- Introducción
- Primeros pasos
- Modelado de procesos
- Comprender el modelado del proceso
- Abrir el lienzo de modelado
- Modelar tu proceso
- Alinear y conectar elementos BPMN
- Autopilot™ para Maestro (vista previa)
- Implementación del proceso
- Depuración
- Simular
- Publicar y actualizar procesos de agente
- Escenarios de implementación comunes
- Extracción y validación de documentos
- Operaciones de proceso
- Supervisión de procesos
- Optimización de procesos
- Información de referencia

Guía del usuario de Maestro
Bucles
Misma tarea sobre una lista, una a una (multiinstancia secuencial)
Configuración relacionada: lee Ejecución multiinstancia para la colección, los alias de elementos y la agregación.
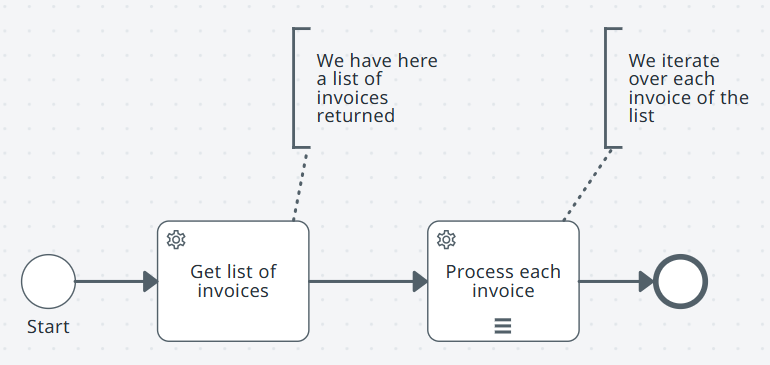
Utilizar cuando
- Las tareas deben aparecer en orden.
- Cada paso depende de un resultado previo.
- La integridad de la secuencia importa.
Patrón en términos simples
-
Inicio.
-
Tarea de servicio con multiinstancia secuencial: conciliar transacción en la Colección.
-
Finalizar Todos reconciliados.
Nota:El modo secuencial conserva el orden.
Otros escenarios
- Finanzas: publica líneas de facturas en secuencia.
- Seguros: revisa las reclamaciones en orden de recepción.
- Salud: procesa los resultados de las pruebas por paciente.
- Comercio minorista: aprueba de forma secuencial las devoluciones de la tienda.
- Fabricación: inspecciona los artículos por lote.
Misma tarea sobre una lista, todos a la vez (multiinstancia paralela)

Utilizar cuando
- Los elementos son independientes.
- Los elementos son independientes
- El orden no afecta al resultado.
Patrón en términos simples
-
Inicio.
-
Tarea de servicio con multiinstancia en paralelo: ejecutar un análisis de seguridad para cada servidor de la colección.
-
Tarea de usuario: revisar los resultados.
-
Finalizar escaneo completo.
Nota:Usa la agregación para recopilar salidas por elemento.
Otros escenarios
- Finanzas: el crédito del cliente se comprueba simultáneamente.
- Seguros: evalúa varias pólizas en paralelo.
- Fabricación: inspecciona varias líneas de forma concurrente.
- Comercio minorista: actualiza los precios de la tienda de inmediato.
- Sector público: revisa los permisos de los distritos juntos.
Repetición anidada dentro de un subproceso
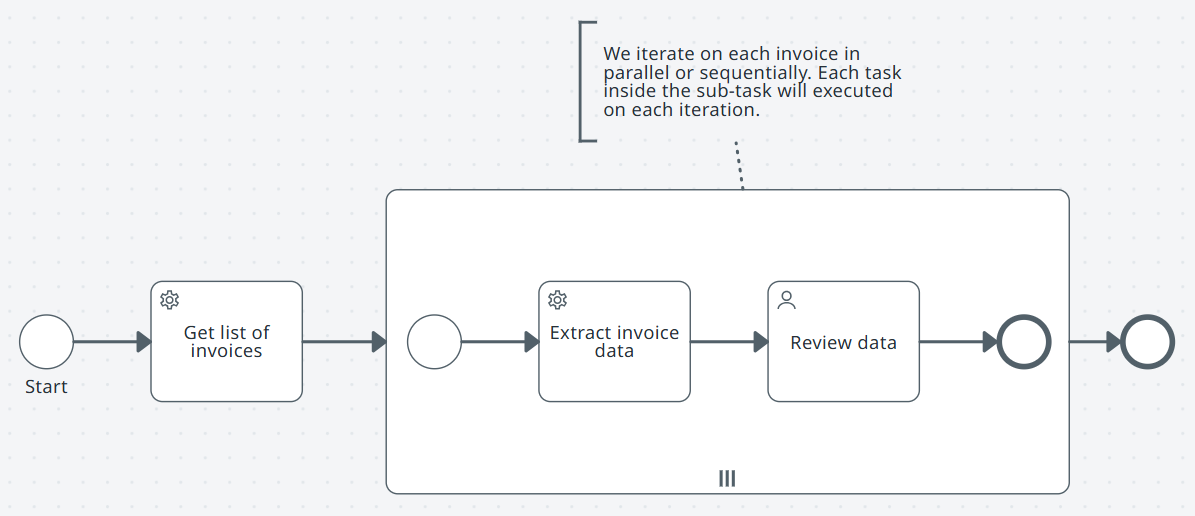
Utilizar cuando
- Existen dos niveles de iteración, como el lote y el elemento.
- Necesitas una estructura limpia que mantenga organizados los bucles.
Patrón en términos simples
-
Inicio.
-
Subproceso con multiinstancia secuencial: inspecciona un lote, un lote cada vez.
- Dentro del subproceso: tarea de servicio con multiinstancia en paralelo: inspecciona el elemento para cada elemento del lote.
-
El lote finaliza.
Nota:Usa el exterior secuencial y el interior paralelo cuando los lotes no deben solaparse.
Otros escenarios
- Finanzas: procesa estados de cuenta mensuales con varias entradas.
- Salud: auditoría a pacientes por Departamento.
- Comercio minorista: reconcilia las ventas de tiendas por región.
- Fabricación: auditoría a lotes por línea de productos.
- Seguros: revisa las reclamaciones por grupo de Política.
Loop node: combined output and variable scoping
The Loop node iterates over a collection and aggregates the results from all iterations into a single combined output. You can reference this combined output directly in downstream steps, without any additional data transformation.
Variables inside a loop are scoped to each iteration. Each cycle's data is isolated: one iteration's variables are not accessible to another.
Nodes with multiple outputs inside a loop are not yet fully supported. If a loop body contains a node that produces multiple outputs, results may not aggregate as expected.