- Overview
- UI Automation
- About the UI Automation activity package
- Applications and technologies automated with UI Automation
- Project compatibility
- UI-ANA-016 - Pull Open Browser URL
- UI-ANA-017 - ContinueOnError True
- UI-ANA-018 - List OCR/Image Activities
- UI-DBP-006 - Container Usage
- UI-DBP-013 - Excel Automation Misuse
- UI-DBP-030 - Forbidden Variables Usage In Selectors
- UI-DBP-031 - Activity verification
- UI-PRR-001 - Simulate Click
- UI-PRR-002 - Simulate Type
- UI-PRR-003 - Open Application Misuse
- UI-PRR-004 - Hardcoded Delays
- UI-REL-001 - Large Idx in Selectors
- UI-SEC-004 - Selector Email Data
- UI-SEC-010 - App/Url Restrictions
- UI-USG-011 - Non Allowed Attributes
- UX-SEC-010 - App/Url Restrictions
- UX-DBP-029 - Insecure Password Use
- UI-PST-001 - Audit Log Level in Project Settings
- UiPath Browser Migration Tool
- Clipping region
- Computer Vision Recorder
- Activities index
- Activate
- Anchor Base
- Attach Browser
- Attach Window
- Block User Input
- Callout
- Check
- Click
- Click Image
- Click Image Trigger
- Click OCR Text
- Click Text
- Click Trigger
- Close Application
- Close Tab
- Close Window
- Context Aware Anchor
- Copy Selected Text
- Element Attribute Change Trigger
- Element Exists
- Element Scope
- Element State Change Trigger
- Export UI Tree
- Extract Structured Data
- Find Children
- Find Element
- Find Image
- Find Image Matches
- Find OCR Text Position
- Find Relative Element
- Find Text Position
- Get Active Window
- Get Ancestor
- Get Attribute
- Get Event Info
- Get From Clipboard
- Get Full Text
- Get OCR Text
- Get Password
- Get Position
- Get Source Element
- Get Text
- Get Visible Text
- Go Back
- Go Forward
- Go Home
- Google Cloud Vision OCR
- Hide Window
- Highlight
- Hotkey Trigger
- Hover
- Hover Image
- Hover OCR Text
- Hover Text
- Image Exists
- Indicate On Screen
- Inject .NET Code
- Inject Js Script
- Invoke ActiveX Method
- Key Press Trigger
- Load Image
- Maximize Window
- Microsoft Azure Computer Vision OCR
- Microsoft OCR
- Microsoft Project Oxford Online OCR
- Minimize Window
- Monitor Events
- Mouse Trigger
- Move Window
- Navigate To
- OCR Text Exists
- On Element Appear
- On Element Vanish
- On Image Appear
- On Image Vanish
- Open Application
- Open Browser
- Refresh Browser
- Replay User Event
- Restore Window
- Save Image
- Select Item
- Select Multiple Items
- Send Hotkey
- Set Clipping Region
- Set Focus
- Set Text
- Set To Clipboard
- Set Web Attribute
- Show Window
- Start Process
- System Trigger
- Take Screenshot
- Tesseract OCR
- Text Exists
- Tooltip
- Type Into
- Type Secure Text
- Use Foreground
- Wait Attribute
- Wait Element Vanish
- Wait Image Vanish
- Accessibility Check
- Application Event Trigger
- Block User Input
- Check/Uncheck
- Check App State
- Check Element
- Click
- Click Event Trigger
- Drag and Drop
- Extract Table Data
- Find Elements
- For Each UI Element
- Get Browser Data
- Get Clipboard
- Get Text
- Get URL
- Go to URL
- Highlight
- Hover
- Inject Js Script
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Keypress Event Trigger
- Mouse Scroll
- Navigate Browser
- Select Item
- Set Browser Data
- Set Clipboard
- Set Runtime Browser
- Set Focus
- Set Text
- Take Screenshot
- Type Into
- Unblock User Input
- Use Application/Browser
- Window Operation
- Perform browser search and retrieve results using UI Automation APIs
- Web Browsing
- Find Images
- Click Images
- Trigger and Monitor Events
- Create and Override Files
- HTML Pages: Extract and Manipulate Information
- Window Manipulation
- Automated List Selection
- Find and Manipulate Window Elements
- Manage Text Automation
- Load and Process Images
- Manage Mouse Activated Actions
- Automate Application Runtime
- Automated Run of a Local Application
- Browser Navigation
- Web Automation
- Trigger Scope Example
- Enable UI Automation support in DevExpress
- Computer Vision Local Server
- Mobile Automation
- Release notes
- About the mobile device automation architecture
- Project compatibility
- Get Log Types
- Get Logs
- Get Page Source
- Get Device Orientation
- Get Session Identifier
- Install App
- Manage Current App
- Manage Other App
- Open DeepLink
- Open URL
- Mobile Device Connection
- Directional Swipe
- Draw Pattern
- Positional Swipe
- Press Hardware Button
- Set Device Orientation
- Take Screenshot
- Take Screenshot Part
- Element Exists
- Execute Command
- Get Attribute
- Get Selected Item
- Get Text
- Set Selected Item
- Set Text
- Swipe
- Tap
- Type Text
- Terminal
- Release notes
- About the Terminal activity package
- Project compatibility
- Best practices
- Find Text
- Get Color at Position
- Get Cursor Position
- Get Field
- Get Field at Position
- Get Screen Area
- Get Text
- Get Text at Position
- Move Cursor
- Move Cursor to Text
- Send Control Key
- Send Keys
- Send Keys Secure
- Set Field
- Set Field at Position
- Terminal Session
- Wait Field Text
- Wait Screen Ready
- Wait Screen Text
- Wait Text at Position

UI Automation activities
CV Screen Scope
UiPath.CV.Activities.CVScope
Description
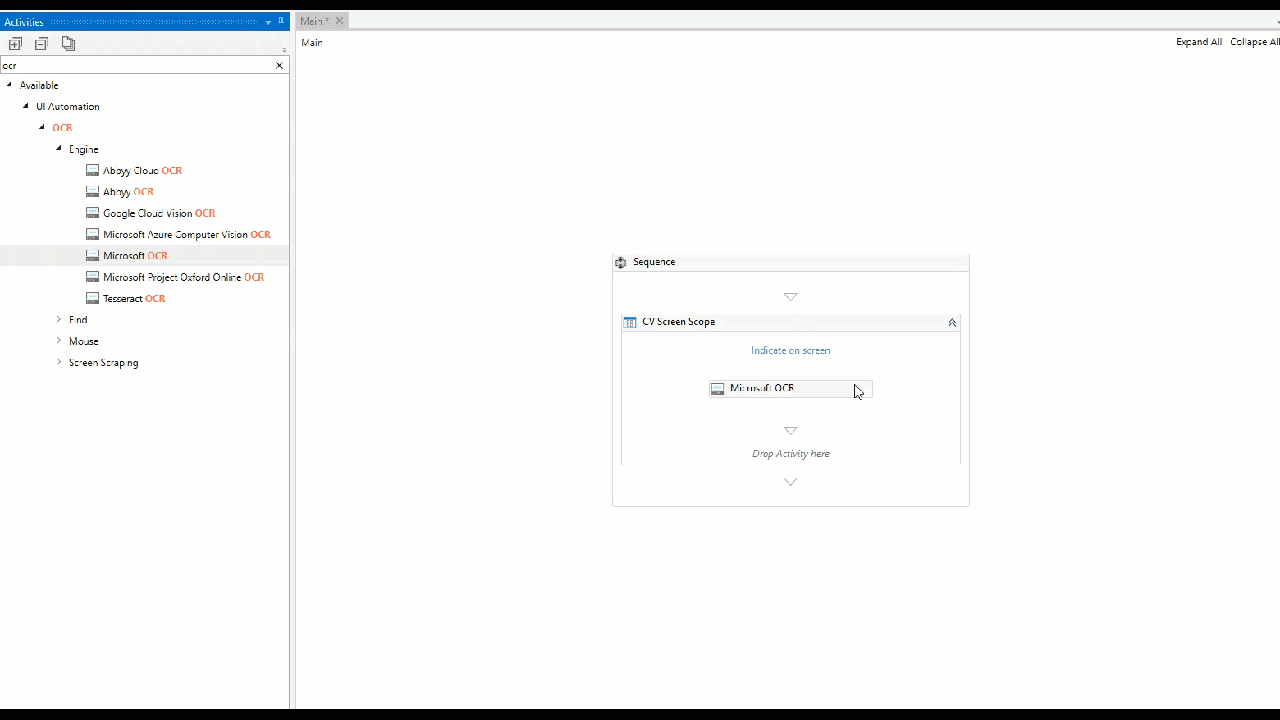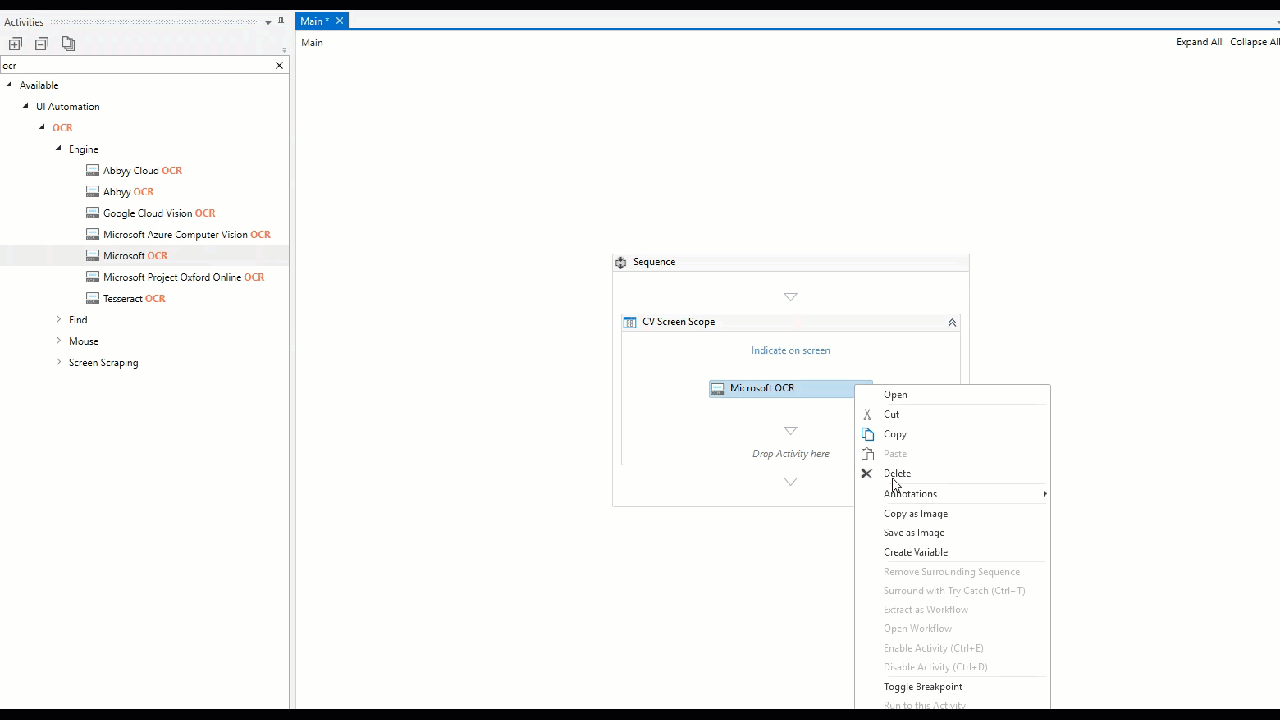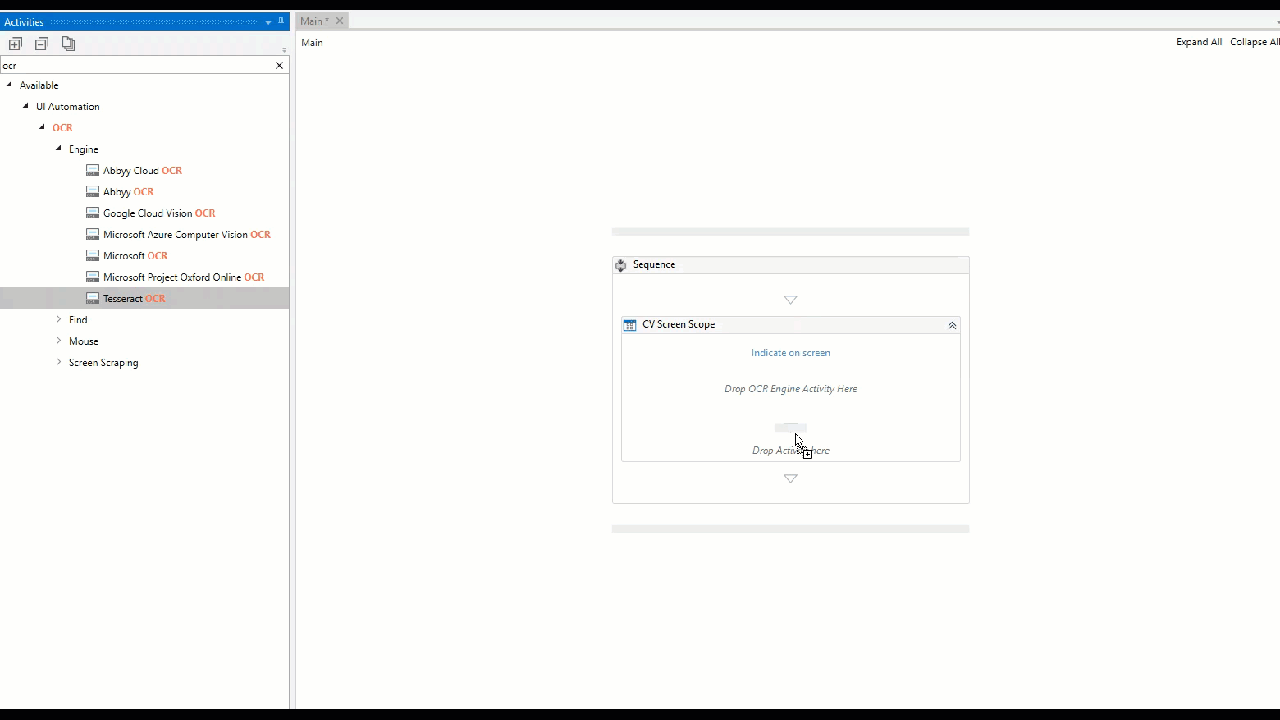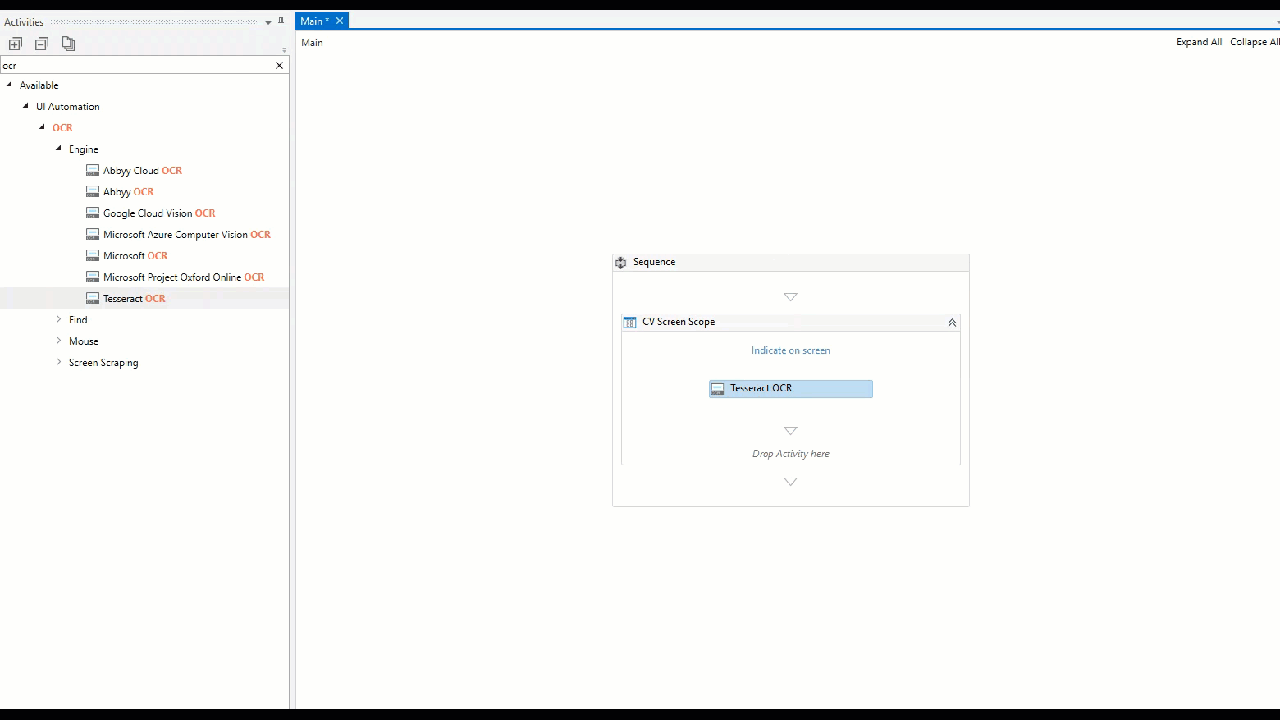
Initializes the UiPath Computer Vision neural network, performing an analysis of the indicated window and provides a scope for all subsequent Computer Vision activities. The activity enables you to select which OCR engine you want to use for scraping the text in the target application. The default OCR engine used for this activity is UiPath Screen OCR. The engine can be changed by manually replacing the default engine with one of your choice.
If you are using an on-premises Linux Computer Vision server deployment, you can also use the UiPath Screen OCR engine with this activity.
Project compatibility
Windows - Legacy | Windows
Configuration
Common
-
ContinueOnError - Specifies if the automation should continue even when the activity throws an error. This field only supports Boolean values (True, False). The default value is False. As a result, if the field is blank and an error is thrown, the execution of the project stops. If the value is set to True, the execution of the project continues regardless of any error.
Note:If this activity is included in Try Catch and the value of the ContinueOnError property is True, no error is caught when the project is executed.
-
DelayBefore - Delay time (in milliseconds) before the activity begins performing any operations. The default value for this field is 300 milliseconds.
-
DisplayName - The display name of the activity.
Input
- CVMethod - A drop-down
list that specifies which detection method you want to use with this
activity. By default, both the ElementDetection and OCR
options are selected. The following options are available:
- None - Uses only Image Automation.
- Element Detection - Uses Computer Vision.
- OCR - Uses OCR.
- Target.ClippingRegion - Defines the clipping rectangle, in pixels, relative to the UiElement, in the following directions: left, top, right, bottom. It supports both positive and negative numbers.
- Target.Element - Use the UiElement variable returned by another activity. This property cannot be used alongside the Selector property. This field supports only UiElement variables.
- Target.Selector - Text property used to find a particular UI element when the activity is executed. It is actually an XML fragment specifying attributes of the GUI element you are looking for and of some of its parents.
- Target.Timeout
(milliseconds) - Specifies the amount of time (in milliseconds) to wait
for the activity to run before the
SelectorNotFoundExceptionerror is thrown. The default value is 30000 milliseconds (30 seconds). - Target.WaitForReady - Before performing the actions, wait for the
target to become ready. By default, this field is set to Interactive.
The following options are available:
- None - Does not wait for anything except the target UI element to exist before executing the action. For example, you can use this option if you want to retrieve just text from a web page or click a particular button, without having to wait for all UI elements to load. Note that this may have unwanted consequences if the button relies on elements which are not yet loaded, such as scripts.
- Interactive - Waits for the UI elements you are working with in the target app to exist before executing the action.
- Complete - Waits for all of the UI elements in the target app
to exist before actually executing the action.
To assess if an application is in the Interactive or Complete state,
the following tags are verified:
- Desktop
applications - A
wm_nullmessage is sent to check the existence of the<wnd>,<ctrl>,<java>, or<uia>tags. If they exist, the activity is executed. - Web
applications:
- Internet Explorer - The
<webctrl>tag is used to check if the Ready state of the HTML document is set to Complete. Additionally, the Busy state has to be set toFalse. - Others - The
<webctrl>tag is used to check if the Ready state of the HTML document is Complete.
- Internet Explorer - The
- SAP applications - First the presence of the
<wnd>tag is verified, after which an SAP-specific API is used to detect if the session is busy or not.
- Desktop
applications - A
Misc
- Private - If selected, the values of variables and arguments are no longer logged at Verbose level.
Scroll
- Scroll Offset - Scroll Offset used in scrolling to find the target of each of the Computer Vision activities in this scope.
Server (synced)
-
ApiKey - The API key used for authenticating to the Computer Vision server. This field supports only strings or String variables. This is a global property, shared between all CV Screen Scope activities in the workflow.
Note:Please note that the API key is only required when connecting to the UiPath Automation Cloud server. You can find more information on acquiring a key here.
Note:Editing the ApiKey property for one scope activity changes the value for all the other scopes in the current workflow, so you don't have to do it manually.
-
URL - The URL of the server that runs the Computer Vision service. By default, this property is set to
https://cv.uipath.com/. This is a global property, shared between all CV Screen Scope activities in the workflow. -
UseLocalServer - If checked the local server will be used for the analysis. To use the local server, the UiPath.ComputerVision.LocalServer package needs to be installed.
Note:When using an on-prem server deployment of the neural network model, to connect to it with the Computer Vision activities, you must change the value of the URL property of the CV Screen Scope activity to the URL of your server. More details on connecting to the server are available here.
In the body of the activity
The application you want to automate can be indicated to the CV Screen Scope activity by using the Indicate On Screen button in the body of the activity. After doing this, a capture of the screen you have indicated is displayed in the body of the activity.
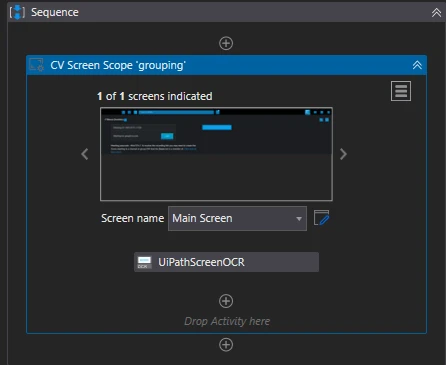
If you indicate multiple screens when automating an application, you can cycle between the screens by using the directional buttons (<, >) to easily check what screens the activity is using.
Screens can also be renamed
by selecting them from the Screen Name drop-down and clicking the  button.
button.