- Überblick
- UI-Automatisierung (UI Automation)
- Über das UIAutomation-Aktivitätspaket
- Mit UI-Automatisierung automatisierte Anwendungen und Technologien
- Projektkompatibilität
- UI-ANA-016 – URL zum Öffnen eines Browsers abrufen
- UI-ANA-017 – ContinueOnError True
- UI-ANA-018 – OCR-/Bildaktivitäten auflisten
- UI-DBP-006 – Containernutzung
- UI-DBP-013 – Falscher Gebrauch von Excel-Automatisierung
- UI-DBP-030 – Verwendung unzulässiger Variablen in Selektoren
- UI-DBP-031 – Aktivitätsverifizierung
- UI-PRR-001 – Klick simulieren
- UI-PRR-002 – Typ simulieren
- UI-PRR-003 – Offener Anwendungsmissbrauch
- UI-PRR-004 – Hartcodierte Verzögerungen
- UI-REL-001 – Große IDX in Selektoren
- UI-SEC-004 – Selektor-E-Mail-Daten
- UI-SEC-010 – App-/URL-Einschränkungen
- UI-USG-011 – Nicht zulässige Attribute
- UX-SEC-010 – App-/URL-Einschränkungen
- UX-DBP-029 – Unsichere Kennwortnutzung
- UI-PST-001 – Prüfungsprotokollebene in Projekteinstellungen
- UiPath-Browsermigrationstool
- Clippingbereich
- Computer Vision Recorder
- Aktivitätenindex
- Aktivieren (Activate)
- Ankerbasis (Anchor Base)
- Browser anhängen (Attach Browser)
- Fenster anhängen (Attach Window)
- Benutzeingabe blockieren (Block User Input)
- Textfeld (Callout)
- Prüfen (Check)
- Klicken (Click)
- Bild anklicken (Click Image)
- Bild-Trigger anklicken (Click Image Trigger)
- OCR-Text anklicken (Click OCR Text)
- Text anklicken (Click Text)
- Trigger anklicken (Click Trigger)
- Anwendung schließen (Close Application)
- Registerkarte schließen (Close Tab)
- Fenster schließen (Close Window)
- Kontextbewusster Anker
- Ausgewählten Text kopieren (Copy Selected Text)
- Element Attribute Change Trigger
- Element vorhanden (Element Exists)
- Elementumfang (Element Scope)
- Element State Change Trigger
- Export UI Tree
- Strukturierte Daten extrahieren (Extract Structured Data)
- Untergeordnete Elemente finden (Find Children)
- Element finden (Find Element)
- Bild finden (Find Image)
- Bildübereinstimmung finden (Find Image Matches)
- OCR-Textposition finden (Find OCR Text Position)
- Relatives Element finden (Find Relative Element)
- Textposition finden (Find Text Position)
- Aktives Fenster abrufen (Get Active Window)
- Vorgänger-Element erhalten (Get Ancestor)
- Attribut erhalten (Get Attribute)
- Ereignisinfo erhalten (Get Event Info)
- Aus Zwischenablage erhalten (Get From Clipboard)
- Volltext erhalten (Get Full Text)
- OCR-Text erhalten (Get OCR Text)
- Passwort erhalten (Get Password)
- Position erhalten (Get Position)
- Quellelement erhalten (Get Source Element)
- Text erhalten (Get Text)
- Sichtbaren Text erhalten (Get Visible Text)
- Zurück (Go Back)
- Weiter (Go Forward)
- Zur Startseite (Go Home)
- Google Cloud Vision OCR
- Fenster ausblenden (Hide Window)
- Markieren (Highlight)
- Hotkey-Trigger (Hotkey Trigger)
- Darauf zeigen (Hover)
- Auf Bild zeigen (Hover Image)
- Auf OCR-Text zeigen (Hover OCR Text)
- Text beim Darauf zeigen (Hover Text)
- Bild vorhanden (Image Exists)
- Auf Bildschirm anzeigen (Indicate On Screen)
- .NET-Code einfügen
- Inject Js Script
- ActiveX-Methode aufrufen
- Tastendruck-Trigger (Key Press Trigger)
- Bild laden (Load Image)
- Fenster maximieren (Maximize Window)
- Microsoft Azure ComputerVision OCR
- Microsoft OCR
- Microsoft Project Oxford Online OCR
- Fenster minimieren (Minimize Window)
- Ereignisse überwachen (Monitor Events)
- Maus-Trigger (Mouse Trigger)
- Fenster verschieben (Move Window)
- Navigieren zu (Navigate To)
- OCR-Text vorhanden (OCR Text Exists)
- Auf Element erscheinen (On Element Appear)
- Auf Element verschwinden (On Element Vanish)
- Auf Bild erscheinen (On Image Appear)
- Auf Bild verschwinden (On Image Vanish)
- Anwendung öffnen (Open Application)
- Browser öffnen (Open Browser)
- Browser aktualisieren (Refresh Browser)
- Benutzerereignis wiedergeben (Replay User Event)
- Fenster wiederherstellen (Restore Window)
- Bild speichern (Save Image)
- Objekt auswählen (Select Item)
- Mehrere Objekte auswählen (Select Multiple Items)
- Hotkey senden (Send Hotkey)
- Ausschneidebereich einstellen (Set Clipping Region)
- Fokus legen auf (Set Focus)
- Text einstellen (Set Text)
- Auf Zwischenablage setzen (Set To Clipboard)
- Web-Attribut setzen (Set Web Attribute)
- Fenster anzeigen (Show Window)
- Prozess starten (Start Process)
- System-Trigger (System Trigger)
- Screenshot anfertigen (Take Screenshot)
- Tesseract OCR
- Text vorhanden (Text Exists)
- Tooltip
- Eingeben in (Type Into)
- Sicheren Text eingeben (Type Secure Text)
- Vordergrund verwenden
- Attribut abwarten (Wait Attribute)
- Warten, bis Element verschwindet (Wait Element Vanish)
- Warten, bis Bild verschwindet (Wait Image Vanish)
- Prüfung der Barrierefreiheit
- Application event trigger
- Benutzeingabe blockieren (Block User Input)
- Check/Uncheck
- Check App State
- Check Element
- Klicken (Click)
- Click Event Trigger
- Ziehen und Ablegen
- Extract Table Data
- Find Elements
- For Each UI Element
- Get Browser Data
- Clipboard abrufen
- Text erhalten (Get Text)
- Get URL
- Zu URL wechseln
- Markieren (Highlight)
- Darauf zeigen (Hover)
- Inject Js Script
- Tastenkombinationen
- Keypress Event Trigger
- Mouse Scroll
- Navigate Browser
- Objekt auswählen (Select Item)
- Set Browser Data
- Clipboard festlegen
- Set Runtime Browser
- Fokus legen auf (Set Focus)
- Text einstellen (Set Text)
- Screenshot anfertigen (Take Screenshot)
- Eingeben in (Type Into)
- Unblock User Input
- Use Application/Browser
- Window operation
- Anhängen
- Prüfen (Check)
- Klicken (Click)
- Ziehen und Ablegen
- Daten extrahieren
- Attribut erhalten (Get Attribute)
- GetChildren
- GetRuntimeTarget
- GetText
- Get URL
- GoToUrl
- Markieren (Highlight)
- Darauf zeigen (Hover)
- IsEnabled
- Tastaturkürzel (Keyboard Shortcut)
- Mouse Scroll
- Offen
- Objekt auswählen (Select Item)
- Screenshot anfertigen (Take Screenshot)
- Eingeben in (Type Into)
- Wartestatus
- Führen Sie eine Browsersuche durch und rufen Sie Ergebnisse mithilfe von UIAutomation-APIs ab
- Web-Browsing
- Finden von Bildern
- Klicken auf Bilder
- Auslösen und Überwachen von Ereignissen
- Erstellen und Überschreiben von Dateien
- HTML-Seiten: Extrahieren und Bearbeiten von Informationen
- Bearbeiten von Fenstern
- Automatisierte Listenauswahl
- Finden und Bearbeiten von Fensterelementen
- Verwalten der Textautomatisierung
- Laden und Verarbeiten von Bildern
- Verwalten von mausaktivierten Aktionen
- Automatisieren der Anwendungslaufzeit
- Automatisierte Ausführung einer lokalen Anwendung
- Browsernavigation
- Web-Automatisierung
- Beispiel für Trigger Scope
- Aktivieren der Unterstützung für die UI-Automatisierung in DevExpress
- Computer Vision Local Server
- Mobile Automation
- Versionshinweise
- Über die Architektur der Automatisierung von Mobilgeräten
- Projektkompatibilität
- Get Log Types
- Get Logs
- Get Page Source
- Get Device Orientation
- Get Session Identifier
- Install App
- Manage Current App
- Manage Other App
- DeepLink öffnen
- Open URL
- Mobile Device Connection
- Richtungswechsel
- Muster zeichnen
- Positional Swipe
- Press Hardware Button
- Set Device Orientation
- Screenshot anfertigen (Take Screenshot)
- Take Screenshot Part
- Element vorhanden (Element Exists)
- Execute Command
- Attribut erhalten (Get Attribute)
- Get Selected Item
- Text erhalten (Get Text)
- Set Selected Item
- Text einstellen (Set Text)
- Wischen
- Tap
- Type Text
- Terminal
- Versionshinweise
- Über das Terminal-Aktivitätspaket
- Projektkompatibilität
- Best Practices
- Find Text
- Get Color At Position
- Get Cursor Position
- Feld erhalten (Get Field)
- Feld an Position erhalten (Get Field at Position)
- Bildschirmbereich erhalten (Get Screen Area)
- Text erhalten (Get Text)
- Text an Position erhalten (Get Text at Position)
- Cursor bewegen (Move Cursor)
- Move Cursor to Text
- Strg-Taste senden (Send Control Key)
- Tasten senden (Send Keys)
- Sichere Tasten senden (Send Keys Secure)
- Feld setzen (Set Field)
- Feld an Position setzen (Set Field at Position)
- Terminalsitzung (Terminal Session)
- Warte auf Feldtext (Wait Field Text)
- Wait Screen Ready
- Warte auf Bildschirmtext (Wait Screen Text)
- Warte auf Text an Position (Wait Text at Position)

UIAutomation-Aktivitäten
Tabellenextraktion
Die Tabellenextraktion, Teil der Modern Experience in Studio, ermöglicht es Ihnen, das Aktivitätspaket UI-Automatisierung zu verwenden, um automatisch strukturierte Daten aus Anwendungen zu extrahieren und sie als DataTable -Objekt zu speichern, das dann in Ihren Automatisierungsprozessen weiter verwendet werden kann.
Dieser Prozess kann mit dem Table Extraction Recorder in Studio durchgeführt werden, auf den über das Menüband zugegriffen werden kann, wenn das UIAutomation v21.4 oder höher in Ihrem aktuellen Projekt installiert ist und Sie die Moderne Umgebung ausgewählt haben.
Der gleiche Assistent wird auch verwendet, wenn Sie eine Aktivität Extract Table Data in Ihrem Workflow verwenden.
Verwenden des Tabellenextraktions-Recorders
Wenn Sie in Ihrem Projekt die moderne Umgebung ausgewählt und das UI-Automatisierungs-Aktivitätspack installiert haben, finden Sie den Tabellenextraktions- Recorder im Menüband in Studio.

Clicking the Table Extraction button in the Ribbon opens up the Table Extraction wizard.

Mit diesem Assistenten können Sie die gesamte Suite von Funktionen, die die Aktivität Extract Table Data bietet, auf sehr einfache Weise konfigurieren.
Um zwischen den verfügbaren UI-Frameworks zu wechseln (Default, UIAutomation oder Active Accessibility), können Sie eine Option aus dem Dropdownmenü auswählen oder F4 drücken.
Der Abschnitt Information führt Sie außerdem durch alle Schritte, die Sie für eine erfolgreiche Extraktion strukturierter Daten durchführen müssen. Um weitere Informationen über den aktuellen Schritt zu erhalten, können Sie den Abschnitt reduzieren.

Um mit dem Extrahieren von Daten zu beginnen, klicken Sie einfach auf die Schaltfläche Daten hinzufügen . Dadurch wird eine Reihe ähnlicher Elemente angegeben, die zum Identifizieren der Tabelle verwendet werden können, die Sie erstellen möchten. Dadurch wird der Anzeigeprozess gestartet, der alle erkannten Elemente der Anwendung hervorhebt, mit der Sie gerade arbeiten. Durch die Auswahl von  können Sie über die Schaltfläche URLs und Bildquellen der extrahierten Daten extrahieren, sofern diese vorhanden sind. Diese werden als neue Spalte zu Ihrer endgültigen Tabelle hinzugefügt.
können Sie über die Schaltfläche URLs und Bildquellen der extrahierten Daten extrahieren, sofern diese vorhanden sind. Diese werden als neue Spalte zu Ihrer endgültigen Tabelle hinzugefügt.

As you can see above, after clicking a column header, the wizard prompts you with a message, asking whether you want to extract all of the available columns, which are automatically identified. Selecting Yes scrapes the entire table.
Wenn Sie ein Element auswählen, das nur einem der Elemente aus der ersten Spalte (niedrigster gemeinsamer Vorfahre) näher ist, wird es automatisch als das erste Element einer neuen Spalte betrachtet.
If the table spans multiple pages, you can simply click Next Button and select the next page navigation button or link.
Jede Spalte kann einzeln bearbeitet oder gelöscht werden, sodass Sie Ihre endgültige Tabelle nach Belieben anpassen können.

Once you have selected all the data you want, simply clicking the Save and return to Studio button automatically closes the wizard and saves everything you have done in your workflow.
Bearbeiten von Extraktionsdaten
You can resume editing an already scraped table by using the Edit extract data option in the contextual menu in the body of the Extract Table Data activity. Using this option reopens the wizard with all of the configurations performed earlier and enables you to pick up where you left off.

Bearbeiten von Spalten
Wenn Sie auf das Zahnradsymbol neben der Spalte klicken, die Sie bearbeiten möchten, wird das Fenster Spalteneinstellungen geöffnet.

Here, you can edit the Column Name. This can be done by simply using the text box and specifying the name you want for the column in the final table.
The Parse data as drop-down menu enables you to select between the three main types of data you can use for the columns, Text, Number, and Date & Time.
The Sample text box displays a sample of a value in the column being parsed as the data type you chose in the Parse data as drop-down.
Text
The Sort drop-down menu specifies whether you want to sort the data in the column or not. By default, None is selected, meaning the data is not sorted in any way. If you want to sort the data in the column alphabetically, you can do so by selecting Ascending or Descending, depending on the method you prefer.
Nummer
Selecting Number in the Parse data as drop-down displays other, number-specific options.

The Sort drop-down menu specifies whether you want to sort the data in the column or not. By default, None is selected, meaning the data is not sorted in any way. If you want to sort the data in the column alphanumerically, you can do so by selecting Ascending or Descending, depending on the method you prefer.
The Decimal separator specifies the symbol you want to use for decimal separation in your final table. By default, this symbol is ..
The Thousands separator specifies the symbol you want to use for thousand separation in your final table. By default, this symbol is ,.
When scraping numbers, they are parsed according to the selected options, and separators and other symbols (e.g. $) are removed.
Datum und Uhrzeit
Selecting Date & Time in the Parse data as drop-down displays other options, specific to date and time formats.

If the column you are editing does not match the format that is specified, the Column Settings window lets you know in the Sample section.
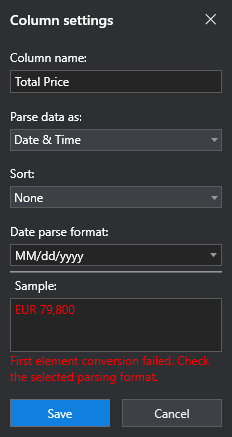
The Sort drop-down menu specifies whether you want to sort the data in the column or not. By default, None is selected, meaning the data is not sorted in any way. If you want to sort the data in the column by date, you can do so by selecting Ascending or Descending, depending on the method you prefer.
The Data parse format drop-down enables you to select from a multitude of date and time formats that are supported.
When selecting dates, they are formatted according to the format that is selected in your operating system. The parsing format selected in the wizard is just to identify the data you are scraping.
Abschnitt „Einstellungen“
The Settings section lets you choose if you want to limit the extraction of elements in the table. By default, this option is set to No limit, which does not limit the extraction in any way, scraping the entire visible table.
The Max rows option limits the scraping according to the number of rows that is mentioned in the field to the right. By default, this is set to 1000 rows.
The Max pages option limits the scraping according to the number of pages that is mentioned in the field to the right. By default, this is set to 100 pages.
Abschnitt „Vorschau“
The Preview section specifies how many columns and rows are identified for the table you have indicated. Also, by clicking the eye button, you can see a preview of the extracted table.
Die Vorschau ist bei der Bearbeitung im Offlinemodus deaktiviert.
MetadatenExtrahieren
The Extract metadata property contains an XML definition of the path identifying the data to be extracted for each column. The path is built starting from the data extraction target (defined by your selector) to the column elements. The path uses attributes such as tag, idx, and text.
Beispiel:
<extract>
<!—columns data identified by a path >
<column exact='1' name=’Description’ attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='div' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='span' idx='1' />
</column>
<column exact='1' name=’Currency’ attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='div' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='span' idx='2' />
</column>
</extract>
<extract>
<!—columns data identified by a path >
<column exact='1' name=’Description’ attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='div' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='span' idx='1' />
</column>
<column exact='1' name=’Currency’ attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='div' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='span' idx='2' />
</column>
</extract>
Wenn die Attribute tag, idxund text nicht ausreichen, um die vom Benutzer angegebenen Beispieldaten zu identifizieren, wird ein CSS-Selektor anstelle des Pfads generiert. Dieser Selektor verwendet die allgemeine Klasse der Beispielelemente.
Beispiel:
<extract>
<!—column data identified by a path >
<column exact='1' name='Description' attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='h3' idx='1' />
</column>
<!—column data identified by a css-selector >
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Currency' attr='text' />
</extract>
<extract>
<!—column data identified by a path >
<column exact='1' name='Description' attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='h3' idx='1' />
</column>
<!—column data identified by a css-selector >
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Currency' attr='text' />
</extract>
For the Description column, tag and index attributes are used to identify the column data.
For the Currency column, the elements are identified via the CSS-selector which contains the common class of the samples.
Optional kann, falls verfügbar, auch ein CSS-Selektor für die Beschreibung verwendet werden:
<extract>
<!—columns data identified by css-selectors >
<column css-selector='.product-title ' name='Description' attr='text' />
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Currency' attr='text' />
</extract>
<extract>
<!—columns data identified by css-selectors >
<column css-selector='.product-title ' name='Description' attr='text' />
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Currency' attr='text' />
</extract>
Die Zeilendefinition verwendet dieselben Identifizierungsmethoden wie die Spalte und wird zum Extrahieren korrelierter Daten verwendet. Eine Zeile enthält ein Element aus jeder Spalte.
Beispiel:
<extract>
<! -- row definition - ->
<row exact='1'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
</row>
<column exact='1' name='Description' attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='h3' idx='1' />
</column>
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Column' attr='text' />
</extract>
<extract>
<! -- row definition - ->
<row exact='1'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
</row>
<column exact='1' name='Description' attr='text'>
<webctrl tag='li' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='a' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='2' />
<webctrl tag='div' idx='1' />
<webctrl tag='h3' idx='1' />
</column>
<column css-selector='.currency-value' name='Column' attr='text' />
</extract>
Tabelleneinstellungen
This property contains an XML definition of the column settings, as they were defined in the scraping wizard. Column properties like Name or Format can be changed directly in this XML definition and will be used at runtime when building the output data table.
Beispiel:
<table xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xmlns:xsd='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema' Type='Structured'>
<Column xsi:type='DataColumn' ReferenceName='Column0' Name=’Description'>
<Format xsi:type='TextColumnFormat' />
</Column>
<Column xsi:type='DataColumn' ReferenceName='Column2' Name=’Currency'>
<Format xsi:type='TextColumnFormat' />
</Column>
</Table>
<table xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xmlns:xsd='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema' Type='Structured'>
<Column xsi:type='DataColumn' ReferenceName='Column0' Name=’Description'>
<Format xsi:type='TextColumnFormat' />
</Column>
<Column xsi:type='DataColumn' ReferenceName='Column2' Name=’Currency'>
<Format xsi:type='TextColumnFormat' />
</Column>
</Table>