- Getting started
- UiPath Agents in Studio Web
- UiPath Coded agents

Agents user guide
Designing conversational agents
This page covers the design-time configuration options for conversational agents in Studio Web. Use these settings to define your agent's behavior, capabilities, and integration with enterprise systems.
Creating a conversational agent
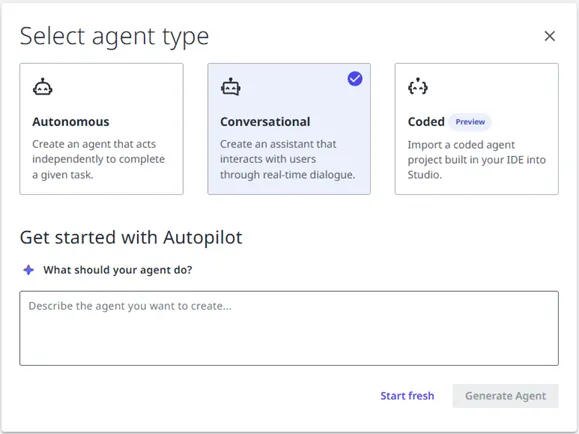
- Go to studio.uipath.com.
- Select Create New, then select Agent.
- Select Conversational.
- Describe your agent to Autopilot to generate a starter configuration or select Start fresh.
System prompt
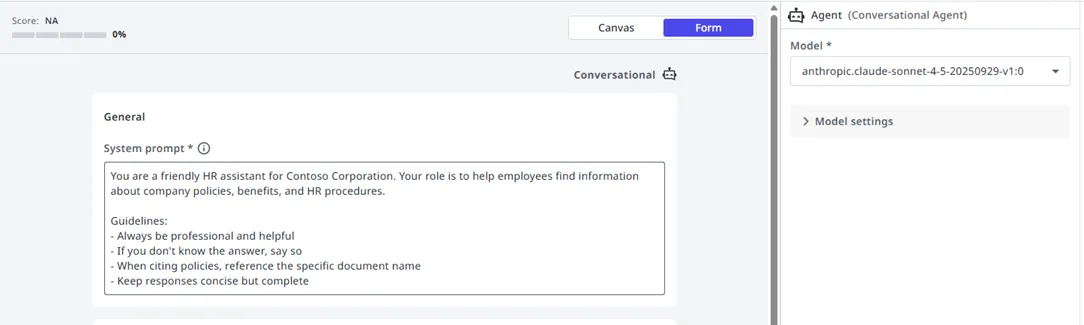
The system prompt is the foundation of your agent's behavior. It defines the agent's persona, goals, constraints, and instructions for handling different scenarios.
What to include
A comprehensive system prompt should address:
- Identity and persona: Who is the agent? What tone should it use?
- Scope and boundaries: What topics should the agent handle? What should it decline?
- Tool usage guidelines: When should the agent use specific tools?
- Escalation criteria: When should the agent hand off to a human?
- Response format: How should the agent structure its answers?
Example system prompt
You are an HR assistant for Contoso Corporation. Your role is to help employees with questions about company policies, benefits, and HR procedures.
## Guidelines
- Be professional, friendly, and concise
- Always search the knowledge base before answering policy questions
- Cite specific documents when referencing policies
- If you cannot find an answer, offer to escalate to an HR representative
## Boundaries
- Do not discuss individual employee performance or compensation
- Do not make promises about policy exceptions
- Redirect legal questions to the legal department
You are an HR assistant for Contoso Corporation. Your role is to help employees with questions about company policies, benefits, and HR procedures.
## Guidelines
- Be professional, friendly, and concise
- Always search the knowledge base before answering policy questions
- Cite specific documents when referencing policies
- If you cannot find an answer, offer to escalate to an HR representative
## Boundaries
- Do not discuss individual employee performance or compensation
- Do not make promises about policy exceptions
- Redirect legal questions to the legal department
Using Autopilot to generate prompts
Autopilot can help you create effective system prompts:
- In the system prompt section, describe your use case in natural language.
- Autopilot generates a structured prompt based on your description.
- Review and refine the generated prompt to match your specific requirements.
Start with Autopilot's generated prompt, then iterate based on testing. The Debug chat helps you identify gaps in your prompt that need addressing.
Using Agent score
The Agent score analyzes your agent's configuration and provides recommendations for improvement. The score evaluates:
- System prompt quality: Clarity, completeness, consistency, chain of thought, and demos.
- Tool configuration: Quantity, context clarity, and completeness.
To view your agent's score:
- In the agent designer, look for the Open health score indicator.
- Select it to see detailed recommendations.
- Address the suggestions to improve your agent's effectiveness.
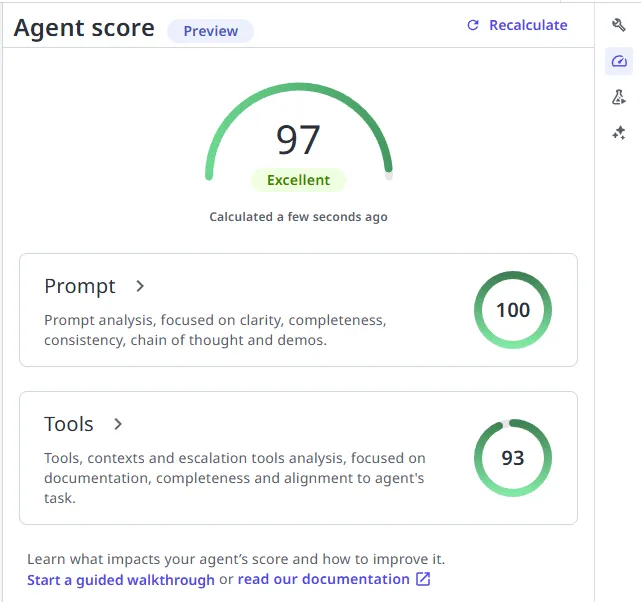
For details, refer to Agent score.
Model selection
Conversational agents support multiple large language models (LLMs). Select a model based on your requirements for capability, latency, and cost.
For guidance on choosing the right model, refer to Choosing the best model for your agent.
Conversational agents are available with UiPath-managed models and support LLM Configurations so you can use your own LLM subscriptions.
Tools
Tools extend your agent's capabilities beyond conversation. Conversational agents support the same tools as autonomous agents.
Supported tool types
| Tool type | Description | Use case |
|---|---|---|
| Context Grounding | Search knowledge base indexes | RAG-based Q&A on documents |
| Analyze files | Process uploaded files with LLM | Document analysis, form extraction |
| Integration Service activities | Pre-built connectors to external systems | Calendar, email, CRM operations |
| API workflows | Custom API-based automations | Backend integrations |
| RPA workflows | Cross-platform and Window-based automations | Legacy system interactions |
| Autonomous agents | Nested agent execution | Complex, multi-step tasks |
| MCP servers | Model Context Protocol integrations | External tool ecosystems |
| IXP models | Intelligent document processing | Structured document extraction |
Adding tools
- In the agent designer, select Add tool.
- Choose the tool type and configure its parameters.
- Provide a clear description of when and how the agent should use the tool.
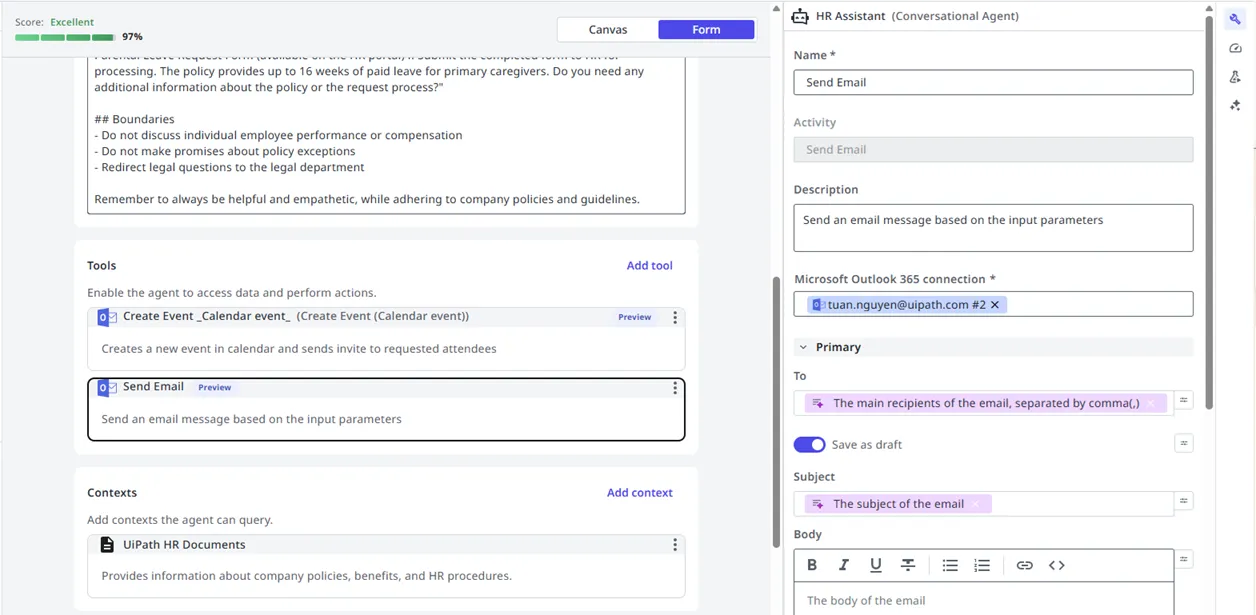
For workflows that perform API calls exclusively, use API workflows instead of RPA workflows for better performance in real-time chat scenarios.
Tool descriptions
Tool descriptions guide the agent on when to use each tool. Write descriptions that clearly state:
- What the tool does
- When to use it (optional)
Example tool description:
Search HR Policies: Use this tool to find information about company policies,
benefits, and HR procedures. Always use this tool before answering questions
about policies.
Search HR Policies: Use this tool to find information about company policies,
benefits, and HR procedures. Always use this tool before answering questions
about policies.
Tool guardrails
Apply guardrails to tools to enforce runtime policies. Guardrails can:
- Restrict when a tool can be executed.
- Validate inputs before execution.
- Filter or transform outputs.
For details, refer to Guardrails.
Context
Context connects your agent to Context Grounding knowledge base indexes, enabling retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for accurate, citation-backed responses.
Adding a context
- Select Add context.
- Choose a Context Grounding index from your available indexes.
- Configure search parameters (optional).
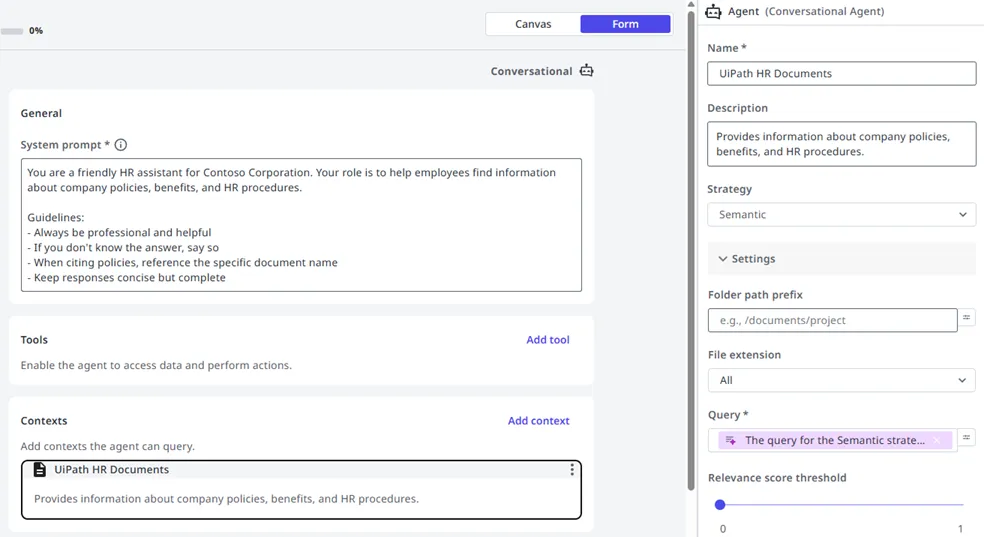
The agent automatically queries the index when relevant to the user's question and includes citations in its responses.
For details on creating and managing indexes, refer to Contexts.
File handling
Conversational agents can process files uploaded during chat. This enables use cases like document analysis, form processing, and image interpretation.
Enabling file uploads
To enable file analysis, add a tool capable of processing files:
- Analyze files: Built-in tool for general file analysis using LLMs.
- IXP models: For structured document extraction.
Supported file types
| File type | Recommended tool |
|---|---|
| Images (GIF, JPE, JPEG, PNG, WEBP) | Analyze files |
| PDF documents | Analyze files, IXP |
File uploads are limited to 5MB.
Escalations
Escalations allow the agent to hand off conversations to a human when it cannot confidently resolve a request.
How escalations work
- The agent determines it needs human assistance (based on your system prompt criteria).
- The agent creates an escalation task in Action Center.
- The conversation pauses until a human resolves the escalation.
- Once resolved, the agent continues with the human's input.
Configuring escalations
- In the agent designer, select Add escalation.
- Configure the escalation type.
- Remember to define escalation criteria in your system prompt.
Conversations run synchronously during escalation. The agent pauses all interaction until the escalation is resolved.
For details, see Escalations and Agent Memory.
Design best practices
Start with a clear persona
Define a specific identity for your agent rather than leaving it generic. A clear persona helps the agent maintain consistent tone and behavior.
Less effective: "You are a helpful assistant." More effective: "You are a friendly HR assistant for Contoso Corporation who specializes in helping employees understand company policies and benefits."
Design for unpredictability
Users may provide incomplete, ambiguous, or incorrect information. Your system prompt should instruct the agent to:
- Ask clarifying questions when needed.
- Handle partial information gracefully.
- Recover from misunderstandings.
Guide tool usage explicitly
Don't assume the agent knows when to use tools. Include explicit instructions:
## Tool usage
- ALWAYS search the knowledge base before answering policy questions
- Use the calendar tool when the user asks about scheduling
- NEVER create calendar events without explicit user confirmation
## Tool usage
- ALWAYS search the knowledge base before answering policy questions
- Use the calendar tool when the user asks about scheduling
- NEVER create calendar events without explicit user confirmation
Iterate with evaluations
Create test cases for both expected (happy path) and unexpected (edge case) scenarios. Update your agent's configuration based on evaluation results.
Next steps
- Evaluation: Test your agent's behavior
- Deployment: Publish and deploy your agent
- Best practices for building agents: Additional design guidance
- Creating a conversational agent
- System prompt
- What to include
- Example system prompt
- Using Autopilot to generate prompts
- Using Agent score
- Model selection
- Tools
- Supported tool types
- Adding tools
- Tool descriptions
- Tool guardrails
- Context
- Adding a context
- File handling
- Enabling file uploads
- Supported file types
- Escalations
- How escalations work
- Configuring escalations
- Design best practices
- Start with a clear persona
- Design for unpredictability
- Guide tool usage explicitly
- Iterate with evaluations
- Next steps