- Overview
- UI Automation
- About the UI Automation activity package
- Applications and technologies automated with UI Automation
- Project compatibility
- UI-ANA-016 - Pull Open Browser URL
- UI-ANA-017 - ContinueOnError True
- UI-ANA-018 - List OCR/Image Activities
- UI-DBP-006 - Container Usage
- UI-DBP-013 - Excel Automation Misuse
- UI-DBP-030 - Forbidden Variables Usage In Selectors
- UI-DBP-031 - Activity verification
- UI-PRR-001 - Simulate Click
- UI-PRR-002 - Simulate Type
- UI-PRR-003 - Open Application Misuse
- UI-PRR-004 - Hardcoded Delays
- UI-REL-001 - Large Idx in Selectors
- UI-SEC-004 - Selector Email Data
- UI-SEC-010 - App/Url Restrictions
- UI-USG-011 - Non Allowed Attributes
- UX-SEC-010 - App/Url Restrictions
- UX-DBP-029 - Insecure Password Use
- UI-PST-001 - Audit Log Level in Project Settings
- UiPath Browser Migration Tool
- Clipping region
- Computer Vision Recorder
- About SAP WinGUI Automation
- Configuration Steps
- Supported SAP WinGUI Elements
- Activities index
- Activate
- Anchor Base
- Attach Browser
- Attach Window
- Block User Input
- Callout
- Check
- Click
- Click Image
- Click Image Trigger
- Click OCR Text
- Click Text
- Click Trigger
- Close Application
- Close Tab
- Close Window
- Context Aware Anchor
- Copy Selected Text
- Element Attribute Change Trigger
- Element Exists
- Element Scope
- Element State Change Trigger
- Export UI Tree
- Extract Structured Data
- Find Children
- Find Element
- Find Image
- Find Image Matches
- Find OCR Text Position
- Find Relative Element
- Find Text Position
- Get Active Window
- Get Ancestor
- Get Attribute
- Get Event Info
- Get From Clipboard
- Get Full Text
- Get OCR Text
- Get Password
- Get Position
- Get Source Element
- Get Text
- Get Visible Text
- Go Back
- Go Forward
- Go Home
- Google Cloud Vision OCR
- Hide Window
- Highlight
- Hotkey Trigger
- Hover
- Hover Image
- Hover OCR Text
- Hover Text
- Image Exists
- Indicate On Screen
- Inject .NET Code
- Inject Js Script
- Invoke ActiveX Method
- Key Press Trigger
- Load Image
- Maximize Window
- Microsoft Azure Computer Vision OCR
- Microsoft OCR
- Microsoft Project Oxford Online OCR
- Minimize Window
- Monitor Events
- Mouse Trigger
- Move Window
- Navigate To
- OCR Text Exists
- On Element Appear
- On Element Vanish
- On Image Appear
- On Image Vanish
- Open Application
- Open Browser
- Refresh Browser
- Replay User Event
- Restore Window
- Save Image
- Select Item
- Select Multiple Items
- Send Hotkey
- Set Clipping Region
- Set Focus
- Set Text
- Set To Clipboard
- Set Web Attribute
- Show Window
- Start Process
- System Trigger
- Take Screenshot
- Tesseract OCR
- Text Exists
- Tooltip
- Type Into
- Type Secure Text
- Use Foreground
- Wait Attribute
- Wait Element Vanish
- Wait Image Vanish
- Accessibility Check
- Application Event Trigger
- Block User Input
- Check/Uncheck
- Check App State
- Check Element
- Click
- Click Event Trigger
- Drag and Drop
- Extract Table Data
- Find Elements
- For Each UI Element
- Get Browser Data
- Get Clipboard
- Get Text
- Get URL
- Go to URL
- Highlight
- Hover
- Inject Js Script
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Keypress Event Trigger
- Mouse Scroll
- Navigate Browser
- Select Item
- Set Browser Data
- Set Clipboard
- Set Runtime Browser
- Set Focus
- Set Text
- Take Screenshot
- Type Into
- Unblock User Input
- Use Application/Browser
- Window Operation
- Perform browser search and retrieve results using UI Automation APIs
- Web Browsing
- Find Images
- Click Images
- Trigger and Monitor Events
- Create and Override Files
- HTML Pages: Extract and Manipulate Information
- Window Manipulation
- Automated List Selection
- Find and Manipulate Window Elements
- Manage Text Automation
- Load and Process Images
- Manage Mouse Activated Actions
- Automate Application Runtime
- Automated Run of a Local Application
- Browser Navigation
- Web Automation
- Trigger Scope Example
- Enable UI Automation support in DevExpress
- Computer Vision Local Server
- Mobile Automation
- Release notes
- About the mobile device automation architecture
- Project compatibility
- Get Log Types
- Get Logs
- Get Page Source
- Get Device Orientation
- Get Session Identifier
- Install App
- Manage Current App
- Manage Other App
- Open DeepLink
- Open URL
- Mobile Device Connection
- Directional Swipe
- Draw Pattern
- Positional Swipe
- Press Hardware Button
- Set Device Orientation
- Take Screenshot
- Take Screenshot Part
- Element Exists
- Execute Command
- Get Attribute
- Get Selected Item
- Get Text
- Set Selected Item
- Set Text
- Swipe
- Tap
- Type Text
- Terminal
- Release notes
- About the Terminal activity package
- Project compatibility
- Best practices
- Find Text
- Get Color at Position
- Get Cursor Position
- Get Field
- Get Field at Position
- Get Screen Area
- Get Text
- Get Text at Position
- Move Cursor
- Move Cursor to Text
- Send Control Key
- Send Keys
- Send Keys Secure
- Set Field
- Set Field at Position
- Terminal Session
- Wait Field Text
- Wait Screen Ready
- Wait Screen Text
- Wait Text at Position

UI Automation activities
About SAP WinGUI Automation
About SAP WinGUI
Enabling SAP WinGUI API scripting allows you to create reliable automations for the SAP WinGUI. Studio and Robots require SAP WinGUI scripting to be enabled on the local machine as well as on the server side. Before you can create your first automation projects for SAP, you need to go over the configuration steps.
UI elements in SAP are known as controls, and you might need a particular approach or activity to detect and use them. Find out more about supported SAP elements.
SAP WinGUI Supported Versions
The following versions of SAP WinGUI are supported for Windows 7, Windows 10, and Windows 11, for both architecture types (32-bit and 64-bit). SAP Logon and SAP Logon Pad are supported on all versions.
- SAP WinGUI 7.40
- SAP WinGUI 7.50
- SAP WinGUI 7.60
- SAP WinGUI 7.70
- SAP WinGUI 8.00
All available themes (such as Quartz, Belize, Blue Crystal, or Corbu) can be used for SAP automation.
SAP WinGUI Activities
The following activities are specifically tailored for SAP automation:
- SAP Logon
- SAP Login
- SAP Expand Tree
- Table Cell Scope
- SAP Call Transaction
- SAP Click Toolbar Button
- SAP Read Statusbar
- SAP Select Menu Item
- Expand ALV Tree
- Expand ALV Hierarchical Table
- SAP Select Dates in Calendar
- SAP Click Picture on Screen
All SAP WinGUI activities above mentioned are supported and work with Object Repository.
SAP WinGUI Additional Information
Wildcards and Regular expressions can be used inside selectors generated for SAP WinGUI elements.
SAP WinGUI selectors support for the identification purpose not only technical ID, but also Text, Tooltip and Type of SAP control attributes. Complex SAP controls such as SAP Tables, SAP Grids and SAP Trees do not have these attributes available, as identification is done differently.
In case SAP WinGUI API scripting is not activated or not allowed in your organization, you can interact with the SAP WinGUI interface with help of Computer Vision activities.
SAP WinGUI Scripting Notification
When SAP WinGUI cannot be automated through SAP API Scripting due to misconfiguration or incomplete configuration, the below error message is displayed:
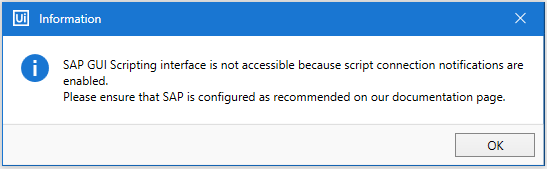
Follow the configuration steps to verify and to correct the settings.
Enforce hard timeout
The Enforce hard timeout setting can be found in Project Settings > UI Automation Classic > SAP. If the setting is set to True, the Robot terminates the SAP activity execution and it throws an error after the timeout specified in the activity target. You can catch and handle the error message in a Try Catch activity. By default, the setting is set to False.
This setting is useful in cases when you might want to end a long running SAP activity, or when SAP becomes stuck or unresponsive, or network or connection issues arise.
Elevation level
Elevation level determines whether an application is running with user permissions or with administrator permissions, the latter allowing you to perform more powerful tasks.
The elevation level for UiPath Studio and SAP needs to match. If there is an elevation level mismatch between these applications, the automation is not possible.