- 基本情報
- Studio Web での UiPath Agents
- UiPath のコード化されたエージェント

Agents ガイド
会話型エージェントを評価する
評価により、会話型エージェントがさまざまな対話パスで確実に動作することを確認できます。このページでは、デバッグ チャットを使用してエージェントをテストする方法、評価セットを作成する方法、および自動化されたテストを実行する方法について説明します。
デバッグ チャット
デバッグ チャットは、エージェントと対話してその動作を検査することができるリアルタイムのテスト環境を提供します。
デバッグ セッションを開始する
- Studio Web で会話型エージェントを開きます。
- [デバッグ] を選択してチャット インターフェイスを開きます。
- メッセージを送信してエージェントの応答をテストします。
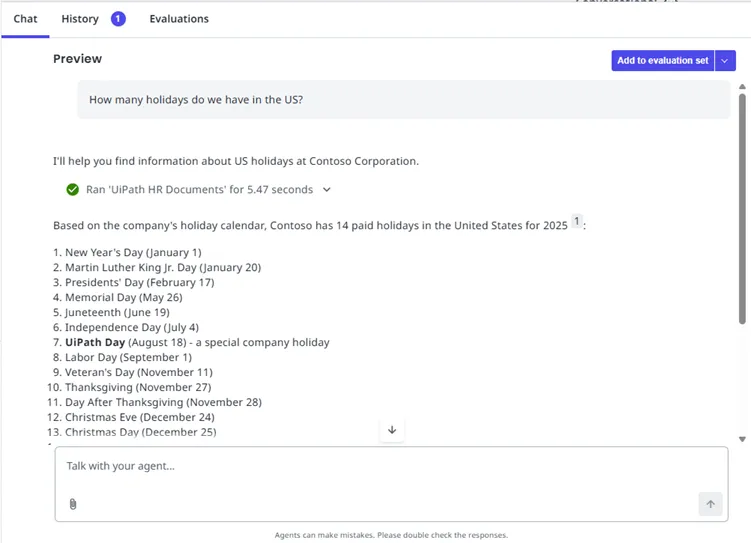
実行トレースを表示する
[履歴] パネルには、エージェントの実行の詳細がリアルタイムに表示されます。
- LLM の呼び出し: モデルに送信されたプロンプトと受信した応答です。
- ツールの呼び出し: 呼び出されたツールと、引数および出力です。
ステップを展開すると、トークン数や遅延などの詳細が表示されます。
![[実行トレース] パネル](https://dev-assets.cms.uipath.com/assets/images/agents/history-trace-panel-59553ddc.webp)
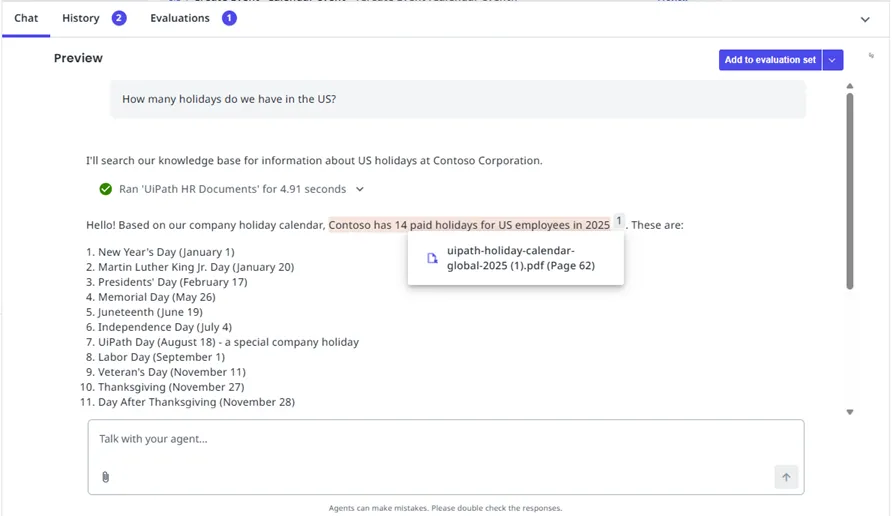
引用を表示する
エージェントがコンテキスト グラウンディングを使用する場合、応答に引用が表示され、回答の情報源となったドキュメントが示されます。
- エージェントの応答で引用マーカーを探します (通常は番号付きの参照)。
- 引用を選択すると、ソース ドキュメントおよび関連する抜粋が表示されます。
- 引用が正確にエージェントの応答の裏付けになっていることを確認します。
会話を評価セットに追加する
対話のテストに成功したら、自動化されたテストのために会話を保存します。
- [チャット] タブで、[評価セットに追加] を選択します。
- 既存の評価セットを選択するか、新しい評価セットを作成します。
会話は以下とともに保存されます。
- 会話履歴: 会話における前のすべてのターンです。
- 現在のユーザー メッセージ: ユーザーの最新のメッセージです。
- 期待されるエージェントの応答: エージェントの実際の応答です (編集可能)。
評価セット
評価セットは、エージェントの動作を検証するテスト ケースのコレクションです。単一ターンと複数ターンの両方のテスト シナリオがサポートされています。
評価に関する詳しいガイダンスについては、「評価」をご覧ください。
単一ターンの評価
単一ターンの評価では、会話履歴のない孤立した質問と回答のペアをテストします。これは、会話の最初のプロンプトをテストする評価テストです。
単一ターンの評価は、以下の目的で使用します。
- 特定のナレッジの検索をテストする
- さまざまな意図に対するツールの選択を検証する
- 応答の形式とトーンを確認する
例:
| ユーザーのメッセージ | 予想される行動 |
|---|---|
| 「米国には休日が何日ありますか?」 | 正しい数を返し、制作文書を引用する |
| 「ジョンとの会議を明日の午後 2 時に設定してください」 | 正しいパラメーターを使用してカレンダー ツールを呼び出す |
複数ターンの評価
複数ターンの評価では、エージェントが会話のコンテキストとフォローアップの質問をどのように処理するかをテストします。この評価テストでは、テストするプロンプトが前の会話に従います。
複数ターンの評価は、以下の目的で使用します。
- ターン間でコンテキストが保持されることをテストする
- 代名詞の照応解析 (「それ」「あれ」「同じ」) を検証する
- 会話の流れと一貫性を確認する
例:
| ターン | メッセージ | 予想される行動 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 「有給休暇ポリシーとは何ですか?」 | 有給休暇ポリシーの概要を返す |
| 2 | 「休暇を申請するにはどうすればいいですか?」 | 有給休暇に関するコンテキストを参照し、申請プロセスを説明する |
| 3 | 「それはメールでできますか?」 | 「それ」が休暇の申請を指すことを理解する |
評価テストを作成する
デバッグ チャットから作成する
- デバッグ チャットで会話を実行します。
- [チャット] パネルから [評価セットに追加] を選択します。
- 指定した評価セットに会話のやり取りが評価テストとして追加されます。
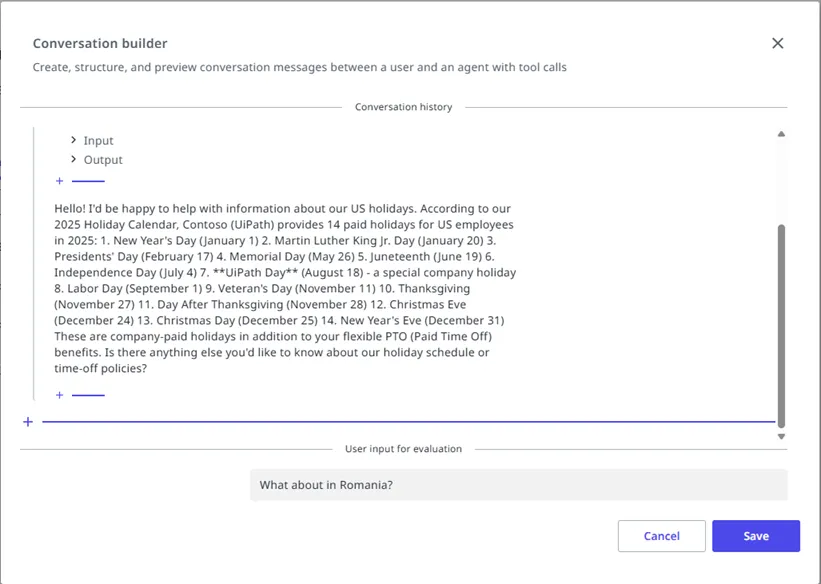
会話ビルダーを使用する
会話ビルダーを使用して、複数ターンのテスト ケースを作成または編集できます。
- Studio Web でエージェントに対して [評価セット] を選択します。
- 評価セットを選択するか、新しい評価セットを作成します。これらのオプションが無効化されている場合は、デバッグ モードになっていないことを確認してください。
- [追加] を選択するか、既存のテストを編集します。
- 会話ビルダーを使用して以下を行います。
- 会話履歴のターンを追加する
- 現在のユーザー メッセージを定義する
- [出力の設定] を使用してアサーションを定義します。
- 決定論的な評価器および LLM-as-a-judge (LLM による評価) ベースの評価器の場合は、期待されるエージェントの応答を指定します。
- 軌跡ベースの評価器の場合は、「動作と出力に関するメモ」を指定します。
ツールのシミュレーション
シミュレーションを使用すると、実際のツール エンドポイントを実行することなくエージェントの動作をテストできます。評価テストごとに、ツールを実際に実行するか、実行をシミュレートするかを指定できます。
シミュレーションを使用すると以下が可能になるため、エージェントの評価が強化されます。
- 安全なテスト: 実際の API やサービスを呼び出すことによる意図しない副作用を回避できます。
- 高速な実行: ネットワーク レイテンシや外部サービスの遅延を無視できます。
- 費用対効果の高い実行: 反復テスト時の API コストを削減できます。
- 再現性: ツールの出力を制御することで一貫した結果を得ることができます。
評価テストごとにシミュレーションの動作を設定できます。
- 評価セットを開きます。
- 編集するテスト ケースを選択します。
- テストの設定で、実行をシミュレートするツールを指定します。
- 各ツールに対して、期待されるシミュレートされた出力を定義します。
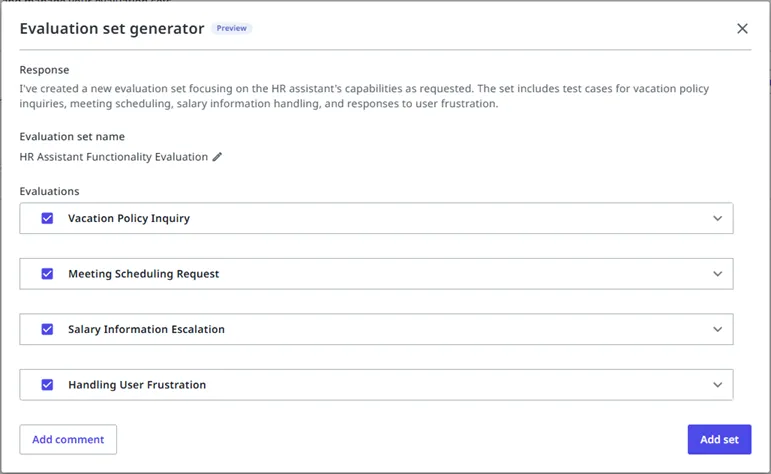
テストを自然言語で生成する
Autopilot を使用して、説明から評価テストを生成します。
- [評価セット] 画面で、[作成] を選択し、[新しい評価セットを生成] を選択します。
- テストするシナリオを自然言語で入力します。
- 生成されたテスト ケースを確認して調整します。
プロンプトの例:
Generate test cases for an HR assistant that:
- Answers questions about vacation policy
- Handles requests to schedule meetings
- Escalates when asked about salary information
- Responds appropriately when the user is frustrated
Generate test cases for an HR assistant that:
- Answers questions about vacation policy
- Handles requests to schedule meetings
- Escalates when asked about salary information
- Responds appropriately when the user is frustrated
Autopilot によって生成された評価テストでは、自動的に軌跡ベースの評価が使用されます。
評価を実行する
単一のテストを実行する
- 評価セットからテスト ケースを選択します。
- [選択した項目を評価] を選択します。
- 実際の出力と期待される出力を比較して、結果を確認します。
バッチ評価を実行する
- [評価セット] に移動します。
- 目的の評価セットで [実行] を選択して、すべてのテストを実行します。
- 成功率/失敗率を示す結果を確認します。
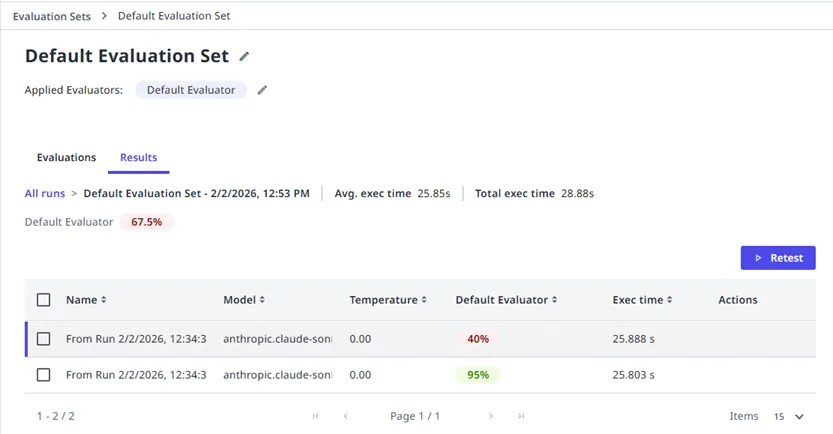
異なるモデルを使用してテストする
同じ評価セットを異なるモデルに対して実行して、パフォーマンスを比較します。
- 評価セットで [評価の設定] を選択し、対象にするモデルを追加します。
- 評価を実行します。
- 複数のモデル間で結果を比較して、ユース ケースに最適なモデルを特定します。
これは以下を把握するのに役立ちます。
- 特定のシナリオに対して最高のパフォーマンスを発揮するモデル
- 応答の品質と遅延のトレードオフ
- 異なるモデルを選択することによるコストへの影響
評価のメトリック
評価では、エージェントの動作について以下の複数の側面が評価されます。
| メトリック | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 応答の正確性 | 応答に正しい情報が含まれているか |
| ツールの選択 | エージェントは適切なツールを選択したか |
| 引用の質 | 引用は関連性があり、正確か |
| トーンと形式 | 応答は期待されるスタイルに合致しているか |
| コンテキストの保持 | エージェントはターン間でコンテキストを維持するか |
評価のベスト プラクティス
好結果が得られたパスと得られなかったパスの両方をテストする
理想的なシナリオだけをテストしないようにしてください。以下のシナリオを含めます。
- あいまいな質問
- 範囲外の要求
- エッジ ケースとエラー条件
- 多言語の入力 (サポートされている場合)
代表性の高いテスト スイートを作成する
実際の使用パターンを反映した評価セットを構築します。
- 運用環境での一般的なユーザー クエリを分析する
- 同じ質問のバリエーションを含める
- さまざまなユーザー ペルソナとコミュニケーション スタイルをテストする
結果に基づいて反復処理する
評価の失敗を使用してエージェントを改善します。
- 失敗したテストのパターンを特定します。
- システム プロンプトまたはツールの設定を更新します。
- 評価を再実行して、改善内容を検証します。
- 見つかったエッジ ケースに対して新しいテストを追加します。