- Overview
- UI Automation
- About the UI Automation activity package
- Applications and technologies automated with UI Automation
- Project compatibility
- UI-ANA-016 - Pull Open Browser URL
- UI-ANA-017 - ContinueOnError True
- UI-ANA-018 - List OCR/Image Activities
- UI-DBP-006 - Container Usage
- UI-DBP-013 - Excel Automation Misuse
- UI-DBP-030 - Forbidden Variables Usage In Selectors
- UI-DBP-031 - Activity verification
- UI-PRR-001 - Simulate Click
- UI-PRR-002 - Simulate Type
- UI-PRR-003 - Open Application Misuse
- UI-PRR-004 - Hardcoded Delays
- UI-REL-001 - Large Idx in Selectors
- UI-SEC-004 - Selector Email Data
- UI-SEC-010 - App/Url Restrictions
- UI-USG-011 - Non Allowed Attributes
- UX-SEC-010 - App/Url Restrictions
- UX-DBP-029 - Insecure Password Use
- UI-PST-001 - Audit Log Level in Project Settings
- UiPath Browser Migration Tool
- Clipping region
- Computer Vision Recorder
- About SAP WinGUI Automation
- Configuration Steps
- Supported SAP WinGUI Elements
- Activities index
- Activate
- Anchor Base
- Attach Browser
- Attach Window
- Block User Input
- Callout
- Check
- Click
- Click Image
- Click Image Trigger
- Click OCR Text
- Click Text
- Click Trigger
- Close Application
- Close Tab
- Close Window
- Context Aware Anchor
- Copy Selected Text
- Element Attribute Change Trigger
- Element Exists
- Element Scope
- Element State Change Trigger
- Export UI Tree
- Extract Structured Data
- Find Children
- Find Element
- Find Image
- Find Image Matches
- Find OCR Text Position
- Find Relative Element
- Find Text Position
- Get Active Window
- Get Ancestor
- Get Attribute
- Get Event Info
- Get From Clipboard
- Get Full Text
- Get OCR Text
- Get Password
- Get Position
- Get Source Element
- Get Text
- Get Visible Text
- Go Back
- Go Forward
- Go Home
- Google Cloud Vision OCR
- Hide Window
- Highlight
- Hotkey Trigger
- Hover
- Hover Image
- Hover OCR Text
- Hover Text
- Image Exists
- Indicate On Screen
- Inject .NET Code
- Inject Js Script
- Invoke ActiveX Method
- Key Press Trigger
- Load Image
- Maximize Window
- Microsoft Azure Computer Vision OCR
- Microsoft OCR
- Microsoft Project Oxford Online OCR
- Minimize Window
- Monitor Events
- Mouse Trigger
- Move Window
- Navigate To
- OCR Text Exists
- On Element Appear
- On Element Vanish
- On Image Appear
- On Image Vanish
- Open Application
- Open Browser
- Refresh Browser
- Replay User Event
- Restore Window
- Save Image
- Select Item
- Select Multiple Items
- Send Hotkey
- Set Clipping Region
- Set Focus
- Set Text
- Set To Clipboard
- Set Web Attribute
- Show Window
- Start Process
- System Trigger
- Take Screenshot
- Tesseract OCR
- Text Exists
- Tooltip
- Type Into
- Type Secure Text
- Use Foreground
- Wait Attribute
- Wait Element Vanish
- Wait Image Vanish
- Accessibility Check
- Application Event Trigger
- Block User Input
- Check/Uncheck
- Check App State
- Check Element
- Click
- Click Event Trigger
- Drag and Drop
- Extract Table Data
- Find Elements
- For Each UI Element
- Get Browser Data
- Get Clipboard
- Get Text
- Get URL
- Go to URL
- Highlight
- Hover
- Inject Js Script
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Keypress Event Trigger
- Mouse Scroll
- Navigate Browser
- Select Item
- Set Browser Data
- Set Clipboard
- Set Runtime Browser
- Set Focus
- Set Text
- Take Screenshot
- Type Into
- Unblock User Input
- Use Application/Browser
- Window Operation
- Perform browser search and retrieve results using UI Automation APIs
- Web Browsing
- Find Images
- Click Images
- Trigger and Monitor Events
- Create and Override Files
- HTML Pages: Extract and Manipulate Information
- Window Manipulation
- Automated List Selection
- Find and Manipulate Window Elements
- Manage Text Automation
- Load and Process Images
- Manage Mouse Activated Actions
- Automate Application Runtime
- Automated Run of a Local Application
- Browser Navigation
- Web Automation
- Trigger Scope Example
- Enable UI Automation support in DevExpress
- Computer Vision Local Server
- Mobile Automation
- Release notes
- About the mobile device automation architecture
- Project compatibility
- Get Log Types
- Get Logs
- Get Page Source
- Get Device Orientation
- Get Session Identifier
- Install App
- Manage Current App
- Manage Other App
- Open DeepLink
- Open URL
- Mobile Device Connection
- Directional Swipe
- Draw Pattern
- Positional Swipe
- Press Hardware Button
- Set Device Orientation
- Take Screenshot
- Take Screenshot Part
- Element Exists
- Execute Command
- Get Attribute
- Get Selected Item
- Get Text
- Set Selected Item
- Set Text
- Swipe
- Tap
- Type Text
- Terminal
- Release notes
- About the Terminal activity package
- Project compatibility
- Best practices
- Find Text
- Get Color at Position
- Get Cursor Position
- Get Field
- Get Field at Position
- Get Screen Area
- Get Text
- Get Text at Position
- Move Cursor
- Move Cursor to Text
- Send Control Key
- Send Keys
- Send Keys Secure
- Set Field
- Set Field at Position
- Terminal Session
- Wait Field Text
- Wait Screen Ready
- Wait Screen Text
- Wait Text at Position

UI Automation activities
Supported SAP WinGUI Elements
The SAP interfaces contain a variety of specific controls with which you can interact as exemplified in this page.
SAP Buttons
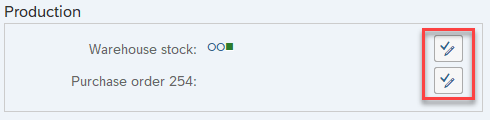
Represents any button found in the SAP WinGUI windows. There are several types, each defined by a particular element:
Icons
Icons are interactive buttons which do not display text labels.
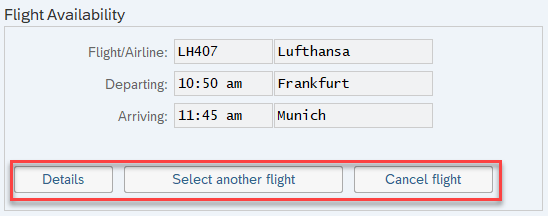
Push Buttons
A push button is a simple UI element which gives you direct access to a command in the application.
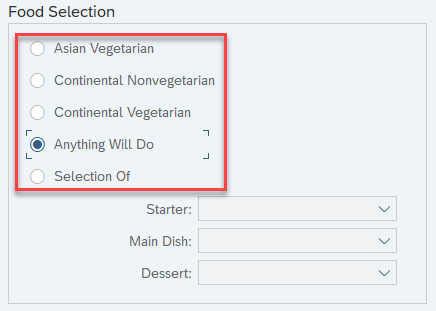
Radio Buttons
Radio buttons present a set of options. There are at least two radio buttons in a list, and you can only select one.
You can use the Click activity to interact with buttons.
SAP Calendar
The SAP Calendar allows you to select single dates or periods of time.
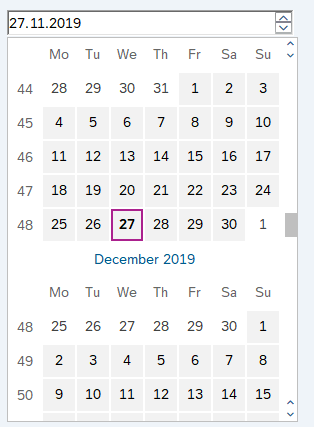
You can use the Select Dates in Calendar activity to interact with the SAP Calendar.
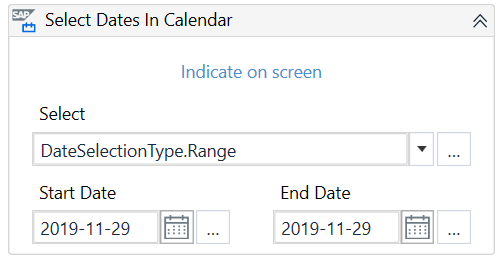
This SAP control is not supported by Recording in Studio.
SAP Checkbox
Checkbox elements represent a list of multiple choices. One, more, or no options can be selected.
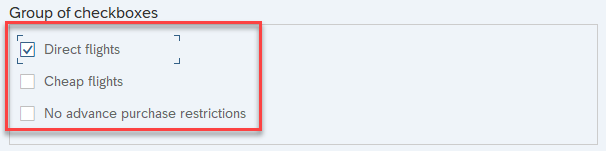
You can use the Click activity to interact with checkboxes.
SAP Context Menu
Represents a list of items inside a context menu. Note that multiple child context menus can be available in a parent context menu.

You can use the Click activity to interact with the SAP Context Menu. The AA element detection framework is required for interactive selection.
SAP Dialog Box
Represents an external window which can hold different types of other SAP controls such as buttons, text messages, or pop-up windows.
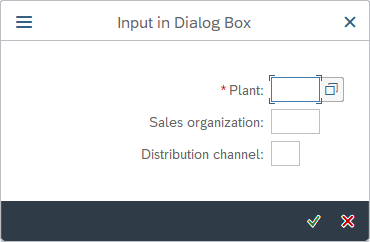
Selectors inside a dialog box are generated according to the element they represent.
If you want to close a dialog box using the Close button, you need to use the AA element detection framework.
SAP Dropdown Lists
Dropdown lists allow you to select items from predefined lists.
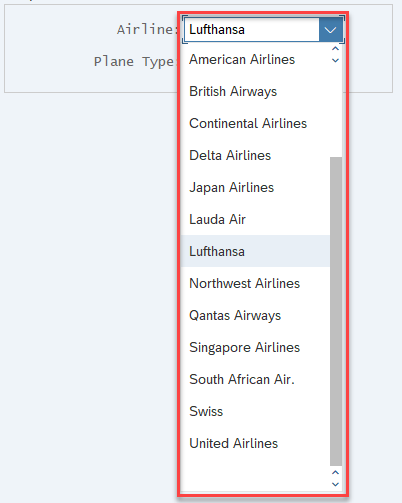
You can use the Select Item activity to interact with list items.
SAP HTML Content
The HTML controls are used to display HTML content inside the SAP WinGUI.

To interact with an HTML page inside the SAP WinGUI, you need to use the AA element detection framework. UIAutomation activities can be used to build processes for SAP HTML content.
SAP Input Field
Represents a specialized field which accepts user input.
You can use the Type Into activity to interact with input fields.
SAP Logon
SAP Logon is a locally installed program that you use to directly log on to an SAP system.
You can use the SAP Logon activity to open SAP.
This activity requires 2 parameters:
-
The exact SAP connection name from the SAP Logon or the SAP Logon Pad window used to log on to your SAP system
-
The path to your SAP Logon or SAP Logon Pad program. The default path is obtained from the corresponding system registry entry.
 Note:
Note:The Indicate on screen function is not required. The SAP scripting interface is used to connect to your SAP system.
SAP Login
Provides the possibility to log into an SAP system.
You can then use the SAP Login activity.
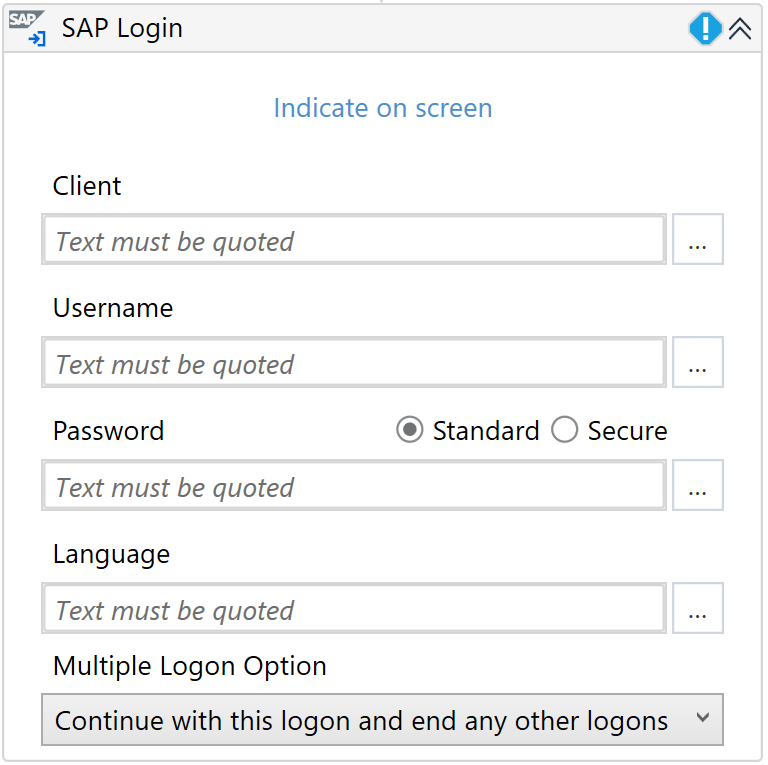
The Multiple Logon Option dropdown gives you the possibility to decide which action should be performed if a user attempts to log into the system several times and the license information for multiple logon window popups is shown. You can select from the following options:
- Continue with this logon and end any other logons in system
- Continue with this logon, without ending any other logons in system
- Terminate this logon
SAP Menu
Allows you to select items from the SAP Menu. The SAP Menu is only available in the main SAP WinGUI window.
You can use the SAP Select Menu Item activity to interact with a menu item.
This SAP control is not supported by Recording in Studio.
SAP Picture
Displays a picture in the SAP WinGUI.
You can use the SAP Click Picture on Screen activity to click the specified image.
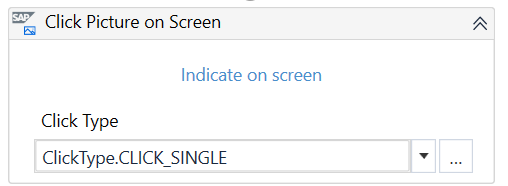
This SAP control is not supported by Recording in Studio.
SAP Statusbar
Represents a section at the bottom of the SAP WinGUI window which displays messages. It does not show system and login information.

You can use the SAP Read Statusbar activity to extract the message type, text, and data from the SAP Statusbar.
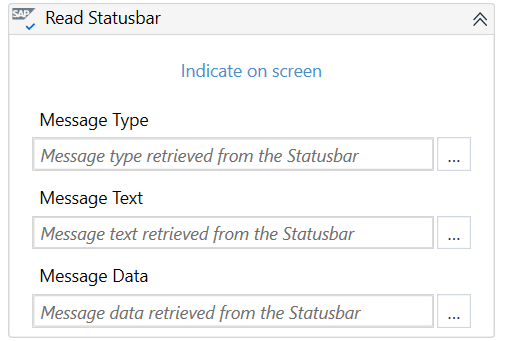
This SAP control is not supported by Recording in Studio.
SAP Session Information
Displays detailed information about the current SAP session, such as System, Client, logged User or current opened program and transaction.
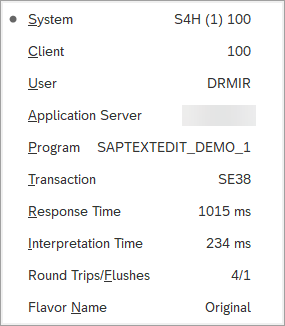
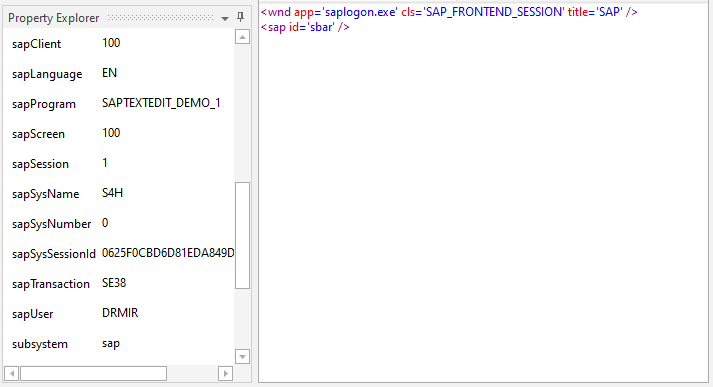
The following optional selector attributes are available in UIExplorer, and can be used with other activities such as the Get Attribute activity when you build your SAP automation:
sapClient, sapLanguage, sapProgram, sapScreen, sapSession, sapSysName, sapSysNumber, sapSysSessionId, sapTransaction, sapUser
SAP Tab
SAP Tab represents a set of buttons which let you access specific information and controls.
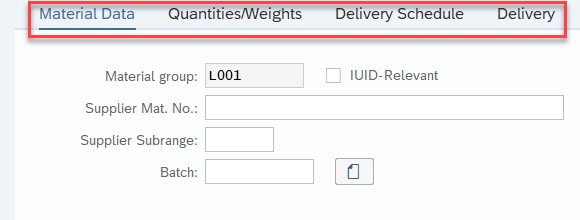
You can use the Click activity to select a single tab at a time, or you can use the Select Item activity to choose the tab of interest from a list.
Special automation case
Some SAP transactions have slash / in their names, which may lead to identification issues, while using a wildcard in the selector.
For example, in SAP Transaction: /COCKPIT/1, the selector for one of SAP Tab inside the transaction can be:
<sap id='usr/subSUB_MAIN:/COCKPIT/SAPLDISPLAY46:0389/subSUB_HDR:/COCKPIT/SAPLDISPLAY46:04051/tabsG_STRIP_HDR/tabpTAB4' />
The dynamic part of the selector is: SAPLDISPLAY46:0389, where the number 0389 is dynamically changing and does not allow a stable identification.
The structure of the selector is:
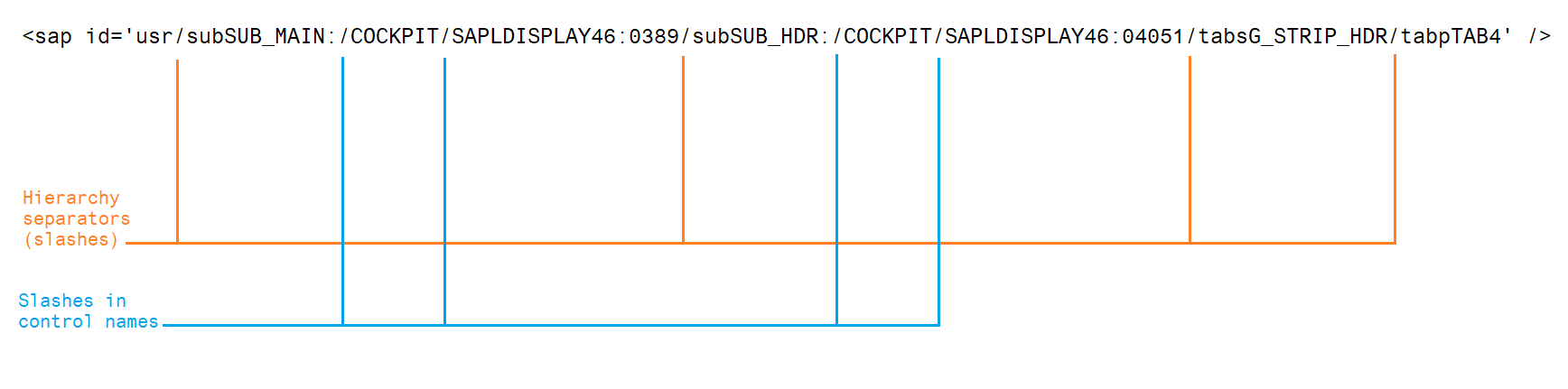
For purpose of stable identification, you would need to use wildcard in between hierarchy separators and then all (and only) the slashes between those separators/slashes need to be replaced by ?
Before <sap id='usr/subSUB_MAIN:/COCKPIT/SAPLDISPLAY46:0389/subSUB_HDR:/COCKPIT/SAPLDISPLAY46:04051/tabsG_STRIP_HDR/tabpTAB4' />
After <sap id='usr/subSUB_MAIN:?COCKPIT?SAPLDISPLAY46:038*/subSUB_HDR:/COCKPIT/SAPLDISPLAY46:04051/tabsG_STRIP_HDR/tabpTAB4' />
SAP Tables
The SAP Table represents a standard set of controls for elements displayed in a tabular structure.
Common Operations
In SAP, there are multiple types of tables available. The most common used are Standard (default) tables, Grid Tables and ALV Tables. All kind of SAP Tables can be automated with Studio.
You can use the following activities to interact with SAP Tables and their content:
SAP Standard Table
The SAP Standard Table supports all of the common operations that are available, as mentioned above.
SAP Grid Table
The SAP Grid Table supports all of the common operations that are available, as mentioned above, as well as Select/Deselect operations and Data Scraping.
Select/Deselect
With help of the Click activity or the Check activity you are able to perform all the necessary operations during your SAP automation project, such as:
- Select/Deselect Column
- Select/Deselect Row
- Select/Deselect All
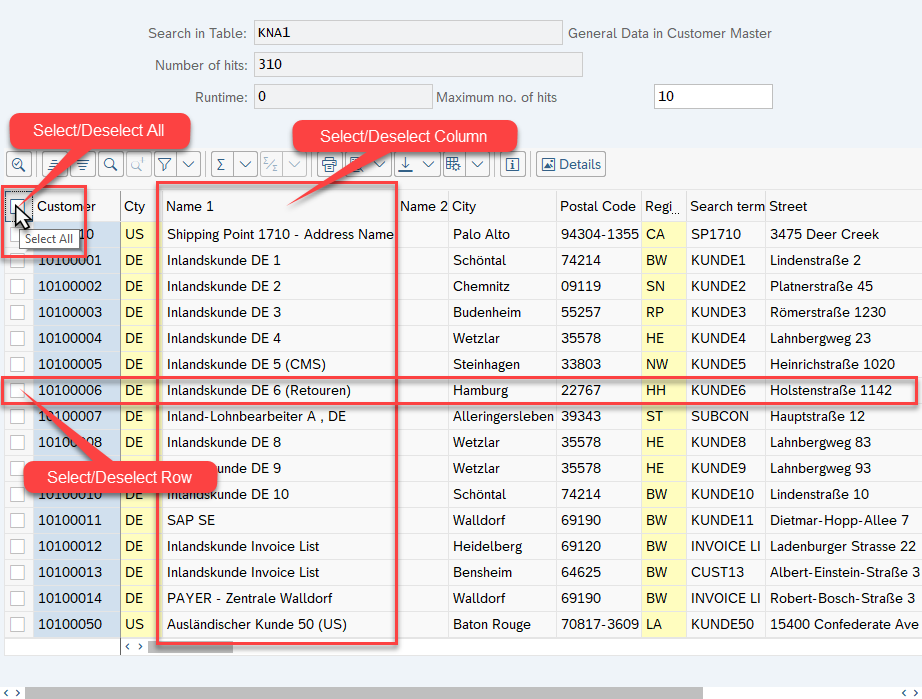
Table Cell Filtering
You can perform all the common operations, as mentioned above, on a table cell.
Using the Table Cell Scope activity, you can also filter content for table cells (for columns and rows). You can identify columns in an SAP Table by its display name, but also by other attributes, such as ColumnName. Additionally, you can filter on columns and rows to use any other property to identify elements.
In case the Column Tooltip has a similar name to another column, we automatically switch the identification of that column to a different attribute, such as ColumnName, as seen in the example below.
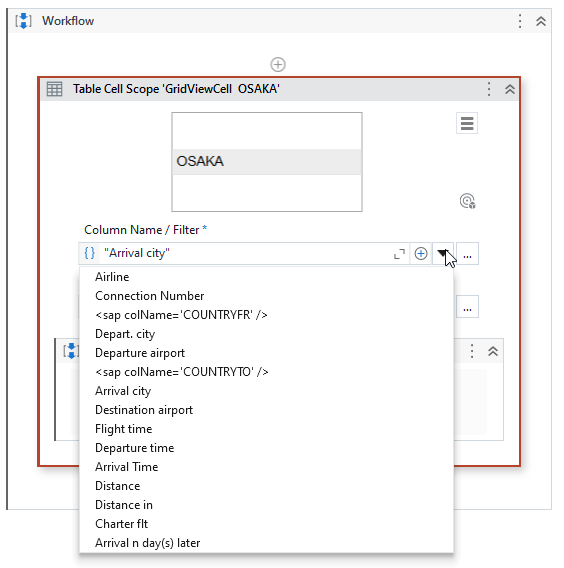
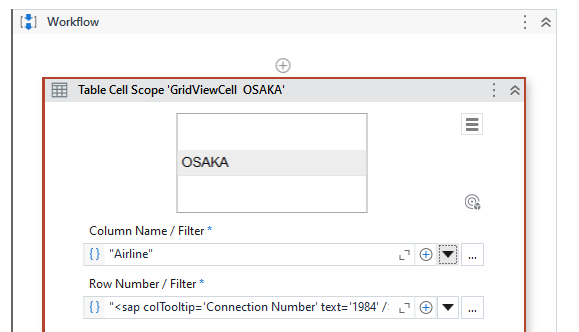
You can also use advanced filtering on Row Number, which allows identification based on multiple attributes, as seen in the example below.
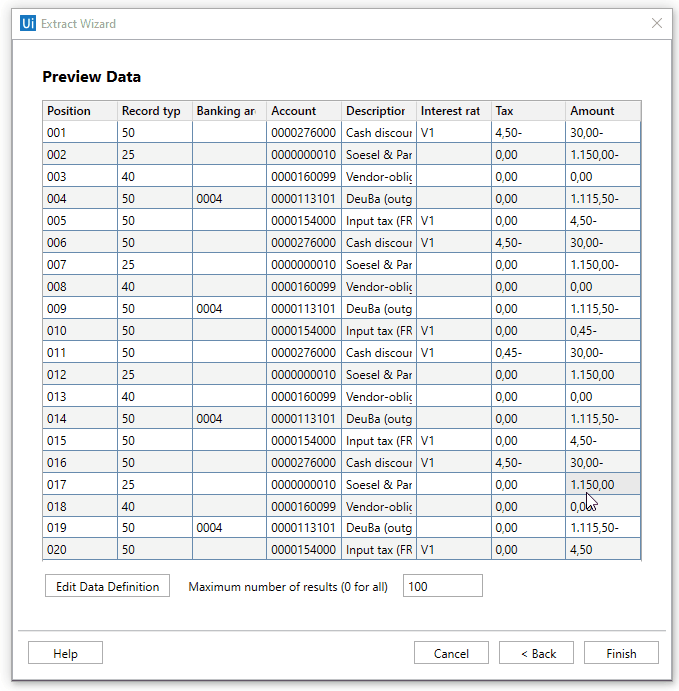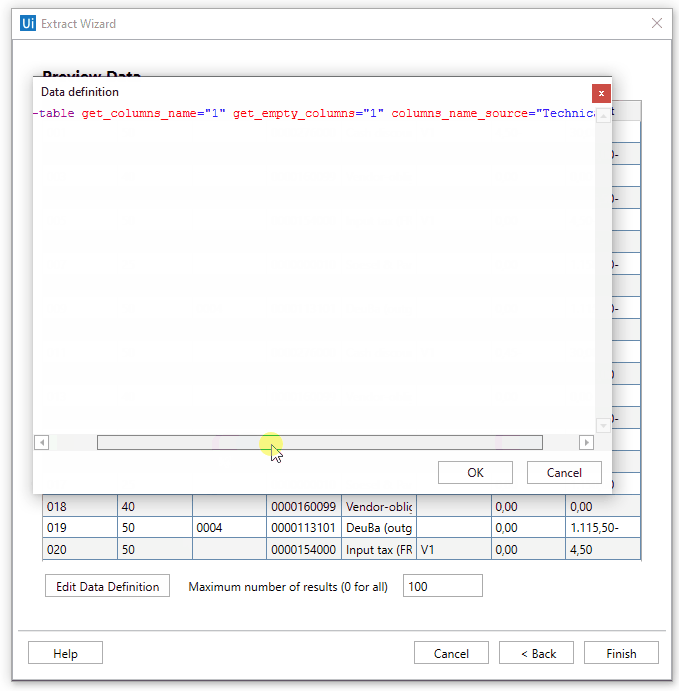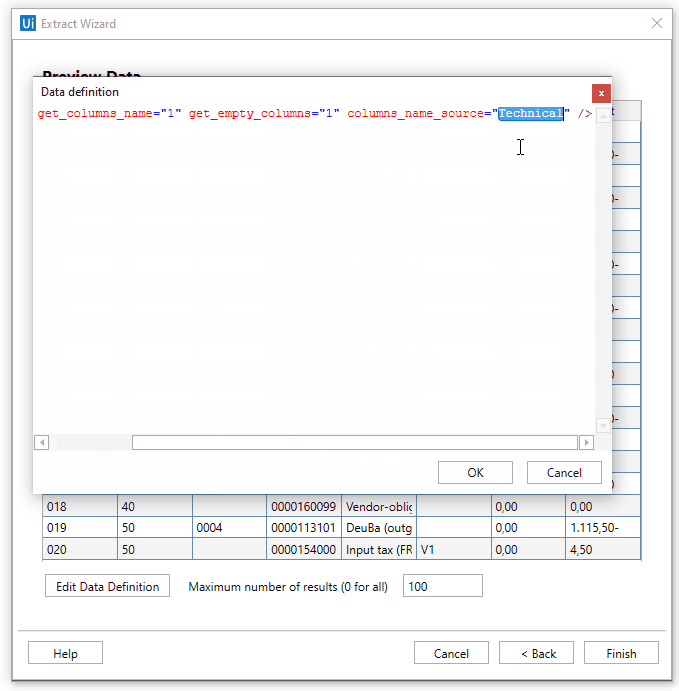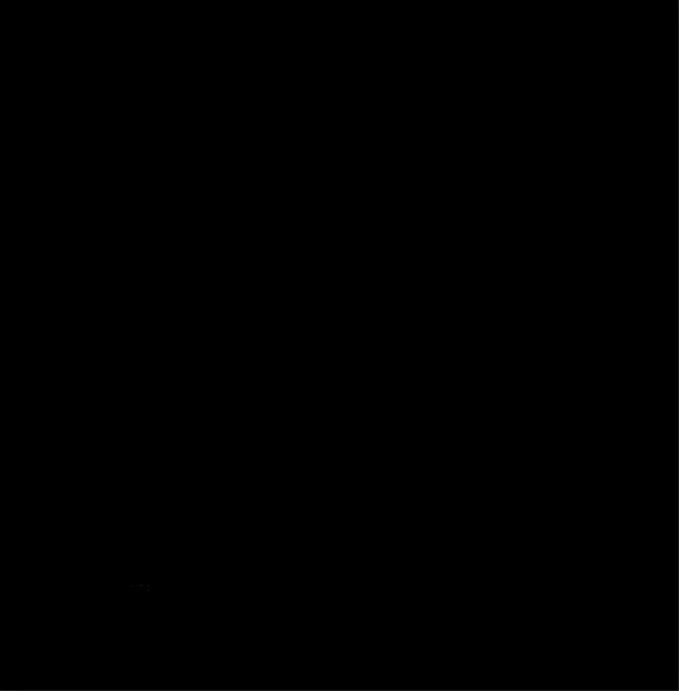
Data Scraping
Data scraping enables you to extract structured data from SAP Tables, as exemplified below.
In case you are automating a table that contains multiple columns that have the same name, the scraping mechanism automatically increments the column names (e.g. column1, column2, column3, etc.).
The Extract Structure Data activity provides additional possibilities while extracting the data from the SAP GridView table. You can use the following values for the columns_name_source parameter to define the way you want to get the table information:
- Longest - The full name of column is extracted and used.
- Shortest - The short name of column is extracted and used.
- Displayed - The visible/displayed name in SAP WinGUI is used.
- Technical - The technical header name of the column is extracted and used.
- Tooltip - The tooltip name which appears after hovering the mouse over a column name.
SAP ALV Table
The SAP ALV Table supports all common operations that are available, as mentioned above, as well as Data Scraping for simple and multiple header tables and Screen Scraping. One or multiple ALV tables on the SAP screen can be extracted.
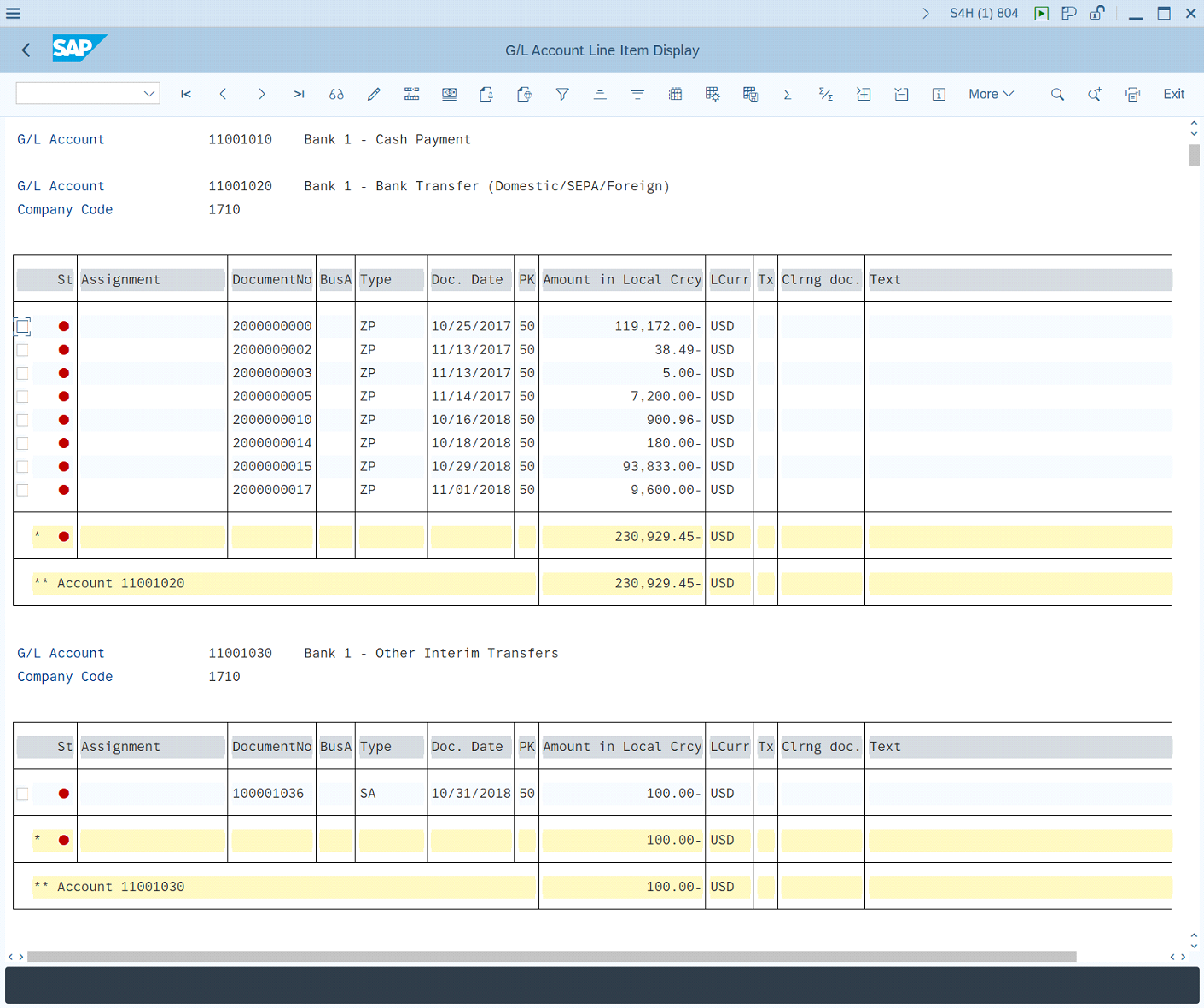
Data Scraping
This works exactly the same way as mentioned above in Data Scraping for SAP Grid Tables. Pay attention that in some cases, the column tooltip name can be different from the display name in SAP ALV Tables.
Use columns_name_source='Tooltip' parameter to define the right way to get the table information.
Multiple header tables
Studio can extract the proper data from tables that have headers spread in two or more lines.
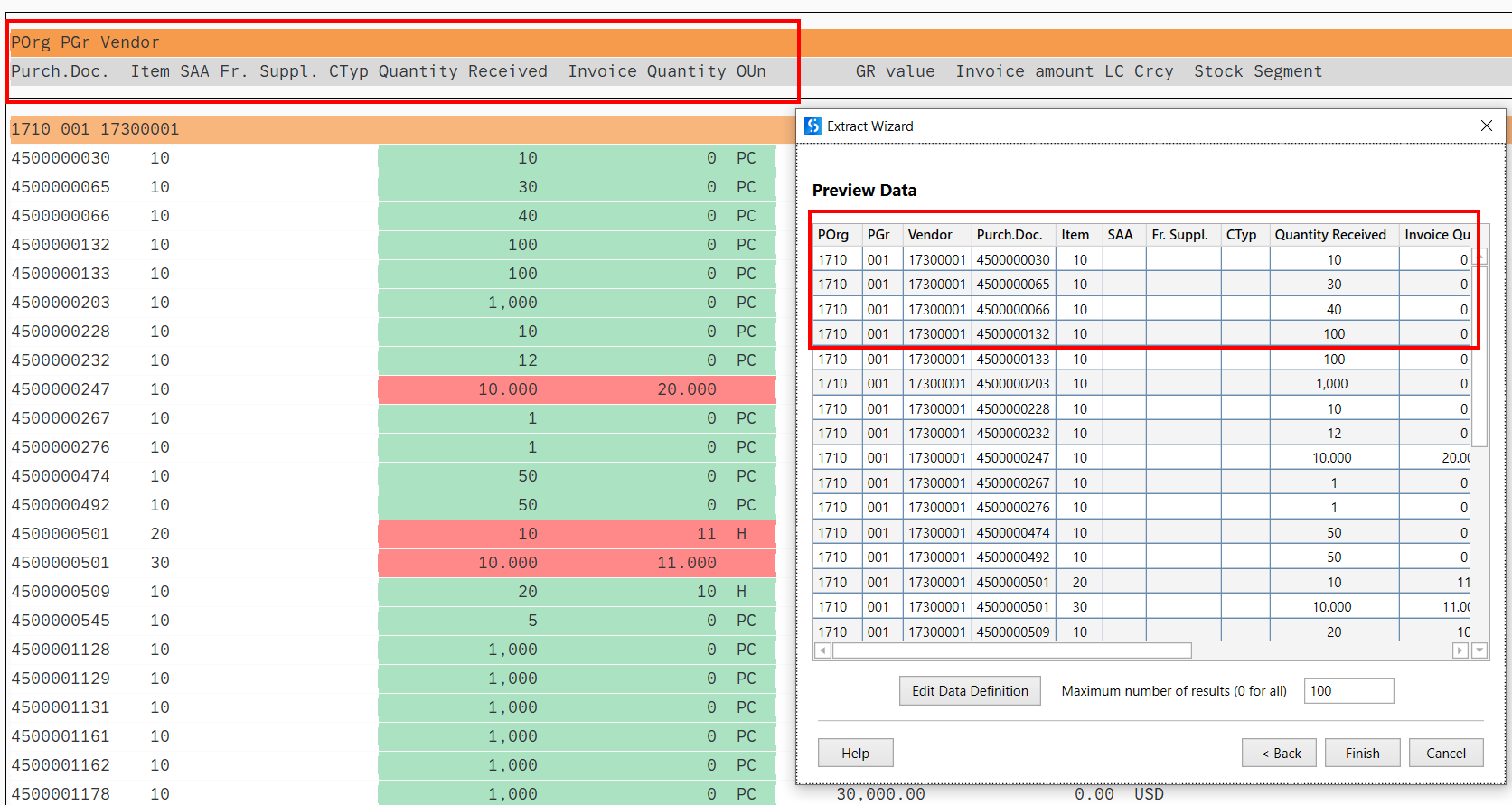
To do this, the metadata exposes the following:
join_type = ['LeftOuter' | 'Inner']
These options correspond to the SQL joins with the respective names. Left outer join also extracts rows for which only the first header is present. The other missing column values are populated with a NULL placeholder text: null_value_text = ['(null)' | 'any other user provided value']
Inner join only extracts rows with complete data, ignoring the ones without data for all the headers.
Screen Scraping
In case you decide to use Screen Scraping, the recommended scraping method is FullText, and the Ignore Hidden check box should be selected. Please note that only visible text on the SAP screen is extracted by using this method.
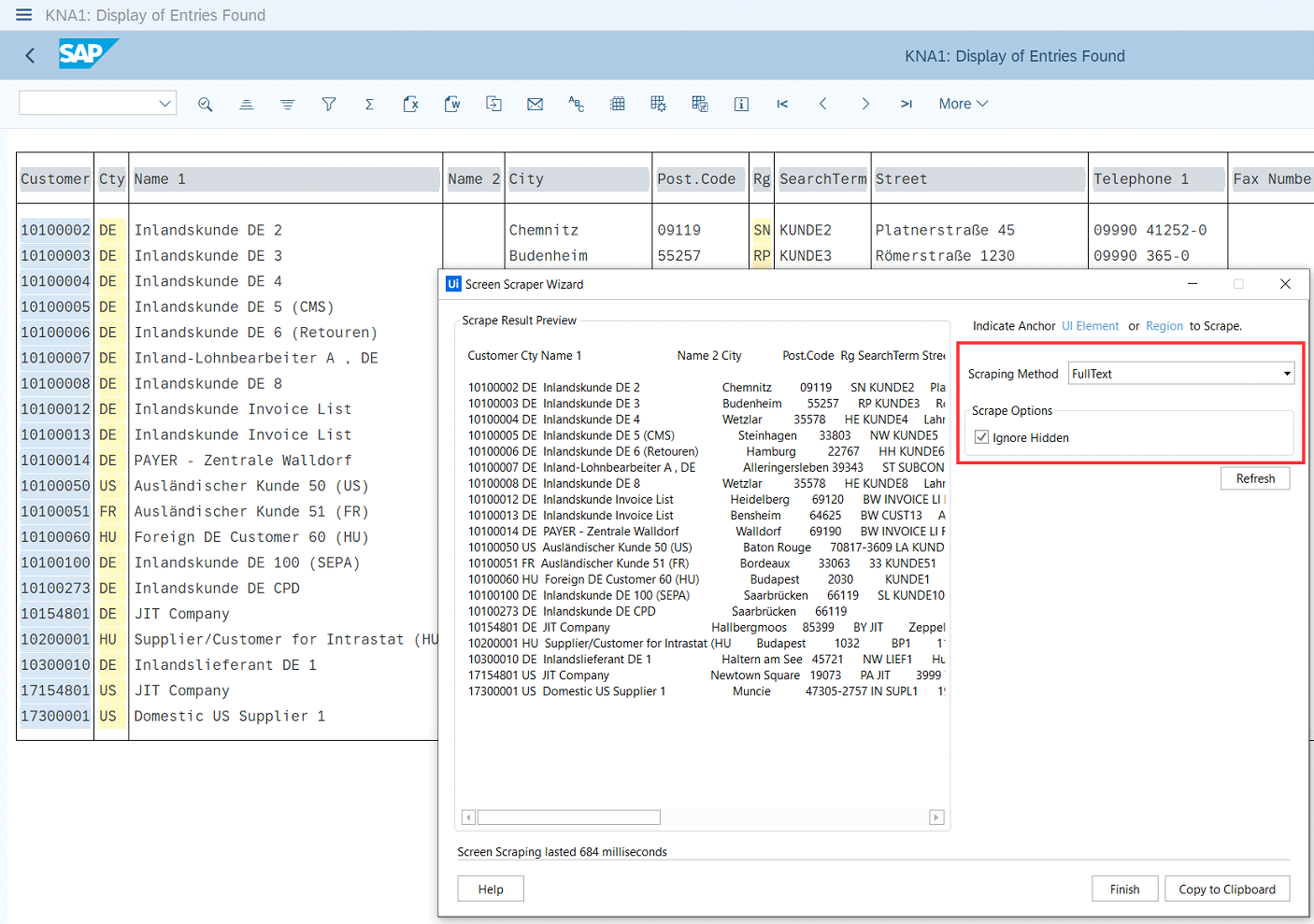
To learn more about Screen scraping, refer to Output or Screen Scraping Methods.
ColorIndex
The ColorIndex, ColorIntensified, and ColorInverse attributes enable you to identify the background color of elements.
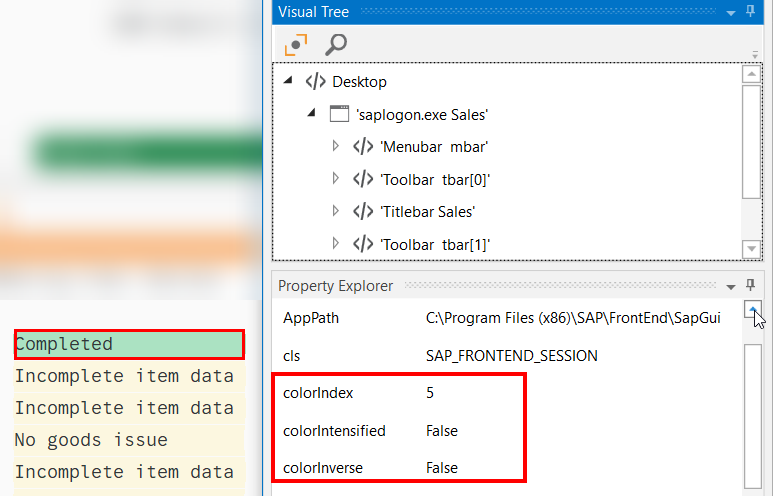
This can be used in both robotic process automation and test automation scenarios.
| Attribute Name | Object Type |
|---|---|
| ColorIndex | int32 |
| ColorIntensified | boolean |
| ColorInverse | boolean |
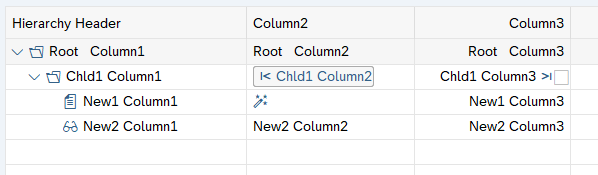
SAP ALV Hierarchical Table
The SAP ALV Hierarchical Table represents a list of elements organized in a table with hierarchical structure.
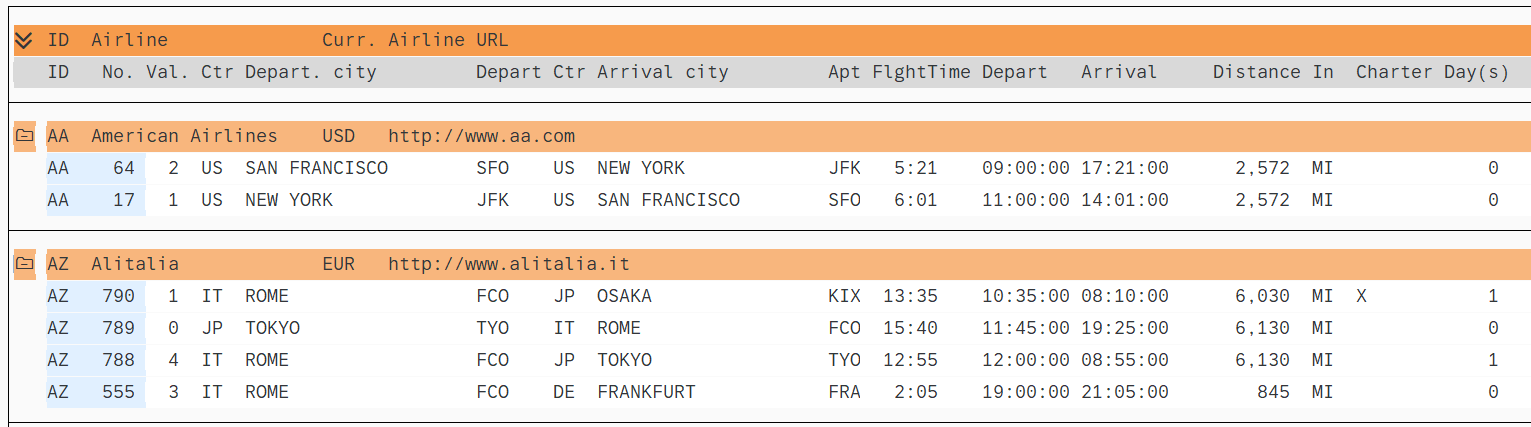
You can use the Expand ALV Hierarchical Table activity to identify any cell inside a SAP ALV Hierarchical Table. After the identification of the cell, all typical UI activities can be performed, such as Click, Get Text, and others.
There are two ways of working with the activity: at design time or at run time.
Design time
During the design time, you have to select any cell of interest inside the table. The activity captures the coordinates of this cell in activity. The changes are possible anytime.
Run time
The target cell is set in focus and the corresponding UiElement is returned as an output argument.
Navigate within the table
For example, if you want to get information about the flight time (6:01) for a specific airline (AA) and for a specific flight number (17).
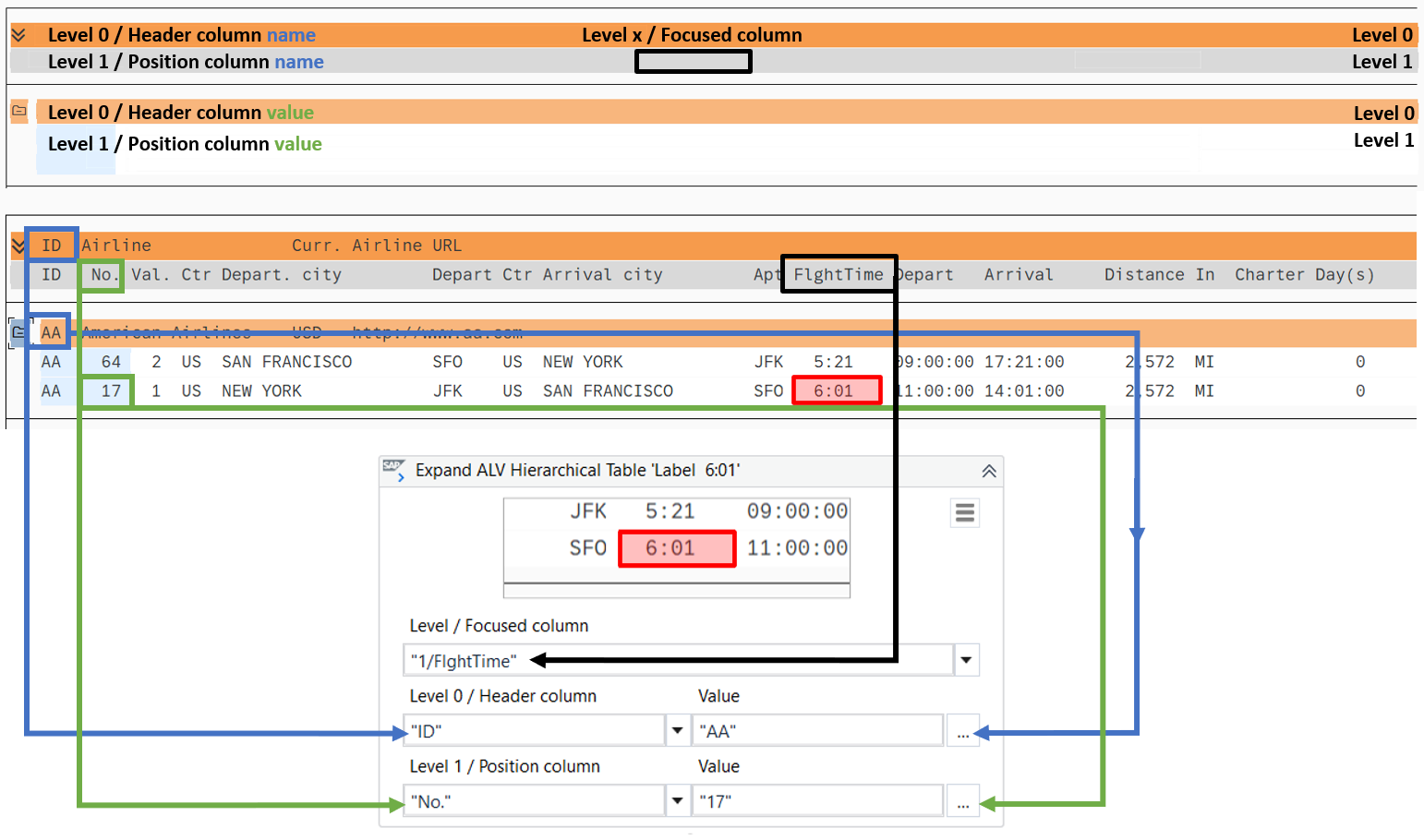
Level / Focused column: defines which element is set as the focused.
Level 0 / Header column: defines which column and value to find in the header column.
Level 1 / Position column: defines which column and value to find in the position column.
The coordinates of cell containing 6:01 are stored as Output value, variable type UiElement.
SAP ALV Tree List
The SAP ALV Tree represents a list of elements organized in a tree structure.
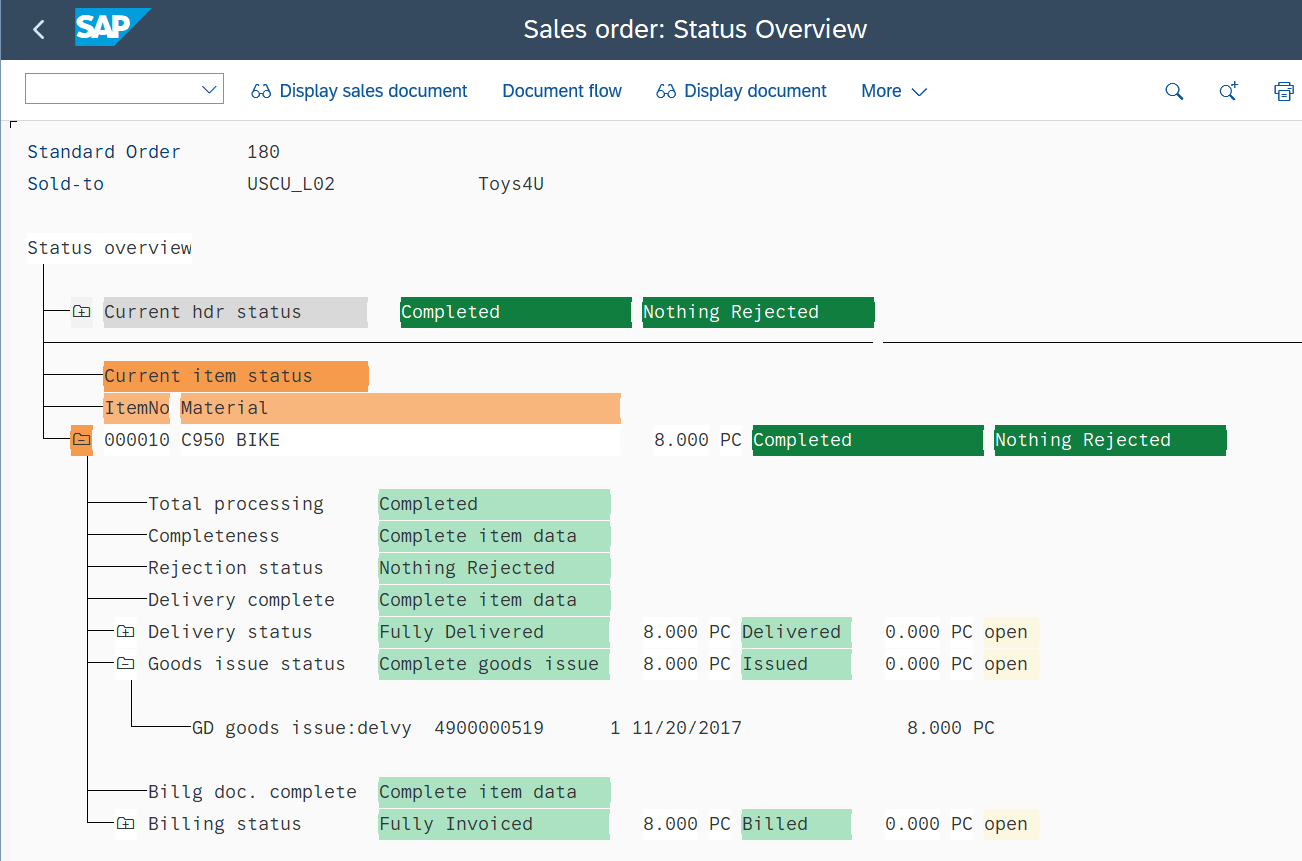
You can use the Expand ALV Tree activity to select an ALV node and display the node path in the activity. This enables you to use any other supported activities to work with the specified element.
SAP Textedit
The SAP Textedit control represents an editable text field/editor.
You can use the following activities to interact with this control:
- The Type Into activity for text fields.
- The Send Hotkey activity for buttons which support hotkeys or the Click Image activity for buttons.
SAP Toolbar
The SAP Toolbar represents a set of buttons, which you can interact with. In SAP, there are multiple types of toolbars, depending on the SAP Transaction or SAP Program.
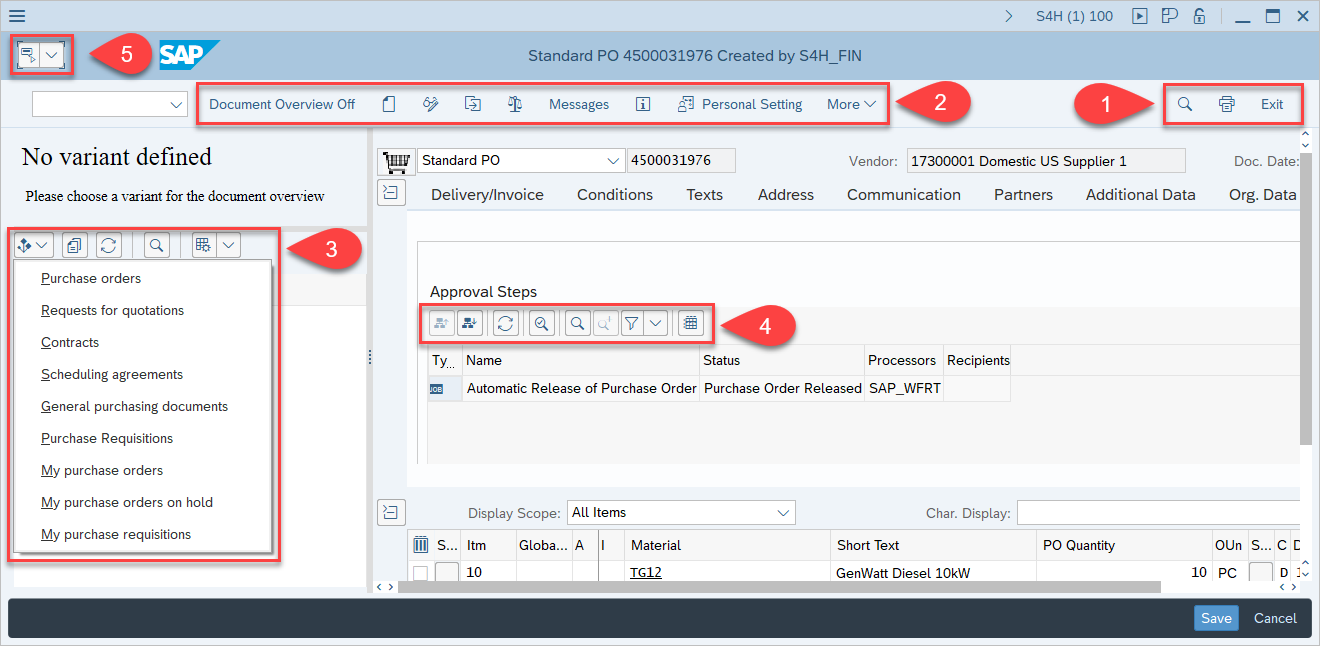
- SAP System Toolbar (1)
- SAP Application Toolbar (2)
- SAP Special Toolbar (3)
- SAP GridTable Toolbar (4)
- SAP Generic Object Services (5)
You can use the Click Toolbar Button activity to interact with buttons inside the toolbars.
This SAP control is not supported by Recording in Studio.
SAP Transaction Code
Represents an alphanumerical code which allows you to access SAP functions or running SAP programs.
Only the transaction code is required when you use the SAP Call Transaction activity.
The transaction code is executed in the current SAP GUI window.
When you provide a transaction code (for example VA01), the activity sends the /nVA01 + Enter (keystroke) command to call a transaction. Please note that unsaved changes in the current transaction are discarded without warning.
SAP Tree
The SAP Tree represents a list of elements organized in a tree structure. Several types of SAP Tree controls are available:
-
Simple Tree
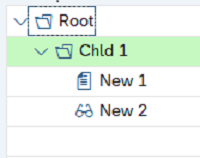
-
List Tree
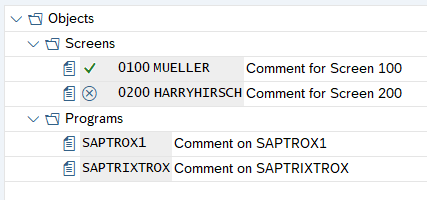
-
Column Tree
You can use the Click or the Get Text activity to interact with a node or an item in any of the SAP Tree control types.
It is recommended to use the SimulateClick property when you interact with SAP Trees.
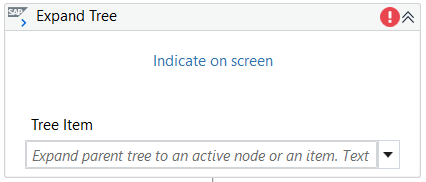
Expand Tree
If the tree contains a large number of child elements, selection is done as follows:
- Expand the tree in SAP WinGUI and select the element of interest.
- Use Indicate on screen to select the entire SAP Tree.
The nodes to the selected item are displayed in the activity.
This SAP control is not supported by Recording in Studio.
If the tree is collapsed and the node or item of interest is not visible, you need to use the SAP Expand Tree activity, which expands the parent tree to an active node or an active item.
- SAP Buttons
- Icons
- Push Buttons
- Radio Buttons
- SAP Calendar
- SAP Checkbox
- SAP Context Menu
- SAP Dialog Box
- SAP Dropdown Lists
- SAP HTML Content
- SAP Input Field
- SAP Logon
- SAP Login
- SAP Menu
- SAP Picture
- SAP Statusbar
- SAP Session Information
- SAP Tab
- Special automation case
- SAP Tables
- Common Operations
- SAP Standard Table
- SAP Grid Table
- Select/Deselect
- Table Cell Filtering
- Data Scraping
- SAP ALV Table
- Data Scraping
- Screen Scraping
- SAP ALV Hierarchical Table
- Design time
- Run time
- Navigate within the table
- SAP ALV Tree List
- SAP Textedit
- SAP Toolbar
- SAP Transaction Code
- SAP Tree
- Expand Tree