- Overview
- App Events
- Flowchart Builder
- Callout
- Complex Scenarios
- Credentials
- Data Service
- About the Data Service activity package
- Project compatibility
- Create Entity Record
- Update Entity Record
- Delete Entity Record
- Get Entity Record by Id
- Query Entity Records
- Query Multiple Entity Records
- Upload File to Record Field
- Download File from Record Field
- Delete File from Record Field
- Create Multiple Entity Records
- Update Multiple Entity Records
- Delete Multiple Entity Records
- Form
- Release notes
- Project compatibility
- Real Time Forms
- Updating form data
- Running forms using JavaScript
- Customizing Forms Using CSS
- Conditional components
- Adding multiple components on the same row in Columns
- Using the Data Table component
- Get File/Folder path
- Reading cell values from a Data Grid component
- Displaying PDF files
- Displaying images in forms
- Scrolling through Data Grids
- Using Dev Tools with forms
- Calculate form component values
- Managing dates in forms
- Opening hyperlinks inside forms
- Displaying a default tab in forms
- Displaying the full label of a component
- Searching long strings in drop-down lists
- Dynamically set form values
- About the pre 23.4 Form experience
- Project Compatibility
- Real Time Forms
- Dynamic Checkboxes
- Conditional Dropdowns
- Displaying a Default Tab
- Displaying Images
- Displaying PDF Files
- Displaying the Full Label
- Dynamic HTML Elements
- Managing Dates
- Searching Long Strings in Drop-downs
- Customizing Forms Using Local CSS Files
- Executing Do Block On Checkbox Change
- Customizing Columns Width
- Updating Form Data
- Resetting Collection Data
- Advanced Logic
- Executing Do Block on Dropdown Option Change
- Reading Cell Values From a Data Grid Component
- Conditional Components
- Scrolling Through Data Grid Components
- Using the Grid Component
- Dev Tools
- Calculated Value
- Dynamic Dropdowns
- Switching Tabs With Button Click
- Opening Hyperlinks Inside Form
- FTP
- IPC
- Automation Ops Pipelines
- Release notes
- About the Pipelines activity package
- Project compatibility
- Activate Solution Deployment
- Analyze
- Build
- Clone
- Delete Solution Package
- Deploy Solution
- Download Package
- Download Solution Package
- Download Solution Package Configuration
- Publish Package
- Publish Solution Package
- Re-sync Solution Project
- Run Existing Test Set
- Run Tests
- Stage
- Uninstall Solution
- Update Process
- Upload Solution Package
- Persistence
- Release notes
- Project compatibility
- Bulk Form Designer
- Start Job And Get Reference
- Wait For Job And Resume
- Add Queue Item And Get Reference
- Wait For Queue Item And Resume
- Wait For Form Task And Resume
- Resume After Delay
- Assign Tasks
- Create External Task
- Wait For External Task And Resume
- Complete Task
- Forward Task
- Get Form Tasks
- Get Task Data
- Get App Tasks
- Add Task Comment
- Update Task Labels
- Create App Task
- Wait For App Task And Resume
- Configure task timer
- Working with App tasks
- Building Your First Form Action
- Advanced Controls for Drop-downs
- Embedding Objects in Form Actions
- Allowing Users to Upload Files to the Storage Bucket
- Adding Advanced Logic Using Java Script
- Setting a Default Tab
- Removing the Delete button from Edit Grid using custom CSS
- Customizing Edit Grid templates
- Using buttons to trigger custom logic
- Using an External Form Layout
- Dynamically expanding form components at runtime
- Aligning the content of a form component from left to right using JSON attributes
- Sample Workflows
- System
- Release notes
- Project compatibility
- Supported character encoding
- RegEx Builder Wizard
- Add Data Column
- Add Data Row
- Add Log Fields
- Add or Subtract from Date
- Add Transaction Item
- Add Queue Item
- Append Item to Collection
- Append Item to List
- Append Line
- Beep
- Break / Exit Loop
- Browse for File
- Browse for Folder
- Build Collection
- Build Data Table
- Bulk Add Queue Items
- Change Case for Text
- Change Type
- Check False
- Check True
- Clear Data Table
- Collection to Data Table
- Comment
- Compress/Zip Files
- Copy File
- Copy Folder
- Combine text
- Comment Out / Disabled Activities
- Continue / Skip Current
- Create File
- Create Folder
- Create List
- Custom Input
- Delete
- Delete File
- Delete Folder
- Delete Storage File
- Delete Queue Items
- Disable Local Trigger
- Do While
- Download file from URL
- Download Storage File
- Enable Local Trigger
- Evaluate Business Rule
- Exists in Collection
- Extract/Unzip Files
- Extract Date and Time from Text
- Extract Text
- File Change Trigger
- File Exists
- Filter Collection
- Filter Data Table
- Folder Exists
- For Each
- For Each File in Folder
- File Change Trigger V3
- Find and Replace
- Find Matching Patterns
- For Each Folder in Folder
- For Each Row in Data Table
- Format Date as Text
- Format Value
- Generate Data Table From Text
- Get Asset
- Get Credential / Get Orchestrator Credential
- Get Current Job Info
- Get Environment Folder
- Get Environment Variable
- Get File Info
- Get Folder Info
- Get Jobs
- Get Processes
- Get Row Item
- Get Secret
- Get Transaction Item
- Get Username/Password
- Get Queue Items
- Global Variable Changed Trigger
- Input Dialog
- Invoke Code
- Invoke Com Method
- Invoke Power Shell
- Invoke Process
- Invoke VBScript
- Invoke Workflow File
- Is Text Matching
- Join Data Tables
- Kill Process
- Launch Workflow Interactive
- List Storage Files
- Log Message
- Lookup Data Table
- Manual Trigger
- Merge Collections
- Merge Data Table
- Message Box
- Modify Date
- Modify Text
- Move File
- Move Folder
- Multiple Assign
- New Item Added to Queue
- Notify Global Variable Changed
- Orchestrator HTTP Request
- Output Data Table
- Parallel
- Parallel for each
- Path Exists
- Postpone Transaction Item
- Process End Trigger
- Process Start Trigger
- Process Tracking Scope
- Raise Alert
- Read List Item
- Read Text File
- Read Storage Text
- Remove Data Column
- Remove Data Row
- Remove Duplicate Rows
- Remove From Collection
- Remove Log Fields
- Replace Matching Patterns
- Repeat Number of Times
- Repeat Trigger
- Rename File
- Rename Folder
- Report Status
- Reset Timer
- Resume Timer
- Retry Scope
- Return
- Run Local Triggers
- Run Agent
- Run Job
- Run Parallel Process
- Set Asset
- Send Email Notification
- Set Credential
- Set Environment Variable
- Set Secret
- Set Task Status
- Set Trace Status
- Set Transaction Progress
- Set Transaction Status
- Should Stop
- Split Text
- Sort Data Table
- Start Timer
- Start Job
- Stop Job
- Stop Local Triggers
- Stop Timer
- Text to Left/Right
- Text to Upper/Lowercase
- Time Trigger
- Trigger Scope
- Track Object
- Timeout Scope
- Update Row Item
- Update List Item
- Upload Storage File
- Wait for Download
- Wait Queue Item
- While
- Workflow Placeholder
- Write Storage Text
- Write Text File
- AddDataRow
- AddQueueItem
- AddTransactionItem
- AppendLine
- BulkAddQueueItems
- ClearDataTable
- CompressZipFiles
- CopyFile
- CreateFile
- CreateFolder
- DeleteFileOrFolder
- DeleteQueueItems
- DeleteStorageFile
- DownloadStorageFile
- ExtractUnzipFiles
- FilterDataTable
- GetAsset
- GetCredential
- GetJobs
- GetQueueItem
- GetQueueItems
- GetResourceForLocalPath
- GetRowItem
- GetTransactionItem
- InvokeProcess
- JoinDataTables
- ListStorageFiles
- LookUpDataTable
- MergeDataTable
- MoveFile
- OrchestratorHTTPRequest
- OutputDataTable
- PathExists
- PostponeTransactionItem
- ReadStorageText
- ReadTextFile
- RemoveDataColumn
- RemoveDuplicateRows
- Replace
- SetAsset
- SetCredential
- SetTransactionProgress
- SetTransactionStatus
- SortDataTable
- StartJob
- StopJob
- UpdateRowItem
- UploadStorageFile
- WaitQueueItem
- WriteStorageText
- WriteTextFile
- Testing
- Release notes
- About the Testing activity package
- Project compatibility
- Project Settings
- Add Test Data Queue Item
- Address
- Attach Document
- Bulk Add Test Data Queue Items
- Create Comparison Rule
- Compare PDF Documents
- Compare Text
- Delete Test Data Queue Items
- Get Test Data Queue Item
- Get Test Data Queue Items
- Given Name
- Last Name
- Random Date
- Random Number
- Random String
- Random Value
- Verify Control Attribute
- Verify Expression
- Verify Expression With Operator
- Verify Range
- Address
- AddTestDataQueueItem
- AttachDocument
- BulkAddTestDataQueueItems
- DeleteTestDataQueueItems
- GetTestDataQueueItem
- GetTestDataQueueItems
- GivenName
- LastName
- RandomDate
- RandomNumber
- RandomString
- RandomValue
- VerifyAreEqual
- VerifyAreNotEqual
- VerifyContains
- VerifyExpression
- VerifyExpressionWithOperator
- VerifyIsGreater
- VerifyIsGreaterOrEqual
- VerifyIsLess
- VerifyIsLessOrEqual
- VerifyIsRegexMatch
- VerifyRange
- Workflow Foundation

Workflow activities
Join Data Tables
UiPath.Core.Activities.JoinDataTables
Description
Combines rows from two tables by using values common to each other, according to a Join rule, which is specified in the Join Type property.
Project compatibility
Windows - Legacy | Windows | Cross-platform
Cross-platform configuration
-
Data Table 1 - The first table that you want to use in the Join operation, stored in a
DataTablevariable. This field supports onlyDataTablevariables. -
Data Table 2 - The second table that you want to use in the Join operation, stored in a
DataTablevariable. This field supports onlyDataTablevariables.Note:The order in which the two tables are supplied is very important, because it influences the structure of the resulting table, according to the option selected in the JoinType property field.
-
JoinType - The type of Join operation you want to use. The following options are available:
- Inner - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and DataTable2 which meet the Join rule. Any rows that do not meet the rule are removed from the resulting table.
- Left - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and only the values from DataTable2 which meet the Join rule. Null values are inserted into the column for the rows from DataTable1 that don't have a match in the DataTable2 rows.
- Full - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and DataTable2, regardless of whether the join condition is met. Null values are added into the rows from both tables that don't have a match.
Note:
If a column from DataTable2 shares the same name with a column from DataTable1, then the name of the column from DataTable2 is changed to
[ColumnName]_1in the resulting table. If a column with the[ColumnName]_1name already exists, the consecutive number that is not already in use is used instead. For example, if DataTable1 has columns named ID, ID_1 and ID_2, and DataTable2 has a column named ID, after the join, the column in DataTable2 is named ID_3.
-
Join Rules - The conditions to join the tables by. Selecting the field opens a simple Filter Builder where you can add rules that compose the filter.
Windows - Legacy, Windows configuration
Properties panel
Common
- DisplayName - The display name of the activity.
Input
- DataTable1 - The first table that you want to use in the Join operation, stored in a
DataTablevariable. This field supports onlyDataTablevariables. - DataTable2 - The second table that you want to use in the Join operation, stored in a
DataTablevariable. This field supports onlyDataTablevariables.Note:The order in which the two tables are supplied is very important, because it influences the structure of the resulting table, according to the option selected in the JoinType property field.
Misc
- Private - If selected, the values of variables and arguments are no longer logged at Verbose level.
Options
- JoinType - The type of Join operation you want to use. The following options are available:
- Inner - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and DataTable2 which meet the Join rule. Any rows that do not meet the rule are removed from the resulting table.
- Left - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and only the values from DataTable2 which meet the Join rule. Null values are inserted into the column for the rows from DataTable1 that don't have a match in the DataTable2 rows.
- Full - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and DataTable2, regardless of whether the join condition is met. Null values are added into the rows from both tables that don't have a match.
Note:
If a column from DataTable2 shares the same name with a column from DataTable1, then the name of the column from DataTable2 is changed to
[ColumnName]_1in the resulting table. If a column with the[ColumnName]_1name already exists, the consecutive number that is not already in use is used instead. For example, if DataTable1 has columns named ID, ID_1 and ID_2, and DataTable2 has a column named ID, after the join, the column in DataTable2 is named ID_3.
Output
- DataTable - The table with the joined values, stored in a
DataTablevariable. This field supports onlyDataTableVariables.
Join Wizard
This wizard helps you configure the properties of the Join Data Tables activity. It can be opened by using the Join Wizard button in the body of the activity in the Designer panel.
From the upper section of the wizard, you can select both of the DataTable variables you wish to use in the operation, the Join type, and the output variable, from the following fields:
- Input DataTable1 - The
DataTablevariable containing the first table you want to use. - Input DataTable2 - The
DataTablevariable containing the second table you want to use. - Output DataTable - The
DataTablevariable in which you want to store the resulting table. - Join Type - The type of Join operation you want to use. The following options are available:
- Inner - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and DataTable2 which meet the Join rule. Any rows that do not meet the rule are removed from the resulting table.
- Left - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and only the values from DataTable2 which meet the Join rule. Null values are inserted into the column for the rows from DataTable1 that don't have a match in the DataTable2 rows.
- Full - Keep all rows from DataTable1 and DataTable2, regardless of whether the join condition is met. Null values are added into the rows from both tables that don't have a match.
From the lower section of the wizard, you can configure the structure of the resulting table, by adding expressions that indicate relations between columns. Each of these expressions has three elements, as follows:
- Column Table 1 - The name of the column in the first table. This field supports only
Stringvariables containing the column name,Int32variables containing the column index orExcelColumnvariables. - Operation - The operation that defines the relation between the columns. The following options are available:
- = - Equal to
- != - Not equal to
- > - Greater than
- < - Less than
- >= - Greater than or equal to
- <= - Less than or equal to
- Column Table 2 - The name of the column in the second table. This field supports only
Stringvariables containing the column name,Int32variables containing the column index orExcelColumnvariables.
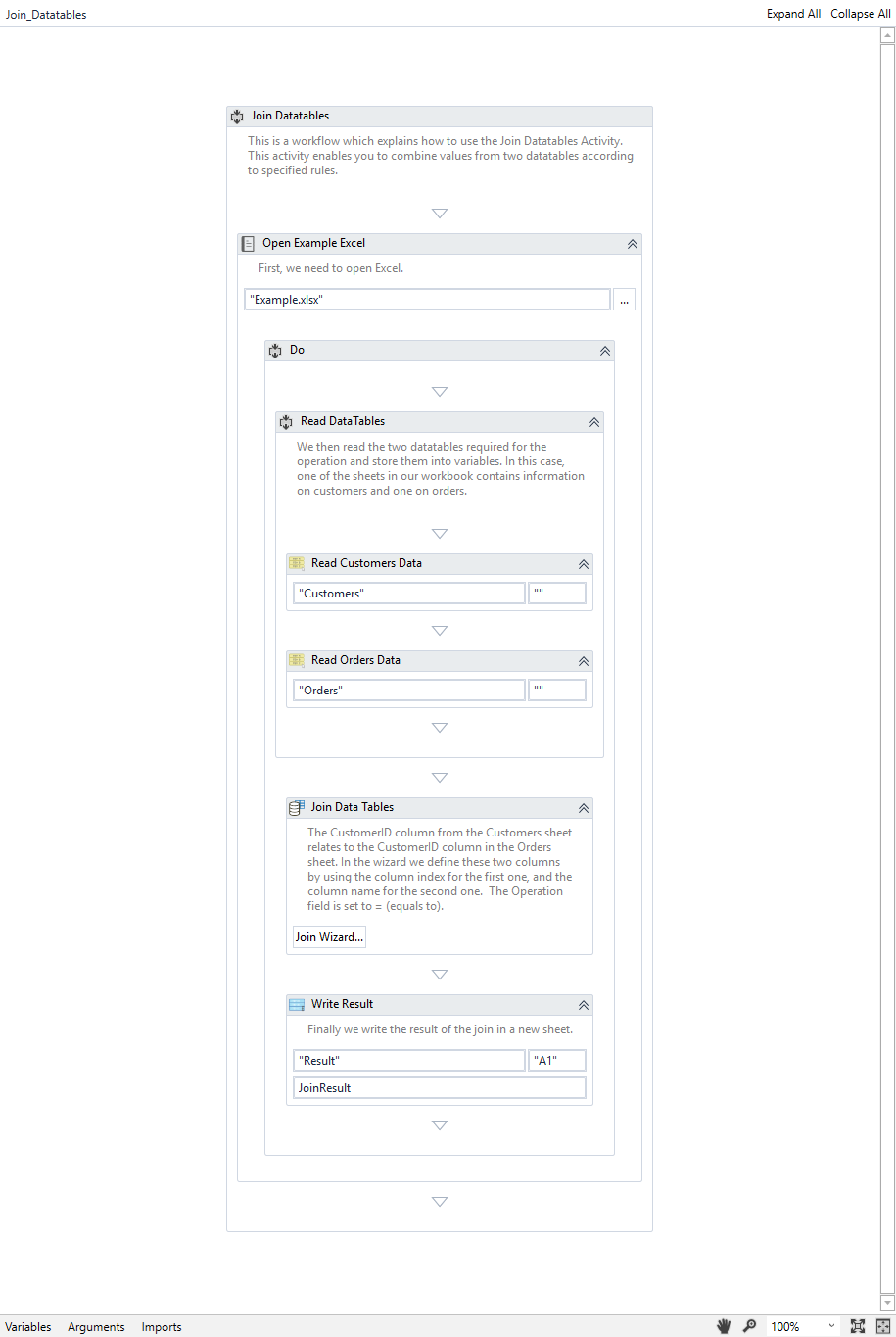
Example of Using the Join Data Tables Activity
To exemplify how to use this activity, we have created a project which joins two sheets of a workbook in another sheet of that workbook. The first sheet contains details about orders, while the second sheet contains details about customers. The two sheets have a common column, CustomerID, which is used for the join operation. The project can be downloaded here.
-
Create a blank Project.
-
Drag a Sequence container into the Designer panel.
-
Drag an Excel Application Scope and place the path of the Excel workbook in the Workbook Path property.
-
Create two
DataTablevariables, one for the Customers sheet and one for the Orders sheet. -
Inside the Excel Application Scope, drag two Read Range activities.
-
Set the two Read Range activities to read each of the sheets in the Excel workbook and store them into their corresponding variables.
-
Create a
DataTablevariable to store the resulting table. -
Drag a Join Data Tables activity in the scope container.
-
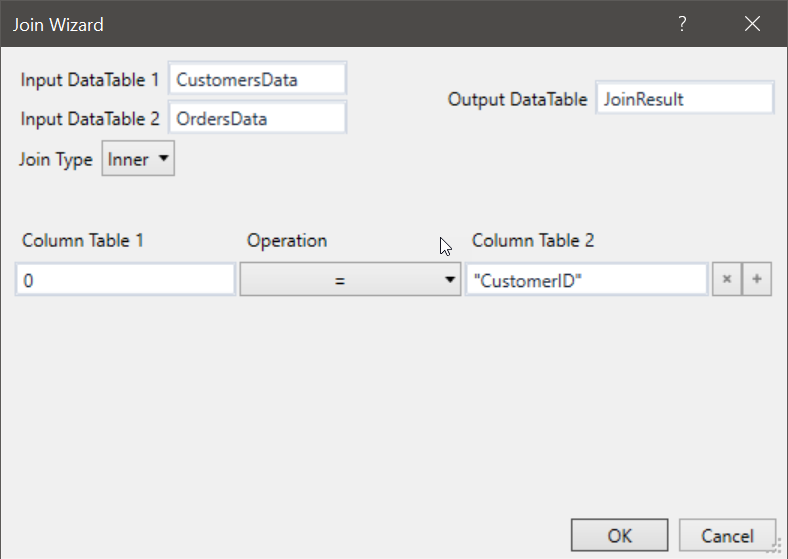
Click the Join Wizard button in the body of the activity. The Join Data Tables Wizard opens.
-
Set the variable containing the Customers sheet into the Input DataTable 1 field.
-
Set the variable containing the Orders sheet into the Input DataTable 2 field.
-
Set the variable created to store the resulting table into the Output DataTable field.
-
In the Join Type drop-down menu select Inner.
-
In the Column Table 1 field, input the column which corresponds to the CustomerID column in the Customers sheet.
-
In the Operation drop-down menu, select =.
-
In the Columns Table 2 field, input the column which corresponds to the CustomerID column in the Orders sheet. The Wizard should look like this:
-
Drag a Write Range activity to the Designer panel.
-
Configure the Write Range to write the
DataTablevariable containing the resulting table into a new sheet in the initial workbook. -
The final workflow should look like this: