- Getting Started
- Setup and Configuration
- Automation Projects
- Dependencies
- Types of Workflows
- Control Flow
- File Comparison
- Automation Best Practices
- Source Control Integration
- Debugging
- Logging
- The Diagnostic Tool
- Workflow Analyzer
- About Workflow Analyzer
- ST-NMG-001 - Variables Naming Convention
- ST-NMG-002 - Arguments Naming Convention
- ST-NMG-004 - Display Name Duplication
- ST-NMG-005 - Variable Overrides Variable
- ST-NMG-006 - Variable Overrides Argument
- ST-NMG-008 - Variable Length Exceeded
- ST-NMG-009 - Prefix Datatable Variables
- ST-NMG-011 - Prefix Datatable Arguments
- ST-NMG-012 - Argument Default Values
- ST-NMG-016 - Argument Length Exceeded
- ST-NMG-017 - Class name matches default namespace
- ST-DBP-002 - High Arguments Count
- ST-DBP-003 - Empty Catch Block
- ST-DBP-007 - Multiple Flowchart Layers
- ST-DPB-010 - Multiple instances of [Workflow] or [Test Case]
- ST-DBP-020 - Undefined Output Properties
- ST-DBP-021 - Hardcoded Timeout
- ST-DBP-023 - Empty Workflow
- ST-DBP-024 - Persistence Activity Check
- ST-DBP-025 - Variables Serialization Prerequisite
- ST-DBP-027 - Persistence Best Practice
- ST-DBP-028 - Arguments Serialization Prerequisite
- ST-USG-005 - Hardcoded Activity Properties
- ST-USG-009 - Unused Variables
- ST-USG-010 - Unused Dependencies
- ST-USG-014 - Package Restrictions
- ST-USG-017 - Invalid parameter modifier
- ST-USG-020 - Minimum Log Messages
- ST-USG-024 - Unused Saved for Later
- ST-USG-025 - Saved Value Misuse
- ST-USG-026 - Activity Restrictions
- ST-USG-027 - Required Packages
- ST-USG-028 - Restrict Invoke File Templates
- ST-USG-032 - Required Tags
- ST-USG-034 - Automation Hub URL
- Variables
- Arguments
- Imported Namespaces
- Coded automations
- Introduction
- Registering custom services
- Before and After contexts
- Generating code
- Generating coded test case from manual test cases
- Troubleshooting
- Trigger-based Attended Automation
- Object Repository
- The ScreenScrapeJavaSupport Tool
- Extensions
- About extensions
- SetupExtensions tool
- UiPathRemoteRuntime.exe is not running in the remote session
- UiPath Remote Runtime blocks Citrix session from being closed
- UiPath Remote Runtime causes memory leak
- UiPath.UIAutomation.Activities package and UiPath Remote Runtime versions mismatch
- The required UiPath extension is not installed on the remote machine
- Screen resolution settings
- Group Policies
- Cannot communicate with the browser
- Chrome extension is removed automatically
- The extension may have been corrupted
- Check if the extension for Chrome is installed and enabled
- Check if ChromeNativeMessaging.exe is running
- Check if ComSpec variable is defined correctly
- Enable access to file URLs and Incognito mode
- Multiple browser profiles
- Group Policy conflict
- Known issues specific to MV3 extensions
- List of extensions for Chrome
- Chrome Extension on Mac
- Group Policies
- Cannot communicate with the browser
- Edge extension is removed automatically
- The extension may have been corrupted
- Check if the Extension for Microsoft Edge is installed and enabled
- Check if ChromeNativeMessaging.exe is running
- Check if ComSpec variable is defined correctly
- Enable access to file URLs and InPrivate mode
- Multiple browser profiles
- Group Policy conflict
- Known issues specific to MV3 extensions
- List of extensions for Edge
- Extension for Safari
- Extension for VMware Horizon
- Extension for Amazon WorkSpaces
- SAP Solution Manager plugin
- Excel Add-in
- Studio testing
- Troubleshooting
- About troubleshooting
- Assembly compilation errors
- Microsoft App-V support and limitations
- Internet Explorer X64 troubleshooting
- Microsoft Office issues
- Identifying UI elements in PDF with Accessibility options
- Repairing Active Accessibility support
- Validation of large Windows-legacy projects takes longer than expected

Studio user guide
About Libraries
A library is a project which contains one or more workflows that can be reused as activities in other projects. Libraries are saved as NUPKG files when published and can be installed as dependencies from the Package Manager.
For example, you could create a library that collects data from an Excel spreadsheet and appends it to another, as explained in the Creating a Basic Library page. Next, the library can be packaged and used in other processes as an activity.
Creating a Library
- Go to the Studio Backstage View > Start > Library. This opens the New Blank Library window.
- Fill in the name and pick a location for the library. The default location is
C:\Users\<current_user>\Documents\UiPath. Add a description, select the project compatibility and language, and then select Create. The new library is created and saved on your local machine.Note:- The library name cannot exceed 128 characters, and the description cannot exceed 500 characters.
- Do not use
libas a library name, as this will result in a compile error in projects where the library is installed.
- The Project Panel displays the tree view with the Project folder, Dependencies, and the
NewActivity.xamlwhich contains the actual workflow.
Each workflow file in a library is available as an activity in projects where the library is installed as a dependency. If you want to make a certain file private, right-click it and select Make Private. In this case, the file is included in the library package, but it is not available as a reusable component in the Activities panel.
By default, the dependencies available for new libraries are the same as those for new projects with the Lowest Applicable Version runtime rule.
Extracting a Project as Library
You can extract any process or test automation project as a library to be reused in other projects. For example, you can convert a test automation project to use its templates in other automation projects.
- Open a project in Studio.
- In the Design ribbon, select Export As and then Library.
- Select the workflows that you want to export as a library. By default, the entire project is deselected, along with the entry points (Main workflow, and Test Cases).
- Configure the following Extract Options:
- Include Test Cases: By default, this option is enabled for a Process project and disabled for a Test Automation project. You should enable this option if you want to include test cases as part of the extracted library.
- Publish and install the library: Automatically selected to publish the package to a shared feed and install the library as a project dependency. You can disable this option if you want to create the library without publishing it. If disabled, the remainder options are not available for configuration.
- Alter your workflows after the package install: Choose to modify the workflows with activities that have been compiled from the library.
- Replacing Mode: Choose the workflow replacing method.
- Select Replace invoked workflows content to change the workflows invoked from entry point, or test cases with corresponding activities from the extracted library.
- Use this option if you use the Isolated and Target Sessions properties for Invoke Workflow activities to run in a separate Windows process, and start in a different session, respectively.
- Select Replace "Invoke Workflow" activities to change the Invoke Workflow activities with activities from the extracted library.
Important:
Do not select this option if you are using the Isolated and Target Sessions properties for Invoke Workflow activities.
- Delete replaced workflows: Delete the workflows that have been replaced by the extracted library activities.
- Set Execution Templates from library: Add execution templates to the library.
- Click Export to confirm the library options.
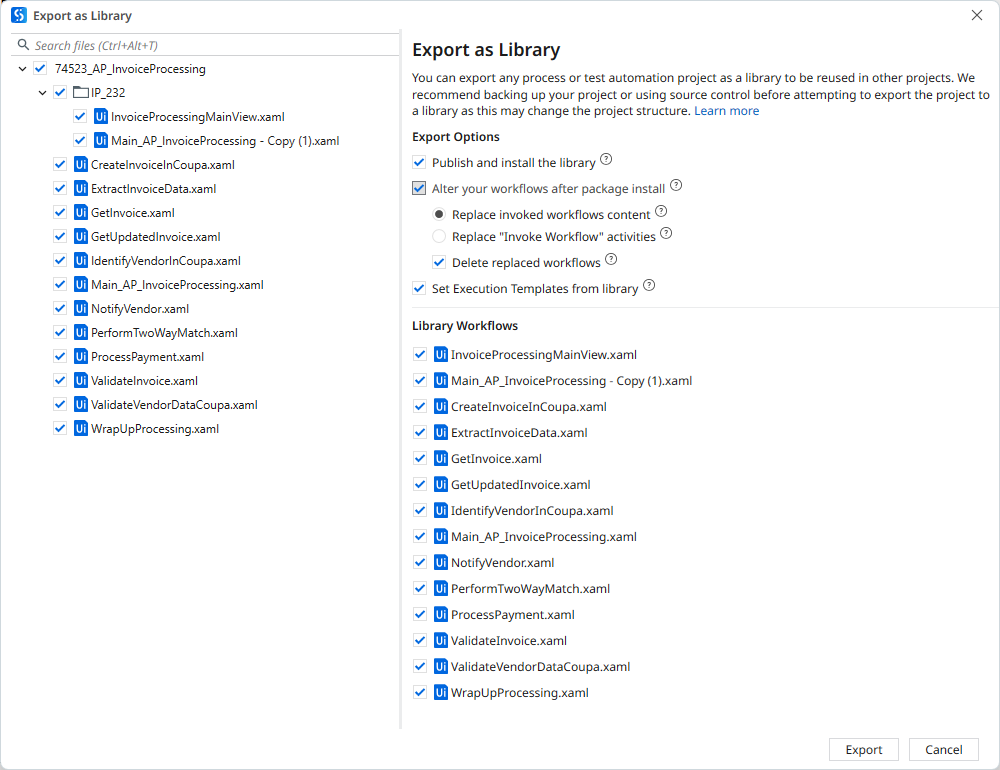
- Click Create to finish library creation.

- (Optional) Publish the library if you've selected Publish and install the library in step 4, and then click Publish.

In case you didn't enable the Publish and install the library option, you'll be prompted to open the library or continue with the current project.

Replacing workflows or invoked activities from the extracted library will not take place for workflows where mock testing is used.
Configuring the Layout of an Activity
Arguments you define in the library become activity properties in the projects where the library is installed as a dependency.
To configure the look and the behavior of an activity when it is used in a project, right-click the workflow file in the library Project panel, and then select Activity Layout. The activity properties window is displayed with different options depending on the library compatibility (Windows - Legacy, Windows, or cross-platform).

Options for Windows and Cross-platform libraries
Select Activity Properties in the left-side menu, and enter the following:
- Display name - The activity's name displayed in the Activities panel. The display name should not be changed when using the library in a project.
- Tooltip - The tooltip that is visible when you hover over the activity in the Activities and Designer panels in projects where the library is installed.
- Help Link - The help link that opens when you select the activity in the Designer panel and press F1 on your keyboard.
- SVG Icon - The SVG icon to display next to the activity name.
Note:
The icon is not visible in Manage Packages if a local file is used for a library published to Orchestrator or to a feed that does not support embedded icons. In this case, specify the icon using a URL.
- Color - The highlight color displayed for the activity in the Designer panel.
The arguments defined in the workflow file are listed under Activity Properties in the left-side menu.
- To customize the generated property, select it and configure the following:
- Display name - The label that appears in the activity for the property.
- Tooltip - The tooltip that is visible when you hover over the activity property.
- Input Type - The type of input for the property. You can use the default input for the property type or select an input option depending on the type:
- Boolean - Use Default, Toggle (default), Condition Builder, Radio Button.
- Numeric (int, double, decimal, long, short, sbyte, byte, ulong, ushort, unit, float) - Use Default, Number Editor, Dropdown. For Dropdown, in the Values field, input each separate value by pressing Enter on your keyboard.
- String - Use Default, Text Composer (default), Rich Text Composer, Dropdown, Autocomplete, Radio Button. For Dropdown, Autocomplete, and Radio Button, in the Values field, input each separate value by pressing Enter on your keyboard.
- String[] - Use Default, String Array.
- Date Time - Use Default, Date Time.
- Time Span - Use Default, Time Span.
- Dictionary - Use Default, Dictionary.
- All other types - Use Default, Input.
- Placeholder - The placeholder text to display for the input when no value is selected.
- Required - Whether the property is required.
- Advanced Only - Whether the property should only be displayed in the advanced options section of the activity. Properties from the advanced options section can also be organized in categories.
- To add a category under which to group multiple related properties, select New Category in the lower-left side of the window. Categories are available only in the advanced options section of the generated activity and can be expanded or collapsed. If a category is empty, it is removed when you click Save to close the window.
- To change the order of properties and categories, or add properties to categories, drag-and-drop the items in the list.

- If your library includes Integration Service activities or invokes workflows containing Integration Service activities, connections used in these activities, as well as other activity properties appear as separate entities when configuring the activity layout. You can reorder and categorize Integration Service connections and properties, as well as edit a property’s Display name and Tooltip.
Note:
- Configuring connections and properties may not work when invoking workflows that invoke coded workflows.
- In processes that include a library activity that uses connections, if an activity which is not part of that library and which utilizes the same connection is added to the process, the second activity will overwrite the library activity’s settings.
Options for Windows - Legacy libraries
Select Activity Properties in the left-side menu and enter the following:
- Tooltip - The tooltip that is visible when you hover over the activity in the Activities and Designer panels in projects where the library is installed.
- Help Link - The help link that opens when you select the activity in the Designer panel and press F1 on your keyboard.
The arguments defined in the workflow file are displayed under Activity Properties in the left-side menu.
- To customize the generated property, select it and configure the following:
- Display name - The label that appears in the activity for the property.
- Tooltip - The tooltip that is visible when you hover over the activity property.
- Required - Whether the property is required.
- Advanced Only - Whether the property should be displayed only in the Properties panel. If selected, the property is not displayed in the Designer panel for the generated activity.
- To change the order in which the properties are displayed in the activity, drag-and-drop them in the list.
Note:
- In the case of
libraries, it is recommended to use
Nothingto assign a null value to a variable, rather than"". This is done to avoid any inconsistencies when using the packaged library as a dependency to a project. - The
ImplementationVersion property of the
System.Activities.ActivityBuilderobject is not supported. Setting a value for this property results in arguments not being saved. This object is displayed in the Properties panel when you select the blank area of the Designer panel.
- In the case of
libraries, it is recommended to use
Adjusting Library Settings
To configure the settings of a library project, open the Project Settings window by clicking Settings in the Project panel.
The following options are available in the General tab:
- Name - edit the name of the project.
- Description - edit the description of the project.
- Project tags - You can add one or more tags to the project, either by creating new ones or by reusing tags already defined in Orchestrator. There are two types of tags: labels and properties (key-value pairs). Tags are included in the published package and they help describe and categorize projects. For more information, see About Automation Projects.
- Automation Hub URL - URL of an Automation Hub idea linked to the project. For more information, see Linking a Project to an Idea in Automation Hub.
- Package Icon - optionally, define a custom icon for the project. You can browse to and select a file, or enter a path or public URL to an
ico,jpeg,jpg, orpngfile up to 1MB in size. After the project is published, the icon is displayed next to the package in the Manage Packages window in Studio. - Compile activities expressions - set to Yes to compile and package all activities expressions with the library. This results in an improved execution time. Available for Windows - Legacy libraries only.
- Ready to Run - set to Yes to optimize the generated assemblies for faster JIT compilation at runtime. Available for Windows - Legacy libraries only.
- Separate Runtime Dependencies - To increase Robot performance and reduce the size of published packages, libraries are separated into design and runtime packages. The design package is used by Studio and the slimmer execution package is used by the Robot.
- Include Sources - Set to Yes to package all
.xamlsources within the published package, including workflows that were previously made private. For Windows - Legacy libraries, the files are saved in the generated assembly file and in thelib\net45folder in the.nupkgfile. For Windows and cross-platform libraries and processes, the files are saved in thecontentfolder in the.nupkgfile.
Publishing a Library
Publishing libraries is similar to publishing processes. For more information, see About Publishing Automation Projects. Unlike processes, publishing a library creates two NUPKG files – a design time package and a runtime package. This applies only to Windows and cross-platform libraries if the Separate Runtime Dependencies Project Settings option is enabled.
- Because of the separation between design time and runtime packages, custom libraries published in Studio 2023.4 are not guaranteed to be compatible with earlier Studio versions.
- You can install only the design time package in a project, since it is replaced by the runtime package when publishing. Installing only the runtime package will cause unexpected issues in Studio.
- Starting with Studio 2023.10.0, the separation between design time and runtime packages occurs only if:
- A
ViewModels.dllfile is generated during the compilation process. TheViewModels.dllfile is generated for Windows and cross-platform libraries when configuring viewmodel activity properties for at least one workflow file inside the library. - The Separate Runtime Dependencies option is enabled.
- A
Limitations When Using Libraries
When using libraries, take into account the following limitations:
-
Due to NuGet limitations:
- You cannot publish libraries to locations that contain user-restricted subfolders using Windows environment path variables.
- Release notes for published libraries are visible only in Orchestrator.
-
Libraries with special characters in the names of
.xamlfiles they contain may not be successfully published. -
If a library contains a
.xamlfile and an argument that have the same name, the library cannot be published. -
Library projects with the Windows - Legacy compatibility cannot be published if they contain Invoke Workflow File activities with the Isolated option selected. An error message is displayed in the Output panel when you try to publish. This limitation does not apply to libraries that use the Windows or cross-platform compatibility.
-
When using Invoke Workflow File activity, make sure the invoked file is located in the same folder as the library project.
-
The Launch Workflow Interactive activity is not supported for libraries.
-
Using Invoke Workflow File inside a library to reference the library itself is not supported.
-
If a library contains an activity that accepts a file path as input, to ensure the path is resolved correctly in projects where the library is installed, add the UiPath.Constants.Project.Location global constant when referencing the path (use this exact capitalization). This disables changing
Environment.CurrentDirectoryto the library folder at the start of execution for a library activity and uses the constant instead.For example, if a file named Employee.txt located in the InputData subfolder in the library project is used inside a Read File activity, provide the path as follows:
UiPath.Constants.Project.Location+"InputData\Employee.txt"Note:The constant must not be used in Invoke Workflow File activities inside libraries.
-
To reference a location from the project folder where a library is installed, pass the path to the library as an argument.
Adding Reusable Components to Automation Projects
- Open or create a new project.
- Under the All Packages category, pick the feed under which the library is saved and install the package.
- Select OK and the package is added to the project definition.
- The activity is found in the custom category of the Activities panel.
Considerations for installing libraries in projects
- Libraries with the cross-platform compatibility can be installed in cross-platform and Windows projects. Windows - Legacy and Windows libraries can only be installed in processes that have the same compatibility.
- Errors may occur when you run a project that contains custom activities from a library that was created in a Studio version prior to 2019.10.1 and published from Studio 2019.10.1 or later. In this scenario, you must recreate and republish the library.
- When using Import Workflows to add a workflow that contains a library in a library project, the dependencies referenced in the library are not imported.
- When importing two versions of the same custom library in a project, the extra custom activities contained only in the second library are not visible in the Activities panel unless you remove the first imported library.
- Using periods (
.) in the library name separates the library into nested groups when viewing it in the Activities panel. - When using custom activities from a library, any default values defined for arguments are automatically pre-filled in the activity’s Properties panel when the activity is added to the workflow. If you clear the value from a property field in the workflow, the corresponding default value is not used at runtime. In this case, an empty value is explicitly passed. In contrast, when using the Invoke Workflow activity, leaving an input blank in the Import Arguments panel results in the default value defined in the called workflow to be used at runtime.
- Creating a Library
- Extracting a Project as Library
- Configuring the Layout of an Activity
- Options for Windows and Cross-platform libraries
- Options for Windows - Legacy libraries
- Adjusting Library Settings
- Publishing a Library
- Limitations When Using Libraries
- Adding Reusable Components to Automation Projects