- Release Notes
- Getting Started
- Setup and Configuration
- Automation Projects
- Dependencies
- Types of Workflows
- Control Flow
- File Comparison
- Automation Best Practices
- Source Control Integration
- Debugging
- Logging
- The Diagnostic Tool
- Workflow Analyzer
- About Workflow Analyzer
- ST-NMG-001 - Variables Naming Convention
- ST-NMG-002 - Arguments Naming Convention
- ST-NMG-004 - Display Name Duplication
- ST-NMG-005 - Variable Overrides Variable
- ST-NMG-006 - Variable Overrides Argument
- ST-NMG-008 - Variable Length Exceeded
- ST-NMG-009 - Prefix Datatable Variables
- ST-NMG-011 - Prefix Datatable Arguments
- ST-NMG-012 - Argument Default Values
- ST-NMG-016 - Argument Length Exceeded
- ST-NMG-017 - Class name matches default namespace
- ST-DBP-002 - High Arguments Count
- ST-DBP-003 - Empty Catch Block
- ST-DBP-007 - Multiple Flowchart Layers
- ST-DPB-010 - Multiple instances of [Workflow] or [Test Case]
- ST-DBP-020 - Undefined Output Properties
- ST-DBP-021 - Hardcoded Timeout
- ST-DBP-023 - Empty Workflow
- ST-DBP-024 - Persistence Activity Check
- ST-DBP-025 - Variables Serialization Prerequisite
- ST-DBP-026 - Delay Activity Usage
- ST-DBP-027 - Persistence Best Practice
- ST-DBP-028 - Arguments Serialization Prerequisite
- ST-USG-005 - Hardcoded Activity Arguments
- ST-USG-009 - Unused Variables
- ST-USG-010 - Unused Dependencies
- ST-USG-014 - Package Restrictions
- ST-USG-017 - Invalid parameter modifier
- ST-USG-020 - Minimum Log Messages
- ST-USG-024 - Unused Saved for Later
- ST-USG-025 - Saved Value Misuse
- ST-USG-026 - Activity Restrictions
- ST-USG-027 - Required Packages
- ST-USG-028 - Restrict Invoke File Templates
- ST-USG-032 - Required Tags
- ST-USG-034 - Automation Hub URL
- Variables
- Arguments
- Imported Namespaces
- Coded automations
- Introduction
- Registering custom services
- Before and After contexts
- Generating code
- Generating coded test case from manual test cases
- Trigger-based Attended Automation
- Object Repository
- The ScreenScrapeJavaSupport Tool
- Extensions
- About extensions
- SetupExtensions tool
- UiPathRemoteRuntime.exe is not running in the remote session
- UiPath Remote Runtime blocks Citrix session from being closed
- UiPath Remote Runtime causes memory leak
- UiPath.UIAutomation.Activities package and UiPath Remote Runtime versions mismatch
- The required UiPath extension is not installed on the remote machine
- Screen resolution settings
- Group Policies
- Cannot communicate with the browser
- Chrome extension is removed automatically
- The extension may have been corrupted
- Check if the extension for Chrome is installed and enabled
- Check if ChromeNativeMessaging.exe is running
- Check if ComSpec variable is defined correctly
- Enable access to file URLs and Incognito mode
- Multiple browser profiles
- Group Policy conflict
- Known issues specific to MV3 extensions
- List of extensions for Chrome
- Chrome Extension on Mac
- Group Policies
- Cannot communicate with the browser
- Edge extension is removed automatically
- The extension may have been corrupted
- Check if the Extension for Microsoft Edge is installed and enabled
- Check if ChromeNativeMessaging.exe is running
- Check if ComSpec variable is defined correctly
- Enable access to file URLs and InPrivate mode
- Multiple browser profiles
- Group Policy conflict
- Known issues specific to MV3 extensions
- List of extensions for Edge
- Extension for Safari
- Extension for VMware Horizon
- Extension for Amazon WorkSpaces
- SAP Solution Manager plugin
- Excel Add-in
- Studio testing
- Troubleshooting
- About troubleshooting
- Assembly compilation errors
- Microsoft App-V support and limitations
- Internet Explorer X64 troubleshooting
- Microsoft Office issues
- Identifying UI elements in PDF with Accessibility options
- Repairing Active Accessibility support
- Validation of large Windows-legacy projects takes longer than expected

Studio user guide
Extension for Amazon WorkSpaces
Installing the extension
The UiPath Extension allows you to automate Amazon WorkSpaces virtual desktops natively. The extension can be installed from UiPath Studio or the Command Prompt.
Prerequisites
Before installing the extension, make sure to install the Amazon WorkSpaces client.
You can choose to install the extension either for the current user or for all users. The installation types must match, namely, the extension installation type must match the Amazon WorkSpaces client installation type. If the installation types do not match, the extension installation will fail.
Amazon WorkSpaces can be configured with either the PCoIP (PC-over-IP) or the DCV (Desktop Cloud Visualization) protocol. * Automating Amazon WorkSpaces using PCoIP requires UiPath.UIAutomation.Activities, UiPath Studio, and UiPath Remote Runtime v24.10 or higher. * Automating Amazon WorkSpaces using DCV requires UiPath.UIAutomation.Activities, UiPath Studio, and UiPath Remote Runtime v25.2 or higher.
Configuring the extension for DCV
Amazon Workspaces using the DCV protocol requires DCV extensions to be enabled. Because the support for WorkSpaces extensions is disabled by default, you must set the Configure extensions setting to Server and client – Enable extensions for both server and client.
To configure the extension for a DCV group policy, refer to Manage Group Policy settings for DCV in the Amazon WorkSpace documentation.
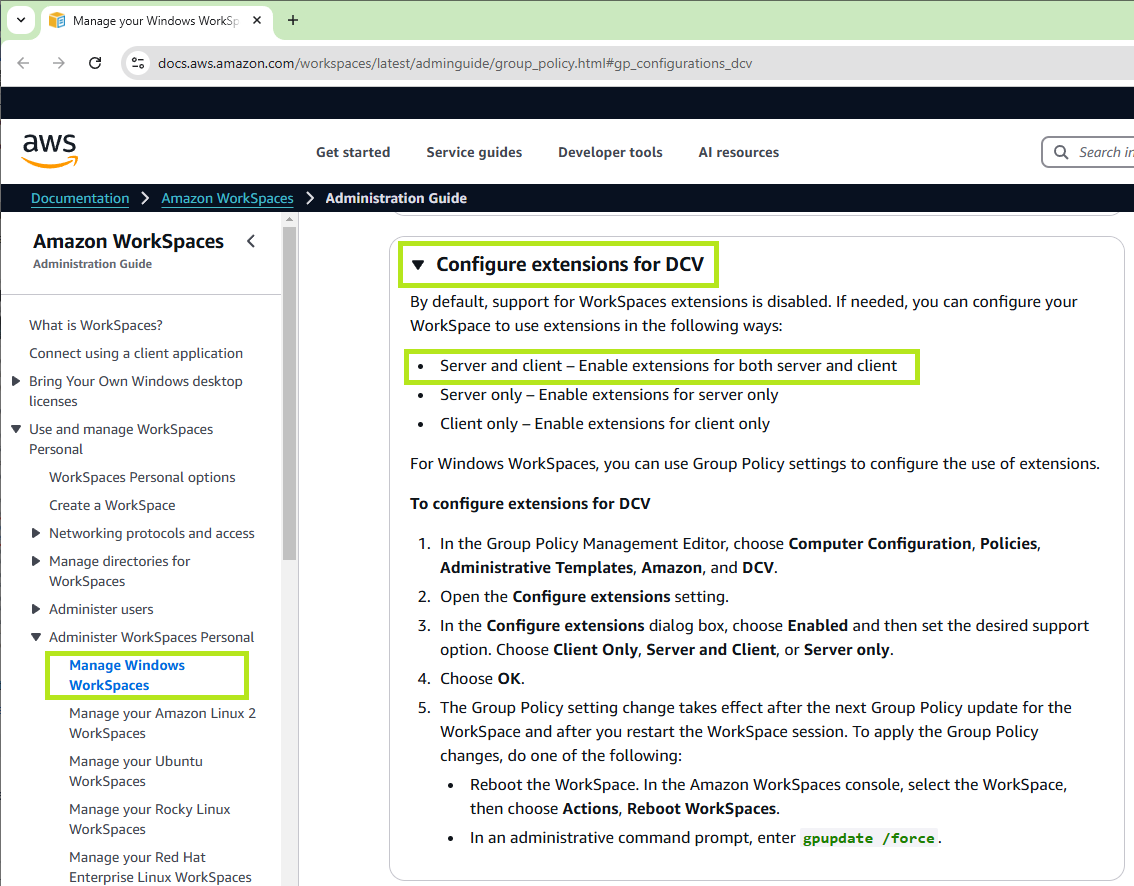
Once you enable the group policy, the following Windows registry keys are written:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Amazon\WSP] "hc_toggle_extensions"=dword:00000001 "hc_toggle_extension_options"=dword:00000000
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Amazon\WSP] "hc_toggle_extensions"=dword:00000001 "hc_toggle_extension_options"=dword:00000000
You can also configure extensions from a permissions file, by referencing the following features:
extensions-client- Allows you to start the installed extensions on the Amazon DCV client.extensions-server- Allows you to start the installed extensions on the Amazon DCV server.
For more information, refer to Adding permissions in the Amazon DCV documentation.
From UiPath Studio
- Open UiPath Studio.
- Navigate to Backstage View > Tools > UiPath Extensions.
- Under Amazon WorkSpaces, select the preferred installation type from the drop-down menu:
- All Users to install the extension for all users of this machine. For this installation type, you must have local Administrator privileges and the Amazon WorkSpaces client needs to be installed for all users.
- Current User to install the extension for the current user. For this installation type, you do not need local Administrator privileges, but Amazon WorkSpace client needs to be installed per user.
- Select Install. A confirmation dialog box is displayed.
- Restart your Amazon WorkSpaces client for the changes to take effect.
- The UiPath Extension for Amazon WorkSpaces is now installed and is located at
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\UiPath\UiPath.Common\.
From the Command Prompt
- Select the Windows Start button and type
cmdin the search field. - Right click Command Prompt and run it as administrator.
- Change the directory to the UiPath installation folder:
cd C:\Program Files\UiPath\Studio\UiPathfor per-machine Studio installations.cd %localappdata%\Programs\UiPath\Studio\UiPathfor per-user Studio installations.
- Use the
SetupExtensions.exe /amazon-workspaces-clientcommand to install the extension per user orSetupExtensions.exe /amazon-workspaces-client-globalto install it per-machine (for all users). A confirmation dialog box is displayed. - Restart your Amazon Workspaces client for the changes to take effect.
- The UiPath Extension for Amazon WorkSpaces is now installed.
To generate native selectors for Amazon WorkSpaces technologies, you also need to deploy the UiPath Remote Runtime component on all your Amazon WorkSpaces virtual desktops, as explained on UiPath Remote Runtime.
The UiPathRemoteRuntime.msi installer can be downloaded from:
- Product Downloads in the UiPath Customer Portal.
- Resource Center in the UiPath Automation Cloud. To access Resource Center, log in to your Automation Cloud Organization, click the Help button on the navigation bar and choose the Downloads option.
Uninstalling the extension
From UiPath Studio
- Close your running Amazon WorkSpaces client.
- Open UiPath Studio.
- Navigate to Backstage View > Tools > UiPath Extensions.
- Select Amazon WorkSpaces > Uninstall, and confirm your choice.
The extension is uninstalled for the selected installation type (All Users or Current User).
From the Command Prompt
- Close all your running Amazon WorkSpaces virtual desktops.
- Select the Windows Start button and type
cmdin the search field. - Right-click Command Prompt and run it as administrator.
- Change the directory to the UiPath installation folder:
cd C:\Program Files\UiPath\Studio\UiPathfor per-machine Studio installations.cd %localappdata%\Programs\UiPath\Studio\UiPathfor per-user Studio installations.
- Use the
SetupExtensions.exe /amazon-workspaces-client /uninstallcommand to uninstall the extension for the current user orSetupExtensions.exe /amazon-workspaces-client-global /uninstallto uninstall it for all users (per machine). A confirmation dialog box is displayed.
The UiPath Extension for Amazon WorkSpaces is uninstalled.