- Erste Schritte
- UiPath Agents in Studio Web
- Über UiPath Agents
- Lizenzierung
- Aufforderungen
- Arbeiten mit Dateien
- Kontexte
- Eskalationen und Agent-Speicher
- Bewertungen
- Spuren von Agents
- Agent-Punktzahl
- Verwaltung von UiPath Agents
- Codierte UiPath Agents

Benutzerhandbuch zu Agents
Konversations-Agents
Konversations-Agents sind eine Klasse von UiPath-Agents, die für dynamische Multi-Turn-Echtzeit-Dialogfelder mit Benutzern entwickelt wurden. Im Gegensatz zu autonomen Agents, die Aufgaben aus einem einzigen Prompt ausführen, interpretieren und reagieren Konversations-Agents auf einen kontinuierlichen Fluss von Nachrichten, während sie den Konversationskontext, die Ausführung von Tools und menschliche Eskalationen verwalten.
Setzen Sie Konversations-Agents ein, wenn Ihr Automatisierungsszenario Folgendes erfordert:
- Laufende Klärung oder ein Dialog
- Personalisierte Anleitung basierend auf der Benutzerabsicht
- Einfacher Rückgriff auf einen Menschen bei geringem Vertrauen
Konversations-Agents im Vergleich zu autonomen Agents
| Funktionen | Conversational Agent | Autonomer Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Interaktionsmodell | Mehrstufiger, wechselseitiger Dialog | Einzelne Aufgabenausführung basierend auf einem ersten Prompt |
| Primärer Einsatz | Echtzeit-Benutzerunterstützung, interaktive Informationserfassung | Ausführen einer Aufgabe über einen definierten Prompt |
| Benutzereingaben | Kontinuierliche Chatnachrichten | Ein einziger strukturierter Prompt |
| Hauptstärke | Beibehalten des Konversationskontexts und Umgang mit Mehrdeutigkeiten | Ausführung eines Plans über Tools hinweg |
Wann Sie Conversational Agents einsetzen sollten
Verwenden Sie Konversations-Agents, wenn Ihre Automatisierung kontextbezogene Interaktionen in Echtzeit umfasst:
- Selfservice-Erfahrungen: Helpdesk-Support, HR-Onboarding-Assistenten, IT-Fehlerbehebung bei Bots
- Interaktive Anleitung: Mehrstufige Prozesse, Formulare oder Entscheidungsstrukturen
- Kontextuelle Konversationen: Szenarien, in denen Benutzer Anschlussfragen stellen oder Informationen inkrementell bereitstellen
- Benutzeroberflächen in natürlicher Sprache: Konversatives Abfragen von Anwendungen, Systemen oder Wissensdatenbanken
Verwenden Sie stattdessen autonome Agents, wenn die Aufgabe in einem einzigen Prompt mit allen erforderlichen Eingaben, die im Voraus bereitgestellt werden, vollständig beschrieben werden kann:
- Verarbeitung strukturierter Dokumente (Extraktion von Daten aus Rechnungen oder Verträgen)
- Automatisierte Berichtserstellung basierend auf einer vordefinierten Logik
- Zusammenfassungs- oder Transformationsaufgaben mit klaren Anforderungen für einmalige Ausführungen
Konversations-Agents vs. Autopilot for Everyone
Wie hängen Konversationsagenten mit Autopilot for Everyone zusammen?
Diese beiden Erfahrungen arbeiten Seite an Seite:
- Autopilot for Everyone: Der universelle Assistent von UiPath, der für Produktivitätsaufgaben und die Interaktion mit der UiPath-Plattform optimiert wurde.
- Konversations-Agents: Spezialisierte Agents, die Sie für bestimmte Anwendungsfälle erstellen (z. B. ein Personalrichtlinienassistent oder IT-Helpdesk-Bot).
Sie können direkt von Autopilot for Everyone aus auf Ihre Konversations-Agents zugreifen, wodurch ein zentraler Knotenpunkt für alle Ihre Konversations benötigt wird.
Unsere Empfehlung: Wir empfehlen Ihnen, neue Konversationsanwendungsfälle auf der Plattform Konversations-Agents zu erstellen. Es bietet eine umfassende Entwurfszeiterfahrung mit integrierter Auswertung, erweiterter Beobachtbarkeit und vollständigem API-Zugriff.
Konversations-Agents unterstützen derzeit keine lokale Desktop-Automatisierung. Wenn Ihr Anwendungsfall das Auslösen von Automatisierungen auf der lokalen Maschine des Benutzers erfordert, ist diese Funktion für einen zukünftigen Release geplant.
Der Lebenszyklus des Agents
Die Erstellung und der Betrieb eines Konversations-Agents umfasst vier Phasen:
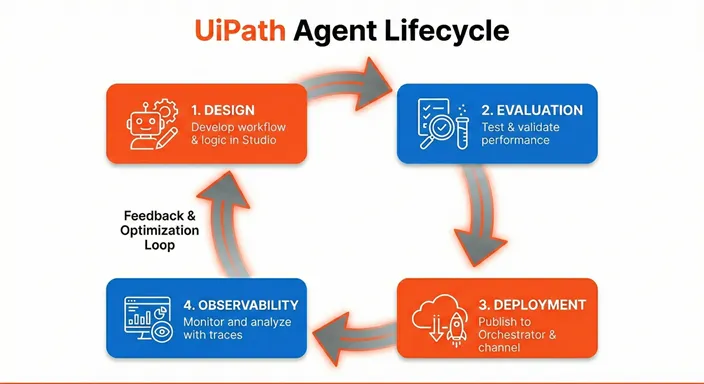
Design
Nutzen Sie Studio Web, um die Persona Ihres Agents zu definieren, Tools zu konfigurieren, Kontextgrundlage für die Wissensabfrage hinzuzufügen und Eskalationsworkflows einzurichten. Mit dem Low-Code-Designer können Sie Agents visuell erstellen, ohne Code schreiben zu müssen.
Auswertung
Testen Sie Ihren Agent mit dem integrierten Debug-Chat, um Multi-Turn-Interaktionen zu validieren. Erstellen Sie Auswertungssätze aus echten Konversationen, um die Leistung in verschiedenen Szenarien zu messen, einschließlich Single-Turn-Antworten und Multi-Turn-Dialog-Flows.
Bereitstellung
Veröffentlichen und stellen Sie Ihren Agent in Orchestrator bereit und machen Sie ihn über verschiedene Kanäle verfügbar: Instanzverwaltung, Autopilot for Everyone, Microsoft Teams, Slack oder eingebettet in ein iFrame in Drittanbieter-Apps oder UiPath-Apps.
Beobachtbarkeit
Überwachen Sie die Leistung Ihres Agents über Dashboards zur Instanzverwaltung, Debuggen mithilfe von Ablaufverfolgungen und Prüfungen mithilfe der AI Trust Layer-Prüfung. Überprüfen Sie Ablaufverfolgungsprotokolle, sammeln Sie Benutzerfeedback und nutzen Sie diese Erkenntnisse, um das Design Ihres Agents zu überarbeiten und die Feedback-Schleife zu vervollständigen.
Nächste Schritte
- Erste Schritte: Erstellen Sie in wenigen Minuten Ihren ersten Konversations-Agent
- Design: Konfigurieren Sie Prompts, Tools und Kontexte
- Lizenzierung: Verstehen von Verbrauch und Preisen
- Einschränkungen und häufig gestellte Fragen: Aktuelle Einschränkungen und Fehlerbehebung