- Copy/Paste Range
- Create Pivot Table
- Delete Column
- Delete Rows
- Delete Sheet
- Duplicate Sheet
- Export to CSV
- Fill Range
- Filter
- Filter Pivot Table
- Find First/Last Data Row
- Find/Replace Value
- For Each Excel Row
- For Each Excel Sheet
- Format As Table
- Format Cells
- Get Cell Color
- Get Excel Chart
- Get Excel Sensitivity Label
- Get Selected Range
- Insert Column
- Insert Chart
- Insert Rows
- Insert Sheet
- Invoke VBA
- Lookup
- Match Function
- Protect Sheet
- Read Cell Formula
- Read Cell Value
- Read Range
- Refresh Excel Data Connections
- Refresh Pivot Table
- Remove Duplicates
- Rename Sheet
- Run Spreadsheet Macro
- Save Excel File
- Save Excel File As
- Save Excel File As PDF
- Select Range
- Sort Range
- Text to Columns
- Unprotect Sheet
- Update Excel Chart
- Use Excel File
- VLookup
- Write Cell
- Write CSV
- Write DataTable to Excel
- Excel Application Scope
- Append To CSV
- Read CSV
- Write CSV
- Delete Column
- Filter Table
- Get Table Range
- Insert Column
- Sort Table
- Append Range
- Close Workbook
- Get Cell Color
- Read Cell
- Read Cell Formula
- Read Column
- Read Range
- Read Row
- Select Range
- Set Range Color
- Write Cell
- Write Range
- Save Workbook
- Create Table
- Get Workbook Sheet
- Get Workbook Sheets
- Refresh Pivot Table
- Create Pivot Table
- Get Selected Range
- Copy Sheet
- Delete Range
- Auto Fill Range
- Copy Paste Range
- Execute Macro
- Insert/Delete Columns
- Insert/Delete Rows
- Invoke VBA
- LookUp Range
- Remove Duplicates Range
- Excel Process Scope
- Manage CSV Files
- Filter CSV Files
- Verify CSV Files
- Compare CSV Files
- Sort Data in Excel Files
- Filter and Delete Rows in Excel Files
- Read, Write, and Append Data in Excel
- Table Functions
- Read From Excel Files
- Manage Multiple Excel Files
- Filter Excel files by cell color
- Verify Excel Workbook Data
- Compare Numeric Values
- Interpret Excel Results
- Manage Range Selection
- Manipulate Range Selections
- Manage Pivot Tables
- Manage Databases in Excel
- Google Workspace
- Release notes
- About the Google Workspace activities package
- Project compatibility
- Project settings
- Google Workspace HTTP Request
- Run Script
- Apply File Labels
- Clear File Label Fields
- Copy File
- Create Folder
- Delete File or Folder
- Delete File or Folder Permission
- Download File
- For Each File or Folder
- Get Drive Labels
- Get File or Folder Info
- Get File Labels
- Get File/Folder
- Get File List
- Get File or Folder Permissions
- Move File
- Remove File Labels
- Rename File or Folder
- Share File or Folder
- Update File or Folder Permission
- Upload Files
- Apply Gmail Labels
- Archive Email
- Delete Email
- Download Email
- Download Email Attachments
- For Each Email
- Forward Email
- Get Email by ID
- Get Email List
- Get Gmail Labels List
- Get Email Thread
- Get Newest Email
- Get Single Gmail Label
- Mark Email as Read/Unread
- Move Email
- Remove Gmail Labels
- Reply to Email
- Send Email
- Turn On Automatic Replies
- Turn Off Automatic Replies
- Wait for Calendar Event Created and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Received and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Replied and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Updated and Resume
- Wait for Email Received and Resume
- Wait for Email Sent and Resume
- Wait for File Created and Resume
- Wait for File Updated and Resume
- Wait for Folder Created and Resume
- Wait for Sheet Created and Resume
- Wait for Sheet Cell Updated and Resume
- Wait for Row Added to the Bottom of a Sheet
- Wait for Task Created and Resume
- Wait for Task Completed and Resume
- Add Attendee
- Create Event
- Delete Event
- Modify Event
- Search Events
- Use Google Drive
- Share File
- Delete File Permission
- Get File Permissions
- Update File Permission
- Copy File
- Create Folder
- Delete File
- Download File
- Find Files and Folders
- Get File Info
- Move File
- Upload File
- Create Document
- Create New Spreadsheet
- Get Mail Messages
- Send Mail Messages
- Change Labels
- Use Google Spreadsheet
- Add Delete Columns
- Add Delete Rows
- Auto Fill Range
- Add New Sheet
- Append Row
- Batch Spreadsheet Updates
- Copy Sheet
- Copy Paste Range
- Delete Range
- Delete Sheet
- Get Cell Color
- Get Sheets
- Read Cell
- Read Column
- Read Range
- Read Row
- Rename Sheet
- Write Cell
- Write Range
- Clear Range
- Download Spreadsheet
- Use Google Document
- Batch Document Updates
- Get Document
- Get Text Index
- Insert Text
- Replace Text
- Read All Text
- Create Script Project
- Get Project Content
- Upload Script File
- Create Deployment
- Run Script
- Mail
- Microsoft 365
- Release notes
- About the Microsoft 365 activity package
- Project compatibility
- Project settings
- Microsoft 365 HTTP Request
- List All Records
- Assign Sensitivity Label
- Create Folder
- Copy File/Folder
- Delete File or Folder
- Download File
- File Check-in/Check-out
- For Each File or Folder
- Get File/Folder
- Get File or Folder Metadata
- Get Sensitivity Labels
- Get File or Folder List
- Move File/Folder
- Rename file or folder
- Share File/Folder
- Upload Files
- Update File or Folder Metadata
- Archive Email
- Delete Email
- Download Email
- Download Email Attachments
- For Each Email
- Forward Email
- Get Email By ID
- Get Email Folders List
- Get Email List
- Get Email Thread
- Get Newest Email
- Mark Email as Read or Unread
- Move Email
- Reply to Email
- Send Email
- Set Email Categories
- Turn On Automatic Replies
- Turn Off Automatic Replies
- Wait for Calendar Event Created and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Received and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Replied and Resume
- Wait for Calendar Event Updated and Resume
- Wait for Cell in Worksheet Updated and Resume
- Wait for Email Received and Resume
- Wait for Email Sent and Resume
- Wait for File Created and Resume
- Wait for File Updated and Resume
- Wait for Row Added to the Bottom of a Table and Resume
- Wait for List Item Added and Resume
- Wait for List Item Updated and Resume
- Wait for Worksheet Created and Resume
- Connections
- AddEmailCategories
- ArchiveEmail
- DeleteEmail
- DownloadEmail
- DownloadEmailAttachment
- DownloadEmailAttachments
- ForwardEmail
- GetEmail
- GetEmailAttachmentsInfo
- GetEmails
- GetMailFolders
- GetNewestEmail
- MarkEmailAsRead
- MarkEmailAsUnread
- MoveEmail
- RemoveEmailCategories
- ReplyToEmail
- SendEmail
- TurnOffAutomaticReplies
- TurnOnAutomaticReplies
- Merge multiple sheets into a new summary Excel sheet
- Automatically accept calendar invites from your manager
- Move files to dedicated folders by type
- Verify if new employment documents (I9 and ID) match
- Add new customers to a SharePoint List
- Delete SharePoint List items newer than yesterday
- Notify me on Slack when an important Outlook Email is received
- Include creation date in new OneDrive file names
- Notify me by email when a new file is created
- Microsoft 365 Scope
- Add Sheet
- Append Range
- Clear Range
- Copy Range
- Copy Sheet
- Create Workbook
- Delete Range
- Delete Sheet
- Get Cell Color
- Get Sheets
- Read Cell
- Read Column
- Read Range
- Read Row
- Rename Sheet
- Write Cell
- Write Range
- Set Range Color
- Create Table
- Get Table Range
- Insert Column
- Delete Column
- Insert Rows
- Delete Rows
- VLookup Range
- Use OneDrive & SharePoint
- Copy File/Folder
- Create Folder
- Delete File/Folder
- Download File
- Export File as PDF
- Find Files And Folders
- Get File/Folder
- Move File/Folder
- Upload File
- Share File/Folder
- For Each File/Folder
- Forward Mail
- Find Meeting Times
- Get Mail
- Move Mail
- Send Mail
- Reply to Mail
- Delete Mail
- Set Mail Categories
- Add Attachment
- Add Attendee
- Add Location
- Create Event
- Delete Event
- Get Calendars
- Modify Event
- RSVP
- Search Events
- Create Group
- Delete Group
- Get Group
- List Groups
- Create Bucket
- Delete Bucket
- List Buckets
- List Bucket Tasks
- Create Plan
- Get Plan
- List Plans
- Create Task
- Delete Task
- Get Task
- List Tasks
- Update Task
- For Each List
- Get List Info
- For Each List Item
- Delete List Item
- Add List Items
- Update List Item
- Get List Items
- Authentication troubleshooting
- AADSTS50011: Redirect URI mismatch
- AADSTS50076: Using multifactor authentication
- AADSTS50079: The user is required to use multifactor authentication
- AADSTS500113: No reply address registered for the application
- AADSTS900971: No reply address provided
- AADSTS65001: The user or administrator has not consented to use the application
- AADSTS65004: User declined to consent to access the app
- AADSTS7000218: The request body must contain the following parameter: client_assertion or client_secret
- AADSTS700025: Client is public so neither 'client_assertion' nor 'client_secret' should be presented
- AADSTS70002: InvalidClient - Error validating the credentials
- AADSTS7000215: Invalid client secret provided
- AADSTS50055: The password is expired
- AADSTS700082: The refresh token has expired due to inactivity
- AADSTS50194: Application is not configured as a multitenant application
- AADSTS53003: Access has been blocked by Conditional Access policies
- Mail troubleshooting
- Calendar troubleshooting
- Files troubleshooting
- Sheets troubleshooting
- Presentations
- Release Notes
- About the Presentations activity package
- Project compatibility
- Add or Update Powerpoint Sensitivity Label
- Add Data Table to Slide
- Add File to Slide
- Add Image or Video to Slide
- Add New Slide
- Add Text to Slide
- Copy Paste Slide
- Create New PowerPoint Document
- Delete Slide
- Format Slide Content
- Get Powerpoint Sensitivity Label
- Paste Item Into Slide
- Replace Text in Presentation
- Run Presentation Macro
- Save PowerPoint File As
- Save Presentation as PDF
- Use PowerPoint Presentation
- Word
- Release Notes
- About the Word activities package
- Project compatibility
- Word Application Scope / Use Word File
- Add or Update Word Sensitivity Label
- Add Hyperlink to Document
- Add Picture
- Append Text
- Create New Document
- Get Word Sensitivity Label
- Insert DataTable in Document
- Paste Chart/Picture Into Document
- Read Text
- Replace Picture
- Replace Text in Document
- Save Document As
- Save Document as PDF
- Set Bookmark Content
- Set Content Property

Productivity activities
OAuth application setup
This section explains how to set up the OAuth application, regardless of the authentication type you use, whether it is Interactive Token, Integrated Windows Authentication, Username and password, Application ID and secret, or Application ID and certificate.
You can either use the UiPath Public App (OAuthApplication = UiPath), which is the default one, or you can register and use your own Azure app (OAuthApplication = Custom):
- UiPath Public App registration: The advantage of using the UiPath public app is that you do not need to configure or maintain the application.
UiPath does not store any user data. The authentication token is saved only on your machine or in your Orchestrator bucket. For more details, check UiPath Public App registration.
- Bring your own app (BYOA): The advantage of using your own application is that you can manage, customize, and assign permissions within your organization more granularly. For more details, check Custom OAuth Application registration - Bring your own app (BYOA).
UiPath Public App registration
The UiPath Public App is registered with the following information:
- Name: UiPathStudioO365App
- Client ID:
f2f43f65-16a6-4319-91b6-d2a342a88744 - Scopes: Calendars.Read, Calendars.Read.Shared, Calendars.ReadWrite, Calendars.ReadWrite.Shared, Chat.ReadWrite, email, EWS.AccessAsUser.All, Files.Read, Files.Read.All, Files.ReadWrite, Files.ReadWrite.All, Group.Read.All, Group.ReadWrite.All, Mail.Read, Mail.Read.Shared, Mail.ReadWrite, Mail.ReadWrite.Shared, Mail.Send, Mail.Send.Shared, offline_access, openid, Presence.Read, Presence.Read.All, profile, Sites.Read.All, Sites.ReadWrite.All, User.Read, User.Read.All.
Custom OAuth Application registration - Bring your own app (BYOA)
This section explains how to create an application for the Microsoft 365 Scope connections.
Overview
To enable the Microsoft 365 classic activities, your application must:
- be integrated with the Microsoft identity platform.
- have the correct Microsoft Graph API permissions assigned to it.
After you register your Microsoft 365 application, Microsot Entra ID assigns a unique application (client) ID that you enter in the Microsoft 365 Scope activity along with the services you assigned permissions to, which are files, mail, and calendar.

Register your own application (BYOA)
This process is described in detail in the Microsoft documentation in Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform. However, the Microsoft user interface may have changed since these steps were first documented.
- Sign into the Azure portal using your personal, work, or school Microsoft 365 account.
- Select Microsoft Entra ID.
- Select the Add button and, from the drop-down list, select App registration.
- On the Register an application page, fill in the following fields Name, Supported account types, and Redirect URI (optional).
- In the Name field, enter a name for your application.
- Under Supported account types, select the option that applies to you:
- Accounts in this organizational directory only (UiPath only - Single tenant) - use this option if your target audience is internal to your organization. This represents a single tenant application.
- Accounts in any organizational directory (Any Microsoft Entra ID tenant - Multitenant) - use this option if your target audience is business or educational customers. This represents a multitenant application.
- Accounts in any organizational directory (Any Microsoft Entra ID tenant - Multitenant) and personal Microsoft accounts (e.g. Skype, Xbox) - use this option to target the widest set of Microsoft identities. This represents a multitenant application.
- Personal Microsoft accounts only For more information about which option to select, refer to Who can sign in to you app?
- Under Redirect URI (optional), enter a URI address, if applicable. The Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL.NET) uses a default redirect URI:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/nativeclient. This value will likely work for you when using the Interactive Token authentication type.- Your selection is dependent on your authentication type. For more details, check How to connect to Microsoft 365 activities).
- In our example, the organization supports multi-tenant authentication, and can only use the Interactive token authentication type which requires a redirect URI.
- If you use Interactive Token and the default Microsoft Redirect URI, you must add a platform of type Mobile and desktop applications. For more details, check Configure platform settings in the Microsoft documentation.
- If your authentication type is Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) or Username and Password, you do not need to register a redirect URI for your application. These flows do a round trip to the Microsoft identity platform v2.0 endpoint, and your application will not be called back on any specific URI.
- When working with Microsoft 365 in a UiPath Studio project targeting .NET 5.0, add
http://localhostto the Redirect URI of the applications you own. For more details, check Desktop app-registration in the Microsoft identity platform documentation.
- Select Register, which redirects you to the Overview page of your registered application.
To complete the application configuration, you must also add API permissions to it.
This setup is just an example. Therefore, you can make selections based on the policies of your organization.
Add API permissions
- Interactive Token authentication uses delegated permissions.
- Permissions can vary depending on the activity, since each activity includes the permissions it needs for its specific features.
After you register your application, add the necessary API permissions as follows:
-
In the Azure portal , go to your registered application.
-
Expand the Manage option, and select API permissions.
-
Select Add a permission, which opens the Request API permissions side panel.
-
Select Microsoft Graph, under the Microsoft APIs tab.
-
Select Delegated permissions to show the list of permissions.
Note:- Delegated permissions are used with Interactive Token.
- Application permissions are used with Application ID and secret.
For more details on permission types, check Configure a client application to access web APIs in the Microsoft Azure documentation.
-
Use the search bar or scroll down the list and select the following permissions:
Note:- Permissions can vary depending on the activity, since each activity includes the permissions it needs for its specific features.
- These permissions are not all mandatory. The following list represents the complete set of permissions required to run all Microsoft 365 activities. You can restrict permissions depending on your particular use case. Check outthe activities documentation pages to learn what permissions they need.
- Calendar
- Calendars.Read
- Calendars.ReadWrite
- Files
- Files.Read
- Files.Read.All
- Files.ReadWrite
- Files.ReadWrite.All
- Sites
- Sites.Read.All
- Sites.ReadWrite.All
- Mail
- Mail.Read
- Mail.ReadWrite
- Mail.Send
- Users
- User.Read
- Shared - scopes required to access resources shared with the user, but not owned by them.
- Mail.Read.Shared
- Mail.ReadWrite.Shared
- Mail.Send.Shared
- Calendars.Read.Shared
- Calendars.ReadWrite.Shared
-
Select Add permissions to return to your list of API permissions.
 8. Make sure your API permissions include your added Calendars, Files, User, and Mail permissions.
8. Make sure your API permissions include your added Calendars, Files, User, and Mail permissions.

Restrict an application to specific websites
If you want to control which websites your application can access, proceed as follows:
First, assign the Sites.Selected permission to your application:
- In the Azure portal , go to your registered application.
- Expand the Manage option, and select API permissions.
- Select Add a permission, which opens the Request API permissions side panel.
- Under the Microsoft APIs tab, select Microsoft Graph.
- Select Application permissions.
- Search for sites and expand the Sites drop-down menu to view all the available site permissions.
- Add a checkmark next to the Sites.Selected permission, and then select Add permission.
Then, allow the application to access a particular website using APIs:
- Go to the Microsoft Graph explorer.
- Create an API of type GET. For example
https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/sites?search=FPH_Test, whereFPH_Testis the name of a SharePoint site.
Figure 1. Microsoft Graph Explorer page with the GET API
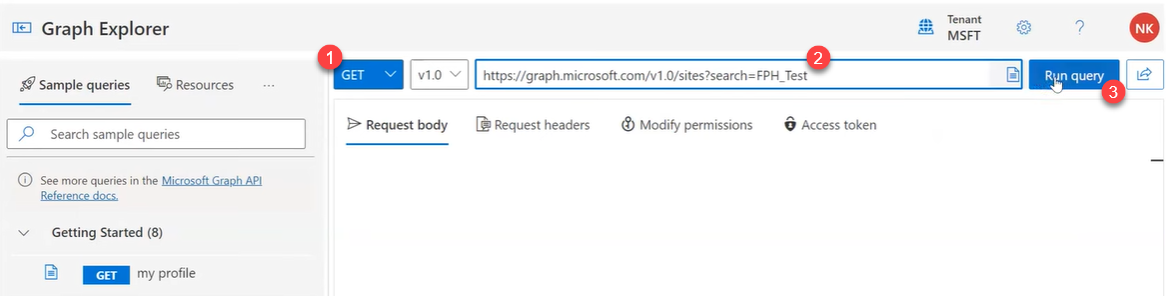
- Select Run query.
- Copy the site ID
6c964666-500d-48e6-9ca6-84acee41c5b9,f955b6bc-9d48-4155-b1f5-e722d5cea1b5from the response body and paste it into a document for later use.
Figure 2. The GET API response body in Microsoft Graph Explorer

-
To allow the application to access this website, create another API, this time of type POST. For example
https://graph/microsoft.com/v1.0/sites/0yxd4.sharepoint.com,6c964666-500d-48e6-9ca6-84acee41c5b9,f955b6bc-9d48-4155-b1f5-e722d5cea1b5/permissions, where6c964666-500d-48e6-9ca6-84acee41c5b9,f955b6bc-9d48-4155-b1f5-e722d5cea1b5is the site ID. -
Since this is a POST API, enter the payload data in JSON format in the Request body. For example:
{ "roles": [ "write" ], "grantedToIdentities": [ { "application": { "id": "14dbd4c1-9ebf-47e8-c3f75bffed2d", "displayName": "BOYA_Nisarg" } } ] }{ "roles": [ "write" ], "grantedToIdentities": [ { "application": { "id": "14dbd4c1-9ebf-47e8-c3f75bffed2d", "displayName": "BOYA_Nisarg" } } ] }Note:- Make sure the payload contains the application name and ID.
- You can find the app ID when you access the application in Azure, under Overview.
-
Select Run query. If the query was ran successfully, the message Created - 201 is shown.
To check which applications can access specific sites, change the API from POST to GET, remove the payload, keep same API, and run the query. You can find in the response body all applications that can access that specific site.