- Erste Schritte
- UiPath Agents in Studio Web
- Über UiPath Agents
- Lizenzierung
- Aufforderungen
- Arbeiten mit Dateien
- Kontexte
- Eskalationen und Agent-Speicher
- Bewertungen
- Spuren von Agents
- Agent-Punktzahl
- Verwaltung von UiPath Agents
- Codierte UiPath Agents

Benutzerhandbuch zu Agents
Batch-Transformation
Mit dem Tool Batch-Transformation können Agents CSV-Dateien mithilfe von JIT-Datenquellen massenweise verarbeiten. Es wurde für Szenarien entwickelt, in denen Sie die gleiche Transformationslogik auf jede Zeile oder jeden Datensatz in einer CSV-Datei anwenden möchten, ohne im Voraus Speicher-Buckets oder Indizes einrichten zu müssen.
Batch-Transformation verwendet eine zur Laufzeit bereitgestellte CSV-Eingabedatei und wendet eine benutzerdefinierte Transformationsaufgabe darauf an. Das Tool bearbeitet die Datei Zeile für Zeile und erzeugt eine oder mehrere Ausgabedateien, die die Originaldaten zusammen mit allen zusätzlichen Spalten oder Zeilen enthalten, die von der Transformationslogik generiert werden.
Typische Anwendungsfälle sind:
- Anreichern von CSV-Dateien mit modellgenerierten Punktzahlen, Beschriftungen oder Klassifizierungen
- Anwenden von Geschäftsregeln oder Entscheidungslogik auf große Datensätze
- Erstellen von Erklärungen oder Rechtfertigungen neben automatisierten Entscheidungen
Datenquellen
- Batch-Transformation unterstützt nur JIT-Datenquellen.
- Nur CSV-Dateien werden als Eingabe unterstützt.
- Dateien werden direkt durch Agent-Eingaben weitergeleitet und zur Runtime automatisch aufgelöst.
- Es ist keine externe Speicherkonfiguration oder Indexerstellung erforderlich.
For details, refer to Best practices for DeepRAG and Batch Transform: JIT vs. index-based strategies.
Konfigurieren der Batch-Transformation
Fügen Sie das Batch-Transformationstool hinzu
- Öffnen Sie Ihren Agent im Designmodus.
- Fügen Sie in der Liste der integrierten Tools Batch Transform zum Agent hinzu.
Nach dem Hinzufügen wird das Batch-Transformationstool als eigener Toolknoten angezeigt, den Sie im rechten Bereich konfigurieren können.
Eingaben konfigurieren
Zur Entwurfszeit geben Sie an, wie das Tool seine Eingabe erhalten soll:
-
Quelldatei : Die Quelle ist eine Dateieingabe (z. B.
input-csv). Zur Runtime wird dies automatisch in die Datei aufgelöst, die bereitgestellt wird, wenn der Agent ausgeführt wird.Hinweis:Sie müssen ein Dateityp-Argument in Data Manager konfigurieren.
-
Batch-Transformationsaufgabe – Die toolspezifische Anweisung, die definiert, wie die Batch-Transformation ausgeführt werden soll. Verwenden Sie dieses Feld, um dem Tool genau mitzuteilen, wie die Eingabedatei verarbeitet werden soll, einschließlich:
- Welche neuen Spalten oder Zeilen generiert werden sollen
- Wie jede Zeile verarbeitet werden soll
- Alle Regeln, Kriterien oder Entscheidungslogik, die angewendet werden soll
Sie könnten das Tool beispielsweise anweisen, zwei neue Spalten zu generieren, z. B. eine Punktzahl und ein Empfehlungs-Flag basierend auf dem Inhalt jeder Zeile. Dies ist kein Agent-Prompt. Der Agent sollte nur eine allgemeine Anweisung enthalten, wann die Batch-Transformation aufgerufen werden soll und wie die finale Ausgabe aussehen soll.
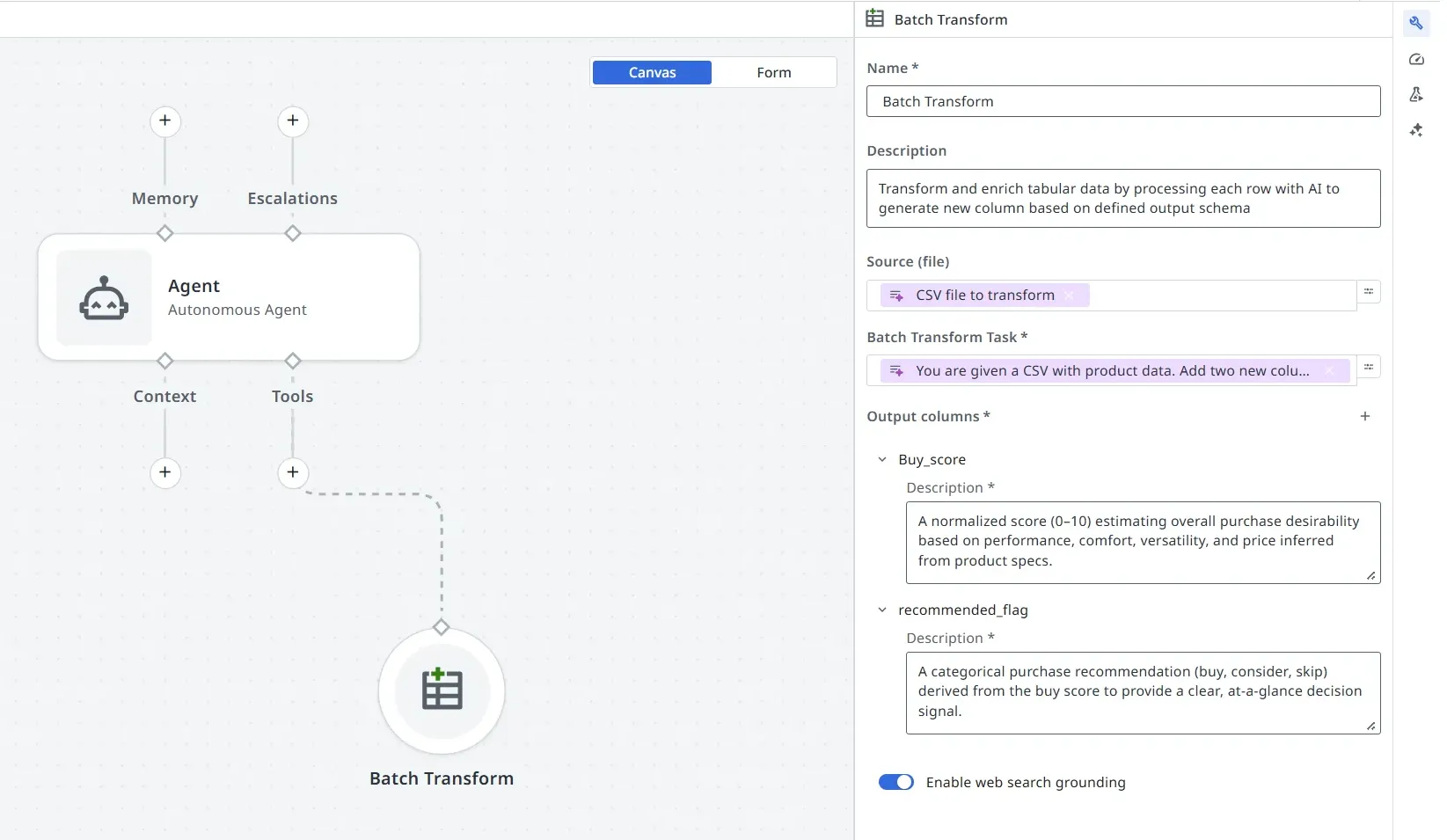
-
Ausgabespalten – Definieren Sie das Schema für alle neuen Spalten, die von der Batch-Transformation generiert werden. Geben Sie für jede Spalte Folgendes an:
- Der Spaltenname
- Eine Beschreibung, was die Spalte darstellt und wie ihre Werte zu interpretieren sind
Sie können neue Ausgabespalten hinzufügen, vorhandene Spaltennamen oder -beschreibungen bearbeiten oder Spalten nach Bedarf entfernen. Die Batch-Transformationsaufgabe sollte die Logik beschreiben, die zum Ausfüllen dieser konfigurierten Spalten verwendet wird.
Aktivieren der Websuchgrundlage (Optional)
Das Batch-Transformationstool enthält eine optionale Einstellung für die Websuchgrundlage, die steuert, ob das Modell beim Generieren von Transformationen Websuchergebnisse verwenden darf.
- Wenn diese Option aktiviert ist, kann das Modell die Eingabedateidaten mit Informationen ergänzen, die während der Verarbeitung jeder Zeile aus dem Web abgerufen wurden.
- Wenn diese Option deaktiviert ist, wird die Transformation ausschließlich unter Verwendung des Inhalts der Eingabedatei, der in der Aufgabe definierten Anweisungen und jeglichen Kontexts, der dem Agent explizit zur Verfügung gestellt wird, durchgeführt.
Batch-Transformation wird ausgeführt
Wenn Sie den Agent ausführen oder debuggen, wird das Batch-Transformationstool als Teil der Agentenausführung ausgeführt:
- Die Eingabedatei wird zur Laufzeit an das Tool übergeben.
- Das Tool bearbeitet die Datei Zeile für Zeile.
- Eine transformierte Ausgabedatei wird generiert.
- Die Ausgabedatei wird als Teil der Agent-Ausgabe zurückgegeben.
Während der Ausführung wird Batch Transform in der Ausführungsablaufverfolgung als dedizierter Toolaufruf angezeigt. Sie können diesen Schritt erweitern, um detaillierte Runtime-Informationen anzuzeigen.
Überprüfen von Ausführungsdetails
Über die Ausführungsablaufverfolgung können Sie die Einzelheiten in der Ausgabe des Toolaufrufs und ggf. in der Ausgabe des Agents überprüfen:
- Eingaben - Die vom Tool verwendete Eingabedatei, einschließlich Dateiname, Typ und Metadaten (sichtbar in der Ausgabe des Toolaufrufs).
- Ausgaben – Die generierte Ausgabedatei, einschließlich Datei-ID, Dateiname und MIME-Typ (angezeigt in der Toolaufrufausgabe, wenn eine Dateiausgabe definiert ist).
- Prompt-Kontext – Die System- und Benutzerprompts, die während der Ausführung des Agents verwendet wurden und erklären, wie die Transformationsaufgabe ausgeführt wurde.
Sie können sowohl die Eingabe- als auch die Ausgabedateien zur Validierung oder Fehlerbehebung direkt aus der Ausführungsablaufverfolgung herunterladen.
Wenn eine Dateiausgabe definiert wird, enthält die endgültige Agent-Ausgabe in der Regel eine Bestätigungsmeldung, die angibt, dass die transformierte Datei generiert wurde, und den Namen der Ausgabedatei angibt.
Auswerten von Batch-Transformationen
Mit Auswertungen können Sie die Qualität und Korrektheit von Batch-verarbeiteten Ausgaben messen. Neben der Auswertung der Ergebnisse auf Dateiebene unterstützen Agents die zeilenspezifische Auswertung, was besonders für strukturierte Ausgaben wie CSV-Dateien nützlich ist.
Zeile-für-Zeile-Auswertung
Bei der Zeile-für-Zeile-Auswertung wird jede Zeile in einer Ausgabedatei unabhängig ausgewertet, anstatt die Datei als einzelne Einheit zu bewerten. Dies bietet einen detaillierten Einblick in die Leistung einzelner Datensätze anhand Ihrer Auswertungskriterien. Dieser Modus ist besonders nützlich, wenn:
- Jede Zeile stellt eine unabhängige Entscheidung oder Klassifizierung dar.
- Sie benötigen differenzierte Metriken zum Metriken von Erfolgen/Fehlern für große Dateien.
- Sie möchten die einzelnen Fehler analysieren.
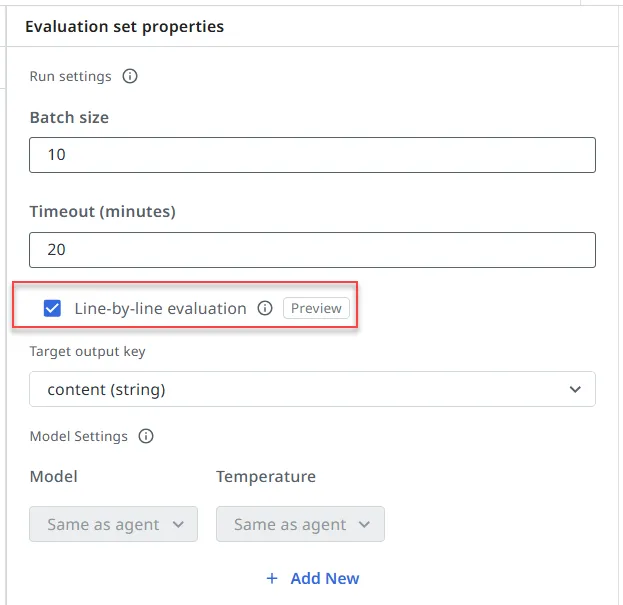
Konfigurieren einer Zeile-für-Zeile-Bewertung
Die Zeile-für-Zeile-Evaluierung wird in den Einstellungen für den Evaluierungssatz konfiguriert:
- Aktivieren Sie die zeilenweise Auswertung in der Konfiguration des Auswertungssatzes.
- Wählen Sie die auszuwertende Ausgabedatei aus. Dies ist erforderlich, wenn ein Agent mehrere Ausgabedateien erzeugt.
- Geben Sie den Dateityp (z. B. CSV) an, mit dem der Auswerter arbeiten soll.
Nach der Konfiguration werden Bewertungen für jede Zeile der ausgewählten Ausgabedatei durchgeführt.
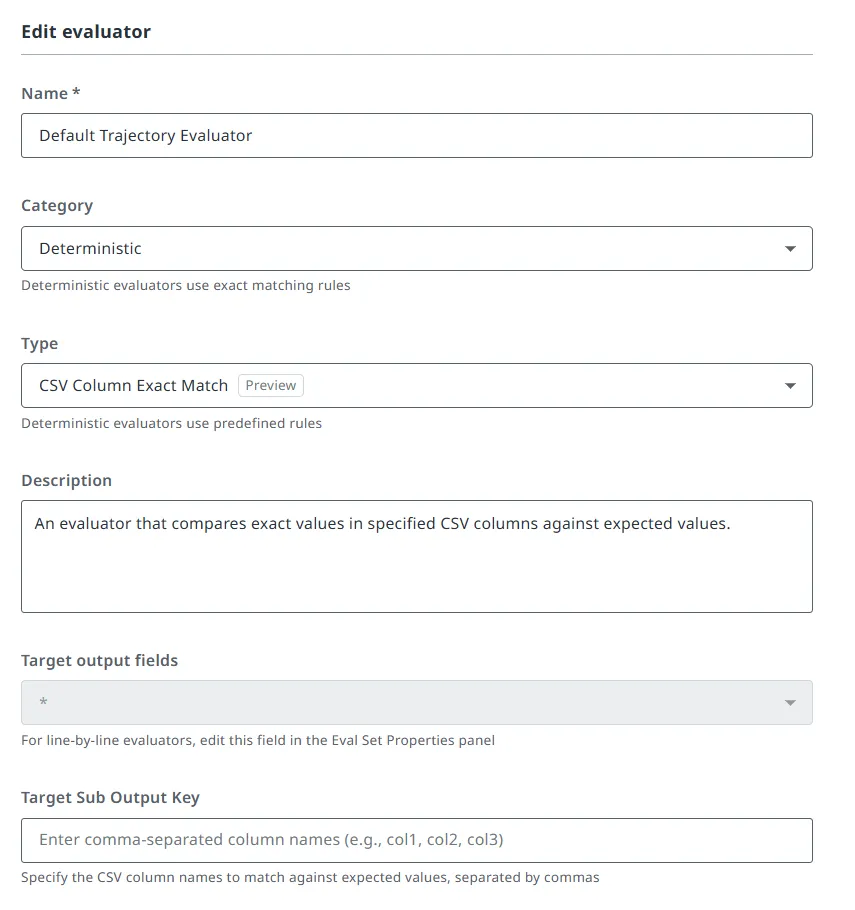
Auswerter der CSV-Spalte für exakte Übereinstimmung
Zur Unterstützung der strukturierten Dateiauswertung steht ein deterministischer Evaluierer namens CSV Column Exact Match Evaluator zur Verfügung. Weitere Informationen dazu finden Sie unter Agentenbewertungen.
Dieser Auswerter:
- Vergleicht eine oder mehrere angegebene Spalten zwischen erwarteten und tatsächlichen Ausgaben
- Führt eine exakte Zeichenfolgenübereinstimmung durch
- Gibt Erfolge/Fehler-Ergebnisse pro Zeile zurück
Der CSV Column Exact Match Evaluierer eignet sich gut zum Validieren von kategorischen Ausgaben wie Beschriftungen, Abgleichtypen oder Statusfeldern.
Ausführen und Überprüfen von Bewertungen
Nach dem Konfigurieren des Evaluierungssatzes:
- Erstellen Sie einen Auswertungslauf mit einer Eingabedatei und der entsprechenden Batch-Transformations-Ausgabedatei.
- Planen oder führen Sie die Auswertung aus.
- Überprüfen Sie die Ergebnisse auf zwei Ebenen:
- Zusammenfassung auf Dateiebene, die angibt, wie viele Zeilen insgesamt erfolgreich waren oder fehlgeschlagen sind.
- Drilldown auf Zeilenebene, der den Erfolgs-/Fehlerstatus, die Werte und die Metadaten für jede einzelne Zeile anzeigt.
Beispielsweise kann eine Auswertung zeigen, dass 141 von 199 Zeilen eine Prüfung auf exakte Übereinstimmung in einer bestimmten Spalte bestanden haben. Von dort aus können Sie einen Drilldown durchführen, um einzelne fehlgeschlagene Zeilen zu überprüfen, erwartete mit den tatsächlichen Werten zu vergleichen und Ausführungsdetails wie die Latenz pro Zeile zu überprüfen.
Die Zeile-für-Zeile-Bewertung bietet:
- Klare Übersicht, welche Datensätze erfolgreich waren oder fehlgeschlagen sind.
- Schnelleres Debuggen der Transformationslogik.
- Quantative Metriken zur Verfolgung von Verbesserungen im Laufe der Zeit.