- Introduction
- Getting started
- Process modeling
- Process implementation
- Process operations
- Process monitoring
- Process optimization
- Reference information

Maestro user guide
Messages and updates
Handle updates without interrupting work (non‑interrupting boundary messages)
Use when
- You need to process updates while a task is in progress.
- Updates should not halt the main work.
Pattern in simple words
-
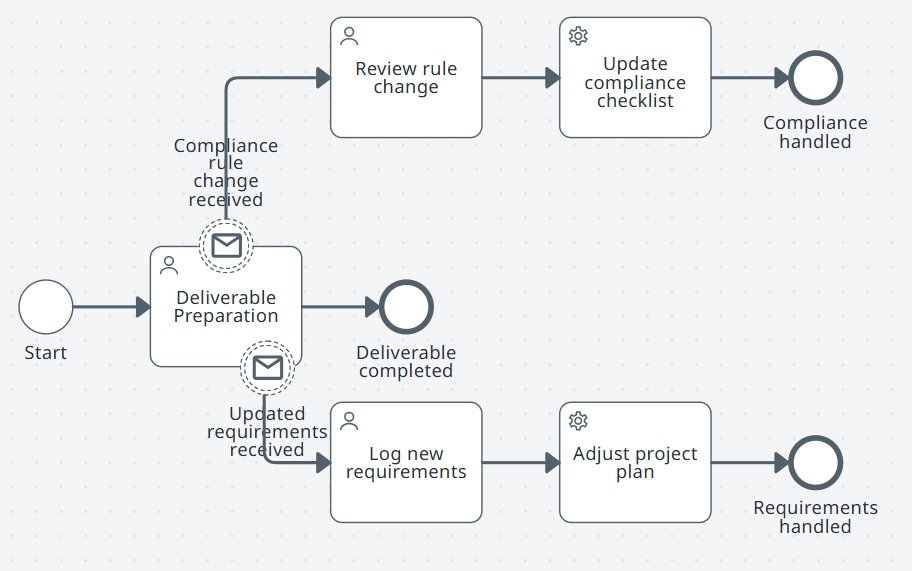
Start.
-
Subprocess: Deliverable preparation.
-
Non‑interrupting boundary message Updated requirements received: User task Log new requirements. Service task Adjust project plan. End Requirements handled.
-
Non‑interrupting boundary message Compliance rule change received: User task Review rule change. Service task Update compliance checklist. End Compliance handled.
-
Main path: Deliverable preparation completes. End Deliverable completed.
Note:Each message triggers a small side flow without stopping the main work.
Other scenarios
- Finance: Credit‑risk review receiving new market data.
- Healthcare: Care‑plan preparation receiving updated lab results.
- Manufacturing: Product design updates from regulation changes.
- Retail: Campaign plan updates with product revisions.
- Telecom: Network upgrade planning updates with compliance changes.
Cancel during a task (interrupting message)
Use when
- Work must stop immediately on a cancel request.
- A clear message should abort the task.
Pattern in simple words
-
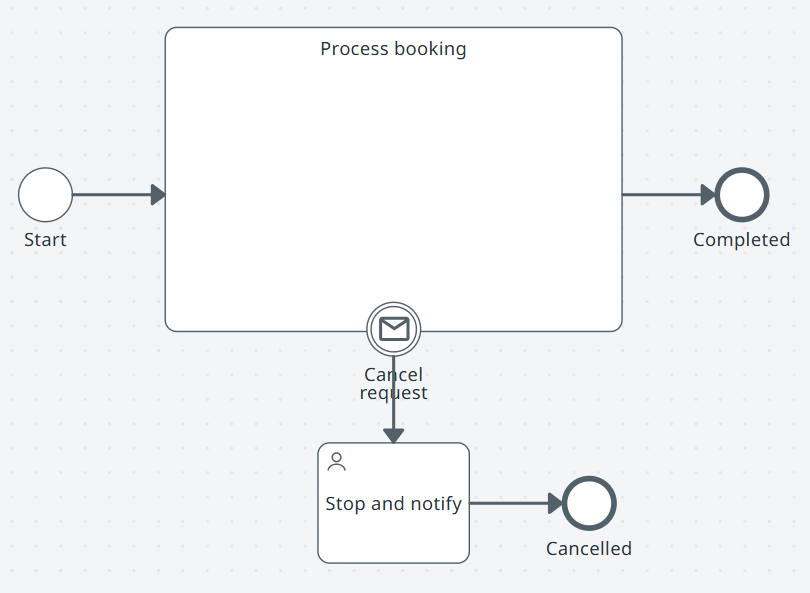
Start.
-
Subprocess: Process booking.
-
Interrupting boundary message Cancel request: User task Stop and notify. End Cancelled.
-
Normal path: Process booking completes. End Completed.
Note:The interrupting message cancels the active work at the subprocess boundary.
Other scenarios
- Finance: Loan withdrawal cancels underwriting.
- Healthcare: Patient cancels a scheduled procedure.
- Manufacturing: Cancel production order before run.
- Retail: Cancel order before shipment.
- Telecom: Cancel new service setup.
Event‑driven dispatcher (message start)
Use when
- A new external message should start a process.
- Each event spawns an independent workflow instance.
Pattern in simple words
-
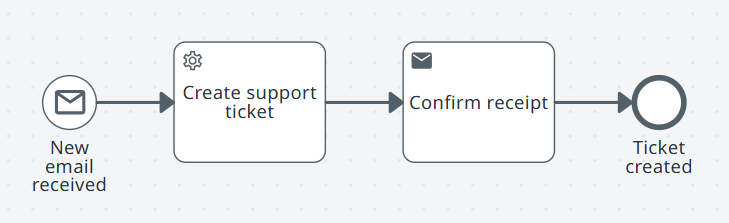
Message start: New email received.
-
Service task: Create support ticket.
-
Send task: Confirm receipt.
-
End Ticket created.
Note:Each incoming message creates a new instance.
Other scenarios
- Finance: Vendor request message starts onboarding.
- Healthcare: Referral message starts patient intake.
- Manufacturing: Defect report starts QA process.
- Retail: Online order starts fulfillment.
- Public sector: Citizen inquiry opens a case record.