- Vue d'ensemble (Overview)
- Automatisation de l'interface utilisateur
- À propos du package d'activités UIAutomation
- Applications et technologies automatisées avec UI Automation
- Compatibilité du projet
- UI-ANA-016 - Extraire l'URL ouverte du navigateur
- UI-ANA-017 - ContinuerSurErreur (ContinueOnError) True
- UI-ANA-018 - Répertorier les activités d'OCR/d'image
- UI-DBP-006 - Utilisation du conteneur
- UI-DBP-013 - Utilisation abusive de l’automatisation Excel
- UI-DBP-030 - Utilisation de variables interdites dans les sélecteurs
- UI-DBP-031 : Vérification de l’activité
- UI-PRR-001 - Simuler un clic
- UI-PRR-002 - Type de simulation
- UI-PRR-003 - Ouverture d'une utilisation abusive de l'application
- UI-PRR-004 - Délais codés en dur
- UI-REL-001 - Idx volumineux dans les sélecteurs
- UI-SEC-004 - Données d’e-mail du sélecteur
- UI-SEC-010 - Restrictions d'applications/d'URL
- UI-USG-011 - Attributs non autorisés
- UX-SEC-010 - Restrictions d'applications/d'URL
- UX-DBP-029 - Utilisation d'un mot de passe non sécurisé
- UI-PST-001 - Niveau du journal d'audit dans les paramètres du projet
- Outil de migration de navigateur UiPath
- Zone de détourage
- Enregistreur de Computer Vision
- À propos des éléments d'interface utilisateur
- Propriétés des activités de l'interface utilisateur
- Exemple d'utilisation des méthodes de saisie
- Méthodes de sortie ou de capture de données d'écran
- Exemple d'utilisation de méthodes de sortie ou de capture de données d'écran
- Génération de tables à partir de données non structurées
- Capture relative de données
- À propos de l'automatisation des images et des textes
- Activités liées à la souris et au clavier
- Exemple d'utilisation de l'automatisation de la souris et du clavier
- Les activités de type texte
- Exemple d'utilisation d'automatisation de texte
- Activités de type OCR
- Activités de type image
- Exemple d'utilisation de l'automatisation d'image et d'OCR
- Index des activités
- Activer (Activate)
- Base d'ancrage (Anchor Base)
- Lier à un navigateur (Attach Browser)
- Lier à une fenêtre (Attach Window)
- Block User Input
- Légende (Callout)
- Vérifier (Check)
- Cliquer (Click)
- Cliquer sur l'image (Click Image)
- Déclencheur de clic image (Click Image Trigger)
- Cliquer sur le texte OCR (Click OCR Text)
- Cliquer sur le texte (Click Text)
- Déclencheur de clic (Click Trigger)
- Fermer l'application (Close Application)
- Fermer l'onglet (Close Tab)
- Fermer la fenêtre (Close Window)
- Context Aware Anchor
- Copier le texte sélectionné (Copy Selected Text)
- Element Attribute Change Trigger
- Élément existant (Element Exists)
- Étendue de l'élément (Element Scope)
- Element State Change Trigger
- Export UI Tree
- Extraire les données structurées (Extract Structured Data)
- Rechercher les enfants (Find Children)
- Rechercher l'élément (Find Element)
- Rechercher l'image (Find Image)
- Rechercher les correspondances de l'image (Find Image Matches)
- Rechercher une position de texte OCR (Find OCR Text Position)
- Rechercher l'élément relatif (Find Relative Element)
- Rechercher la position du texte (Find Text Position)
- Obtenir la fenêtre active (Get Active Window)
- Obtenir l'ancêtre (Get Ancestor)
- Obtenir l'attribut (Get Attribute)
- Obtenir les infos de l'événement (Get Event Info)
- Récupérer du presse-papiers (Get From Clipboard)
- Obtenir le texte complet (Get Full Text)
- Obtenir le texte OCR (Get OCR Text)
- Récupérer le mot de passe (Get Password)
- Obtenir la position (Get Position)
- Obtenir l'élément source (Get Source Element)
- Obtenir le texte (Get Text)
- Obtenir le texte visible (Get Visible Text)
- Revenir en arrière (Go Back)
- Avancer (Go Forward)
- Accéder à l'accueil (Go Home)
- Google Cloud Vision OCR
- Masquer la fenêtre (Hide Window)
- Mettre en surbrillance (Highlight)
- Déclencheur de raccourci (Hotkey Trigger)
- Pointer (Hover)
- Pointer sur l'image (Hover Image)
- Pointer sur le texte OCR (Hover OCR Text)
- Pointer sur le texte (Hover Text)
- Image existante (Image Exists)
- Indiquer sur l'écran (Indicate On Screen)
- Injecter du code .NET
- Inject Js Script
- Invoquer la méthode ActiveX
- Déclencheur de pression de touche (Key Press Trigger)
- Charger l'image (Load Image)
- Agrandir la fenêtre (Maximize Window)
- Microsoft Azure ComputerVision OCR
- Reconnaissance optique des caractères Microsoft (Microsoft OCR)
- Microsoft Project Oxford Online OCR
- Réduire la fenêtre (Minimize Window)
- Surveiller les événements (Monitor Events)
- Déclencheur de souris (Mouse Trigger)
- Déplacer la fenêtre (Move Window)
- Accéder à (Navigate To)
- Texte OCR existant (OCR Text Exists)
- Sur affichage de l'élément (On Element Appear)
- Sur disparition de l'élément (On Element Vanish)
- Sur apparition de l'image (On Image Appear)
- Sur disparition de l'image (On Image Vanish)
- Ouvrir l'application (Open Application)
- Ouvrir le navigateur (Open Browser)
- Actualiser le navigateur (Refresh Browser)
- Relire l'événement utilisateur (Replay User Event)
- Restaurer la fenêtre (Restore Window)
- Enregistrer l'image (Save Image)
- Sélectionner l'élément (Select Item)
- Sélectionner plusieurs éléments (Select Multiple Items)
- Envoyer le raccourci (Send Hotkey)
- Définir la zone de détourage (Set Clipping Region)
- Définir le focus (Set Focus)
- Définir le texte (Set Text)
- Placer dans le presse-papiers (Set To Clipboard)
- Définir l'attribut Web (Set Web Attribute)
- Afficher la fenêtre (Show Window)
- Déclencher le processus (Start Process)
- Déclencheur système (System Trigger)
- Prendre une capture d'écran (Take Screenshot)
- Tesseract OCR
- Texte existant (Text Exists)
- Info-bulle
- Saisir dans (Type Into)
- Saisir un texte sécurisé (Type Secure Text)
- Utiliser le premier plan
- Attendre un attribut (Wait Attribute)
- Attendre que l'élément disparaisse (Wait Element Vanish)
- Attendre que l'image disparaisse (Wait Image Vanish)
- Vérification de l’accessibilité
- Application event trigger
- Block User Input
- Check/Uncheck
- Check App State
- Check Element
- Cliquer (Click)
- Click Event Trigger
- Glisser et déposer
- Extract Table Data
- Find Elements
- For Each UiElement
- Get Browser Data
- Get Clipboard (Obtenir le Presse-papiers)
- Obtenir le texte (Get Text)
- Get URL
- Go To URL
- Mettre en surbrillance (Highlight)
- Pointer (Hover)
- Inject Js Script
- Raccourcis clavier
- Keypress Event Trigger
- Mouse scroll
- Navigate Browser
- Sélectionner l'élément (Select Item)
- Set Browser Data
- Set Clipboard (Définir le Presse-papiers)
- Définir le navigateur du runtime (Set Runtime Browser)
- Définir le focus (Set Focus)
- Définir le texte (Set Text)
- Prendre une capture d'écran (Take Screenshot)
- Saisir dans (Type Into)
- Unblock User Input
- Use Application/Browser
- Window operation
- Joindre
- Vérifier (Check)
- Cliquer (Click)
- Glisser et déposer
- Extraire des données
- Obtenir l'attribut (Get Attribute)
- ObtenirEnfants
- ObtenirCibleRuntime
- GetText
- Get URL
- GoToUrl
- Mettre en surbrillance (Highlight)
- Pointer (Hover)
- IsEnabled
- Raccourci clavier
- Mouse scroll
- Ouvrir
- Sélectionner l'élément (Select Item)
- Prendre une capture d'écran (Take Screenshot)
- Saisir dans (Type Into)
- ÉtatAttente
- Effectuez une recherche par navigateur et récupérez les résultats à l'aide des API UI Automation
- Navigation sur le Web
- Rechercher des images
- Cliquer sur des images
- Déclencher et surveiller des événements
- Créer et remplacer des fichiers
- Pages HTML : extraire et manipuler des informations
- Manipulation des fenêtres
- Sélection de liste automatisée
- Rechercher et manipuler des éléments de fenêtre
- Gérer l'automatisation du texte
- Charger et traiter des images
- Gérer les actions activées par la souris
- Automatiser l'exécution des applications
- Exécution automatisée d'une application locale
- Navigation avec le navigateur
- Automatisation Web
- Exemple de fonctionnalités du déclencheur
- Activer la prise en charge d’UI Automation dans DevExpress
- Computer Vision Local Server
- Automatisation mobile
- Notes de publication
- À propos de l'architecture d'automatisation des appareils mobiles
- Compatibilité du projet
- Get Log Types
- Get Logs
- Get Page Source
- Get Device Orientation
- Get Session Identifier
- Installer l'application
- Gérer l'application actuelle
- Gérer une autre application
- Ouvrir DeepLink
- Ouvrir l'URL
- Mobile Device Connection
- Balayer directionnel
- Dessiner un modèle
- Positional Swipe
- Press Hardware Button
- Set Device Orientation
- Prendre une capture d'écran (Take Screenshot)
- Prendre une partie de capture d'écran
- Élément existant (Element Exists)
- Execute Command
- Obtenir l'attribut (Get Attribute)
- Get Selected Item
- Obtenir le texte (Get Text)
- Set Selected Item
- Définir le texte (Set Text)
- Balayer
- Tap
- Saisir texte
- Premiers pas avec les API d’automatisation mobile
- Gestion des boîtes de dialogue contextuelles dans les automatisations mobiles
- Creating variables from selector attributes
- Créer des workflows d'automatisation mobile
- Utiliser l’automatisation mobile pour les applications de banque mobile
- Automatisation pour les applications React Native
- Terminal
- Notes de publication
- À propos du package d'activités Terminal
- Compatibilité du projet
- Meilleures pratiques
- Rechercher un texte (Find Text)
- Get Color At Position
- Obtenir la position du curseur (Get Cursor Position)
- Obtenir le champ (Get Field)
- Obtenir le champ en position (Get Field at Position)
- Accéder à la zone d'écran (Get Screen Area)
- Obtenir le texte (Get Text)
- Obtenir le texte en position (Get Text at Position)
- Déplacer le curseur (Move Cursor)
- Move Cursor to Text
- Envoyer la touche Contrôle (Send Control Key)
- Envoyer les touches (Send Keys)
- Envoyer les touches en toute sécurité (Send Keys Secure)
- Définir le champ (Set Field)
- Définir le champ en position (Set Field at Position)
- Session de terminal (Terminal Session)
- Attendre le texte de champ (Wait Field Text)
- Wait Screen Ready
- Attendre le texte d'écran (Wait Screen Text)
- Attendre le texte en position (Wait Text at Position)

Activités UIAutomation
Extraction de table
L'extraction de table, qui fait partie de Modern Experience dans Studio, vous permet d'utiliser le package d'activités UI Automation pour extraire automatiquement les données structurées des applications et les enregistrer en tant qu'objet DataTable qui peut ensuite être utilisé dans vos processus d'automatisation.
Ce processus peut être effectué à l'aide de l' Enregistreur d'extraction de table dans Studio, accessible depuis le ruban si le pack UIAutomation v21.4 ou version ultérieure est installé dans votre projet en cours, et que vous avez sélectionné Modern Experience.
Le même assistant est également utilisé lors de l’utilisation d’une activité Extraire les données de table dans votre workflow.
Utilisation de l'enregistreur d'extraction de table
Si vous avez sélectionné Modern Experience dans votre projet et que le package d’activités UI Automation est installé, vous pouvez trouver l’enregistreur d’extraction de table dans le ruban de Studio.

Clicking the Table Extraction button in the Ribbon opens up the Table Extraction wizard.

Cet assistant vous permet de configurer avec facilité l'ensemble des fonctionnalités offertes par l'activité Extract Table Data.
Pour basculer entre les infrastructures d'IU disponibles (Default, UIAutomation, ou Active Accessibility), vous pouvez sélectionner une option dans le menu déroulant ou appuyer sur F4.
En outre, la section Informations vous guidera à travers toutes les étapes à suivre pour extraire avec succès des données structurées. La section peut être réduite afin d'afficher davantage d'informations sur l'étape à laquelle vous vous trouvez actuellement.

Pour commencer le processus d’extraction des données, cliquez simplement sur le bouton Ajouter des données . Cela permet de commencer le processus d’indication d’une série d’éléments similaires qui peuvent être utilisés pour identifier la table que vous souhaitez créer. Cela démarre le processus Indiquer, qui met en surbrillance tous les éléments détectés de l’application avec laquelle vous travaillez actuellement. En sélectionnant le  vous pouvez extraire les URL et les sources d’images des données extraites, si elles sont présentes. Ceux-ci sont ajoutés sous forme de nouvelle colonne à votre table finale.
vous pouvez extraire les URL et les sources d’images des données extraites, si elles sont présentes. Ceux-ci sont ajoutés sous forme de nouvelle colonne à votre table finale.

As you can see above, after clicking a column header, the wizard prompts you with a message, asking whether you want to extract all of the available columns, which are automatically identified. Selecting Yes scrapes the entire table.
Si vous sélectionnez un élément qui est plus proche (ancêtre commun le plus bas) d'un seul des éléments de la première colonne, il est automatiquement considéré comme le premier élément d'une nouvelle colonne.
If the table spans multiple pages, you can simply click Next Button and select the next page navigation button or link.
Chaque colonne peut être modifiée ou supprimée individuellement, vous permettant de personnaliser votre table finale comme bon vous semble.

Once you have selected all the data you want, simply clicking the Save and return to Studio button automatically closes the wizard and saves everything you have done in your workflow.
Modification des données d'extraction
You can resume editing an already scraped table by using the Edit extract data option in the contextual menu in the body of the Extract Table Data activity. Using this option reopens the wizard with all of the configurations performed earlier and enables you to pick up where you left off.

Modification des colonnes
Cliquer sur l'icône de roue dentée à côté de la colonne que vous souhaitez modifier ouvre la fenêtre Paramètres de la colonne (Column Settings).

Here, you can edit the Column Name. This can be done by simply using the text box and specifying the name you want for the column in the final table.
The Parse data as drop-down menu enables you to select between the three main types of data you can use for the columns, Text, Number, and Date & Time.
The Sample text box displays a sample of a value in the column being parsed as the data type you chose in the Parse data as drop-down.
Texte
The Sort drop-down menu specifies whether you want to sort the data in the column or not. By default, None is selected, meaning the data is not sorted in any way. If you want to sort the data in the column alphabetically, you can do so by selecting Ascending or Descending, depending on the method you prefer.
Numérique
Selecting Number in the Parse data as drop-down displays other, number-specific options.

The Sort drop-down menu specifies whether you want to sort the data in the column or not. By default, None is selected, meaning the data is not sorted in any way. If you want to sort the data in the column alphanumerically, you can do so by selecting Ascending or Descending, depending on the method you prefer.
The Decimal separator specifies the symbol you want to use for decimal separation in your final table. By default, this symbol is ..
The Thousands separator specifies the symbol you want to use for thousand separation in your final table. By default, this symbol is ,.
When scraping numbers, they are parsed according to the selected options, and separators and other symbols (e.g. $) are removed.
Date et heure
Selecting Date & Time in the Parse data as drop-down displays other options, specific to date and time formats.

If the column you are editing does not match the format that is specified, the Column Settings window lets you know in the Sample section.
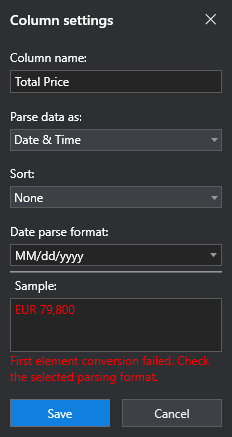
The Sort drop-down menu specifies whether you want to sort the data in the column or not. By default, None is selected, meaning the data is not sorted in any way. If you want to sort the data in the column by date, you can do so by selecting Ascending or Descending, depending on the method you prefer.
The Data parse format drop-down enables you to select from a multitude of date and time formats that are supported.
When selecting dates, they are formatted according to the format that is selected in your operating system. The parsing format selected in the wizard is just to identify the data you are scraping.
Section Paramètres
The Settings section lets you choose if you want to limit the extraction of elements in the table. By default, this option is set to No limit, which does not limit the extraction in any way, scraping the entire visible table.
The Max rows option limits the scraping according to the number of rows that is mentioned in the field to the right. By default, this is set to 1000 rows.
The Max pages option limits the scraping according to the number of pages that is mentioned in the field to the right. By default, this is set to 100 pages.
Section Aperçu
The Preview section specifies how many columns and rows are identified for the table you have indicated. Also, by clicking the eye button, you can see a preview of the extracted table.
L'aperçu est désactivé lors de l'édition en mode hors ligne.
Extract Metadata
The Extract metadata property contains an XML definition of the path identifying the data to be extracted for each column. The path is built starting from the data extraction target (defined by your selector) to the column elements. The path uses attributes such as tag, idx, and text.
Exemple :
<extract>
<!—columns data identified by a path >
<column exact='1' name=’Description’ attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='div' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='span' idx='1' />
</column>
<column exact='1' name=’Currency’ attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='div' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='span' idx='2' />
</column>
</extract>
<extract>
<!—columns data identified by a path >
<column exact='1' name=’Description’ attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='div' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='span' idx='1' />
</column>
<column exact='1' name=’Currency’ attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='div' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='span' idx='2' />
</column>
</extract>
Lorsque les attributs tag, idxet text ne suffisent pas pour identifier les exemples de données indiqués par l'utilisateur, un sélecteur CSS est généré à la place du chemin d'accès. Ce sélecteur utilise la classe commune des exemples d'éléments.
Exemple :
<extract>
<!—column data identified by a path >
<column exact='1' name='Description' attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='h3' idx='1' />
</column>
<!—column data identified by a css-selector >
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Currency' attr='text' />
</extract>
<extract>
<!—column data identified by a path >
<column exact='1' name='Description' attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='h3' idx='1' />
</column>
<!—column data identified by a css-selector >
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Currency' attr='text' />
</extract>
For the Description column, tag and index attributes are used to identify the column data.
For the Currency column, the elements are identified via the CSS-selector which contains the common class of the samples.
En option, si disponible, un sélecteur CSS peut également être utilisé pour la description :
<extract>
<!—columns data identified by css-selectors >
<column css-selector='.product-title ' name='Description' attr='text' />
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Currency' attr='text' />
</extract>
<extract>
<!—columns data identified by css-selectors >
<column css-selector='.product-title ' name='Description' attr='text' />
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Currency' attr='text' />
</extract>
La définition de ligne utilise les mêmes méthodes d'identification que la colonne et est utilisée pour extraire les données corrélées. Une ligne contient un élément de chaque colonne.
Exemple :
<extract>
<! -- row definition - ->
<row exact='1'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
</row>
<column exact='1' name='Description' attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='h3' idx='1' />
</column>
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Column' attr='text' />
</extract>
<extract>
<! -- row definition - ->
<row exact='1'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
</row>
<column exact='1' name='Description' attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='h3' idx='1' />
</column>
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Column' attr='text' />
</extract>
Paramètres de table
This property contains an XML definition of the column settings, as they were defined in the scraping wizard. Column properties like Name or Format can be changed directly in this XML definition and will be used at runtime when building the output data table.
Exemple :
<table xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xmlns:xsd='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema' Type='Structured'>
<Column xsi:type='DataColumn' ReferenceName='Column0' Name=’Description'>
<Format xsi:type='TextColumnFormat' />
</Column>
<Column xsi:type='DataColumn' ReferenceName='Column2' Name=’Currency'>
<Format xsi:type='TextColumnFormat' />
</Column>
</Table>
<table xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xmlns:xsd='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema' Type='Structured'>
<Column xsi:type='DataColumn' ReferenceName='Column0' Name=’Description'>
<Format xsi:type='TextColumnFormat' />
</Column>
<Column xsi:type='DataColumn' ReferenceName='Column2' Name=’Currency'>
<Format xsi:type='TextColumnFormat' />
</Column>
</Table>